
Task 1
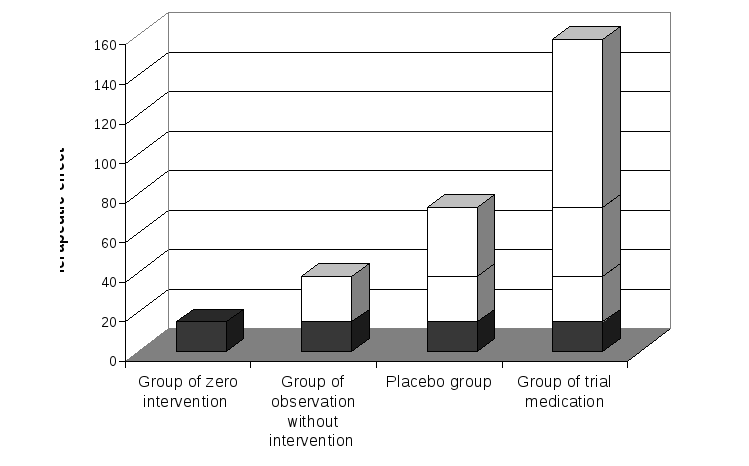
In carrying out a clinical trial of a new antibiotic a sample of patients with a mild form of pneumonia was selected. Four groups of patients were randomly formed. There was no intervention in the first group, patients in the second group were placed under observation, a third group received placebo, and a fourth group – the trial medication. Within a week efficacy evaluation of the treatment was performed. A clinically manifest amelioration of disease was considered as efficacy criterion. In the first group improvement in health was observed in15%, in the second group in 23 %, in the third group in 35% and in the fourth group in 85% of patients. (See figure)
Figure. Different cumulative therapeutic effect in groups with different interventions
 Assignment:
Assignment:
1. Evaluate the input of different causes to a cumulative therapeutic effect and interpret the obtained results
2. Indicate the reasons that affected the results obtained.
Task 2
In conducting a clinical trial to evaluate two medications the patients were broken down into groups in a different way. In the first case the patients were divided by whether their medical record numbers were odd or even ( even number –main group, odd number –control group) while in the second case they were divided according to weekday of admission to hospital (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Sunday—main group, Tuesday, Saturday –control group).
Assignment:
-
Evaluate the validity of management of the first and second study.
-
Give recommendations on how to conduct randomization.
Task 3:
Evaluate the validity of study management in the following instances. Indicate how this study setup could affect the obtained results.
-
In a clinical trial of a new medication to reduce the level of triglycerides in the blood the patients were divided into two groups. The first group received medication, the second group – placebo. The patients knew to which group they were assigned.
-
In a clinical trial of an antibiotic in patients with pneumonia the outcome was assessed against the changes in the X-ray picture. The doctor who performed the test was aware of the patients being assigned to a control or main group. However, the doctor was quick to identify improvements in the X-ray pattern in patients of the experimental group.
-
A clinical trial of a new expensive statin class drug was performed. The study investigator who evaluated the results knew about the group assignment of patients. He combined his duties as a statistician with a job within a pharmaceutical company which ordered this study.
Task 4.
The treatment of AIDS patients is an emotionally charged subject, in particular because the disease affects young people and is associated with an inevitably fatal outcome within a few years after the onset of symptoms. The study of the efficacy of treatment methods is hampered by violation of the common procedures of randomized tests since patients seek to increase their chances of survival. During randomized tests the patients sometimes exchange medications or obtain drugs not used in tests through “drug clubs”. They tend to conceal such acts from investigators and therefore these factors cannot be accounted for when summing up the results of tests.
Assignment:
Define how this intervention into the course of study can affect the results obtained.
Task 5
When conducting a randomized clinical trial of the efficacy of Arbidol medication among children aged 2 to 6 years two groups were formed: the experimental in which 143 patients were enrolled and a control group of 151 patients. The patients in the experimental group received Arbidol in the dose of 0.05 for 6 days while patients of the control group received placebo. The investigation continued for three months whereupon the outcome of the test was evaluated by the number of people who fell ill with the flu and ARVI and the number of complicated cases of flu and ARVI.
In the experimental group 66 patients were found to have contracted the disease with complications being observed in 7 patients, in the control group 95 patients fell ill and complications were detected in 20 patients.
Assignment:
Evaluate by the data presented the efficacy of Arbidol preparation by calculating the indices (see Supplement) for prevention of flu and ARVI progression and development of complications.
Supplement to task 5
|
|
Unfavorable outcome |
Total |
|
|
Observed |
Zero |
||
|
Placebo |
А |
В |
А+В |
|
Medication |
С |
D |
С+D |
Risk when treated with placebo Rpl=А/(А+В )
Risk when treated with trial medication Rtm=С/(С+В)
Absolute reduction of risk АRR=А/(А+В) - С/(С+D)
Number needed to treat NNT= 1/ARR
Relative risk RR=[С/(С+D)]/[А/(А+В)]
Relative risk reduction RRR=1-RR
