
К.Н. Березовская, т.Ф. Рабич
Методические указания по обучению чтению и логико-смысловому анализу научно-технического текста для студентов 1 курса. Упражнение по грамматике
(английский язык)
Содержание
UNIT 1
UNIT 2
UNIT 3
UNIT 4
UNIT 5
UNIT 6
UNIT 7
UNIT 8
UNIT 9
UNIT 10
UNIT 11
UNIT 12
UNIT 13
UNIT 14
UNIT 16
UNIT 17
UNIT 18
UNIT 19
UNIT 20
Упражнения по грамматике
Приложение 1
Приложение 2
UNIT 1
I. Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
movement (n), according to (prep), permit (v),flow (v, n).substance(n), therefore (adv),provide (v),path (n),copper (n),liquid (a, n),release (v),perfect (a) .allow (v), behave (v),act (v),germanium (n) silicon (n).condition (n),mixture (n), device (n).
II. Выпишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
conductor thermistor semiconductor magnetic field insulator switch (n) current switch on (v) resistance switch off (v)
charge (n)
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский
эквивалент:
battery (n), electron (n), material (n), classify (v), group (n), electric (a), category (n), metal,(n), cable (n), ignore (v), temperature (n), positive (a).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
conduct (v) – conductor- – conductance – conductivity;
insulate (v) – insulated – insulating – insulator – insulation;
move (v) – movement – movable;
permit (v) – permission;
substance (n) – substantial – substantially;
provide (v) – provided – -providing – provision;
usual (a) – usually;
easy (a) – easily – easiness;
ready (a) – readily – readiness;
resist (v) – resistant – resistance – -resistivity;
mix (v) – mixer – mixture;
act (v) – active – activity – action;
allow (v) – allowable – allowance.
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие пары слов, образованных по способу конверсии V N, V A:
flow (n) – flow (v), contact (n) – contact (v), charge (n) – charge (v), liquid (n) – liquid (a).
VI. Дайте исходную форму следующих слов:
classified, readily, used, easily, switches, permitting..
VII. Прочтите и переведите следующие микротексты, обращая внимание на указательные местоимения this – “эта”, “это”, “этот”; these – “эти”.
Hans Oërsted discovered that an electric current flowing through a conductor creates (создавать) a magnetic field around it. This discovery was later used to make an electromagnet. 2. In 1833 Faraday discovered the effects of passing (пропускание) an electric current through certain solutions (растворы), He called these effects the laws (законы) of electrolysis, 3. The passage of current may produce light. This can happen (случаться) in a number of ways.
VIII. Прочтите и переведите сдедующие предложения, учитывая, что местоимения this, these в функции заместителей ранее упомянутых существительных переводятся местоимениями “он”, “она”, “оно”.
1. A simple capacitor (конденсатор) is made from two metal plates, called electrodes. These are separated by an insulating material such as air, paper, or mica (слюда). 2. All insulators will allow some flow of electrons, however this can be usually ignored. 3. The main contacts of a switch are called poles. These are connected when the switch is on.
IX. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, учитывая различные значения as: a) союз: “когда”, “так как”, “поскольку”, “ибо”, б) наречие: “как”; as...as – так...как.
1. Resistance represents (представлять) the energy dissipated (рассеивать) by electrons as they move through the atomic structure of a conductor. 2, An electric current can be described as electric charge in motion. 3. As electrons are negatively charged they are attracted by a positive charge and repelled (отталкивать) by a negative charge. 4. Semiconductors can conduct electricity better than insulators but not as readily as metals.
X. Прочтите следующий текст, скажите, о чем в нем идет речь.
CONDUCTORS, INSULATORS AND SEMICONDUCTORS
1. If we connect a battery across a body, there is a movement of free electrons towards the positive end. This movement of е1eсtrons is an electric current. All materials can be classified into three groups according to how readily they permit an electric current to flow. These are: conductors, insulators and semiconductors,
2. In the first category are substances, which provide an easy path for an electric current. All metals are conductors, however some metals do not conduct well. Manganin (манганин), for example, is a poor conductor. Copper is a good conductor, therefore it is widely used for cables. A non-metal, which conducts well, is carbon. Salt water is an example of a liquid conductor.
3. A material, which does not easily release electrons, is called an insulator. Rubber, nylon, porcelain (фарфор) and air are all insulators. There are no perfect insulators. All insulators will allow some flow of electrons, however this can usually be ignored.
4. Semiconductors are midway (промежуточное положение) between conductors and insulators. Under certain conditions they allow a current to flow easily but under others they behave as insulators. Germanium and silicon are semiconductors Mixtures of certain metallic oxides also act as semiconductors. These are known as thermistors. The resistance of thermistors falls rapidly as their temperature rises. They are therefore used in temperature sensing devices.
Прочтите 2 и 3 абзацы текста, найдите ответ на следующие вопросы:
What materials are called conductors? Do all metals conduct well? What metal is a poor conductor? Why is copper widely used for cables? What substance is an example of а liquid conductor? What materials are called insulators? What insulators are mentioned in the text? Do insulators allow any flow of electrons?
XI. Замените подчеркнутые слова синонимами из текста.
1. The flow of free electrons is an electric current. 2. Materials in the first group are called conductors. 3. Materials, which provide a path for an electric current, are conductors. 4. All insulators permit some flow of electrons, 5. Germanium sometimes acts as an insulator and sometimes as a conductor.
UNIT 2
I Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
vary (v), increase (v), decrease (v), cool (v),alloy (n),value (n), degree (n), application (n), require (v), propose (v), ring (n), store (v), continue (v), remove (v), loss (n), occur (v), similarly (adv).
II. Выпишите из Прил.2 значения следующих терминов, эапомните их:
superconductivity coil (n)
memory cell induce (v)
winding (n) circuit (n)
Ш. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент:
circulate (v), theory (n), computer (n), total (a), modern (a), transformer (n), ideal (a).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
vary (v) – variation – various – variable;
apply (v) – application – -applied – applying;
require (v) – requirement – -required – requiring;
continue (v) –continuity – continuous – continuously;
store- (v) – store (n) – storage;
occur (v) – occurrence;
induce (v) – induced – inducing – inductance – inductor;
similar (a) – similarly – similarity.
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие пары слов, учитывая, что префиксы in/un (im, il, ir ) указывают на отрицание качества, обозначенного прилагательным, например: logical – логичный, illogical – нелогичный:
definite – indefinite; perfect – imperfect; important – unimportant, regular – irregular, easy – uneasy, possible – impossible, variable – invariable.
VI. Прочтите и переведите следующие двухкомпонентные сочетания существительных N1+N2, учитывая, что перевод таких словосочетаний следует начинать с последнего слова, являющегося определяемым. Существительное, стоящее слева от него, является определением и переводится: а) существительным в родительном падеже; б) прилагательным; существительным с предлогом:
circuit operation – работа цепи;
line voltage – линейное напряжение, напряжение на линии;
memory cell, current flow, information storage, semiconductor material, switch contacts.
VII. Прочтите и переведите следующие микротексты, учитывая, что русскими эквивалентами являются: а) личные местоимения “он”, “она”, “оно”, заменяющие неодушевленные существительные; б) указательное местоимение “это”.
1. A switch is used in almost every circuit. Its purpose (цель) is to make complete (замыкать) or to break an electric circuit. When a circuit is switched on current will flow through it. When it is switched off it becomes an open circuit and the flow of current is stopped. 2. When a current flows through a conductor it may heat the conductor. The temperature of the conductor rises. A practical use of it is in electric heaters.
VIII. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, учитывая, что союз because переводится – “так как, поскольку”, а сочетание because of – “из-за”.
1. The practical applications of superconductivity are limited because the very low temperatures are required. 2. Copper is widely used in cables because it is a good conductor. 3. The conductivity is never perfect because of resistance to the flow of current in metals.
IX. Прочтите следующий текст, расскажите о возможных практических применениях сверхпроводимости.
SUPERCONDUCTIVITY
1. The resistance of metals varies with their temperature. When they get hot, their resistance increases. When they cool, their resistance falls. The resistance of some metals and alloys decreases as their temperature is lowered, then falls suddenly to a negligible (пренебрежимый) value at temperatures a few degrees above absolute zero (–273°C). In other words, these materials have almost no resistance to an electric current at very low temperatures. They become almost perfect conductors. This is called superconductivity. It occurs with certain materials, for example lead (свинец), and only at very low temperatures.
2. The practical applications of superconductivity are limited because of the very low temperatures required. A number of uses, however, have been proposed. If a current is induced by a magnetic field in a ring of superconducting material, it will continue to circulate when the magnetic field is removed. In theory it could be used in the memory cells of computers. Memory cells made of superconducting materials could store information indefinitely. Because of the zero resistivity of the cells, the information can be retrieved (извлекать) very quickly, as fast as 10–8 seconds.
3. Ninety per cent of the total losses in modern transformers are due to the resistance of the windings. Transformers could be made with windings cooled to the low temperatures at which superconductivity occurs. The resistance of the windings would be zero and the transformer would be almost ideal. Similarly a 100% efficient motor has been proposed using the magnetic field of superconducting coils.
(1,500)
X. Замените подчеркнутые слова синонимами из текста.
1. The resistance of metals changes with their temperature. 2. The resistance of some metals and alloys falls when their temperature is lowered. 3. The practical applications of superconductivity are limited. 4. Superconductivity takes place at very low temperatures.
UNIT 3
I. 'Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
point (n), contain (v), difference (n), supply (v), convert (v), change (v), light (n), heat (n), part (n), consist (v), interrupt (v), comprise (v), compare (v), space (n), bulb (n), connect (v), wire (n), basic (n).
П. Выпишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
source (n) electromotive force
load (n) actuate (v)
transmission cell (n)
control (n) series (parallel) connection
Ш. Прочтите следующие интернациональное слова и дайте их русский эквивалент:
potential (n), system (n), element (n), energy (n), generator (n), form (n), lamp (n), regulate (v), limit (v), function (n), camera (n), satellite (n), relay (n), function (n).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
contain (v) – contained – containing – container;
convert (v) – converted – converting – convertible – conversion;
interrupt (v) – interrupted – interrupting – interruptions;
compare (v) – comparison – comparable – incomparable;
base (n) – basic – basically – baseless;
wire (n) – wireless;
connect (v) – disconnect – connected – connecting – connection;
transmit (v) – transmitter – transmission.
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие слова, образованные по, способу конверсии:
supply (n) – supply (v), form (n) – form (v), load (n) – load (v), control (n) –control (v), function (n) – function (v), limit (n) – limit (v), potential (n) – potential (a), light (n) – light (v), heat (n) – heat (v), change (n) – change (v),base (n) – base (v).
VI. Дайте исходную форму следующих слов:
supplies, called, wires, transmitted, higher, lower, interrupting.
VП. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания:
circuit elements, transmission system, potential difference, television camera, space satellite, ground control.
VШ. Прочтите и переведите следующие микротексты, обращая внимание на различные функции one : a) числительное “один”; б) заместитель ранее упомянутого существительного (переводится существительным, которое заменяет); в) формальное подлежащее (не переводится).
A resistor is one of the most соmmon (распространенный) devices used in electric circuits. Resistors are produced in different sizes (размеры) and classified into fixed and variable (переменный) ones. 2 Rutherford's suggestion (предположение) that the positive charge of the atom is connected in a small central nucleus (ядро) was a revolutionary one. With a Danish physicist, Niels Bohr, he worked out a model of the atom, the one which in many respects (вo многих отношениях) is still accepted (принимать ) today. 3. To understand what laser is, one has to understand how light is generated.
IX. Прочтите и переведите следующий микротекст, обращая внимание на указательные местоимения that – “тот – этот” , those –“те – эти”.
Most semiconductors use germanium and silicon as the base element. Because those elements are good insulators in their pure (чистый) form, they are mixed with another material in order to (для того чтобы) form useful semiconductor; that mixing is called doping (легирование).
X. Прочтите и переведите следующие микротексты, учитывая, что местоимения that (of), those (of) в функции заместителей ранее упомянутых существительных переводятся существительными, которые они эаменяюг.
1. A semiconductor is a material whose electrical conductivity is between that of a conductor and that off an insulator. The conductivity of a conductor decreases as its temperature increases while (в то время как) that of an insulator varies slightly (незначительно), but does increase, with increasing temperature. 3. James Maxwell predicted (предсказывать) that waves (волны) longer than those of light could exist.
XI. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, учитывая различные значения for : а) союз; “так как”, “ибо”; б) предлоги: “для”, “в течение”.
1. A battery is used for supplying electrical energy. 2. Electrical phenomena have been known to man for a very long time. 3. There are no perfect insulators for all insulators will allow some flow of electrons.
ХП. Прочтите следующий текст, перечислите основные элементы цепи и их функции.
CIRCUIT ELEMENTS
Current moves from a point of high potential to one of low potential. It can only do so if there is a path for it to follow. This path is called an electric circuit. All circuits contain four elements; a source, a load, a transmission system and a control.
The source provides the electromotive force. This establishes the difference 01 potential, which makes current flow possible. The source can be any device, which supplies electrical energy. For example, it may be a generator or a battery.
The load converts the electrical energy from the source: into some other form of energy. For instance, a lamp changes electrical energy into light and heat. The load can be any electrical device.
The transmission system conducts the current round the circuit. Any conductor can be part of a transmission system. Most systems consist of wires.
The control regulates the current flow in the circuit. It may control the current by limiting it, as does the rheostat, or by interrupting it, as does a switch.
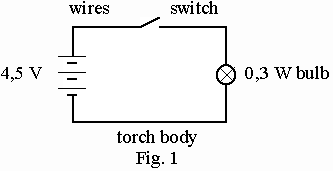
Study Fig. 1. In this simple flashlight (карманный фонарик) source comprises three 1,5 V cells in series. The load is 0,3 bulb. Part of the transmission system is the metal body of the flashlight and the control is a sliding (peoстат).

Compare Fig.2. The function of this circuit is to operate a television camera aboard a space satellite. Here the source is a battery of solar cells. A solar cell is an electric cell, which converts sunlight into electrical energy. The load is the television camera. The transmission system is the connecting wires. The control is a relay actuated by transmissions from ground control. Although the function of this circuit is much more complex than that of the flashlight, it too consists of the four basic elements.
(1,500)
XIII. Задания к тексту.
Прочтите 1 абзац текста, определите функцию one. Переведите текст абзаца.
Прочтите 1-5 абзацы текста. Определите функции местоимений it, these в I и 5 абзацах текста. Переведите текст абзацев.
Прочтите 6 и 7 абзацы текста. Найдите в тексте ответ на следующие вопросы:
What circuit is shown in Fig. 1? What is the function of the circuit shown in Fig. 2? What are the basic elements of this circuit?
Переведите текст абзацев.
Еще раз прочтите текст, перечислите его основные положения.
XIV. Замените подчеркнутые слова синонимами из текста.
1. Current flows from a point of high potential to one of low potential. It can only do so if there is way for it to follow. 2. All circuits consist of four elements. 3. The source supplies electrical energy. 4. The load changes electrical energy from the source into some other form of energy. 5. The control controls the current flow in the circuit. 6. The source in the circuit shown in Fig. 1 consists of three cells connected in series. 7. The control shown in Fig. 2 is a relay operated by ground control.
UNIT 4
I. Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
scientific (a), produce (v), create (v), amount (n), develop (v), wind (v), rotate (v), direction (n), shape (n), obtain (v), require (v), design (n), efficient (a).
II. Запишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
core (n) revolution (n)
armature (n) alternating current (a.c.)
shaft (n) direct current (d.c.)
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент:
generator (n), magnet (n), process (n), dynamo (n), pole (n), peak (n), commutator (n).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:.
science (n) – scientist – scientific –scientifically;
produce (v) – producer – production – productivity;
create (v) – creative – creation – creator;
develop (v) – developed – developing – development;
rotate (v) – rotor – rotation;
obtain (v) – obtainable – obtaining – obtained;
require (v) – required – requiring – requirement;
rapid (a) – rapidly – rapidity;
efficient (a)-efficiently – efficiency.
V Дайте исходную форму следующих слов:
found, made, wound, driven, returns, needed.
VI. Переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на подчеркнутые слова, образованные по способу конверсии.
1. There are semiconductor devices whose resistance changes with changes of temperature. Thermistor is one of them. 2. Batteries and dynamos supply electric power. 3. The practical supply of electricity on a large scale (масштаб) was only possible by the development of electromagnetic machines, generators and transformers. 4. There are different transformers for different uses. 5. The author of the article (статья) uses a new method of calculating these values.
VII. Прочтите и переведите следующий микротекст, учитывая, что слову that в русском языке соответствуют: а) союзы “что”, “чтобы”, вводящие дополнительные придаточное предложения; б) союзное слово “который”, вводящее определительные придаточные предложения.
1. The connection between magnetism and electricity was first investigated (исследователь) in 1819 by the Danish scientist, Hans Öersted. He discovered that an electric current has a magnetic effect and that a conductor that is carrying a current is surrounded (окружать) by a magnetic field. This discovery was used by an English scientist, William Sturgeon, to make an electromagnet that consists of a soft (мягкий) iron bar (брусок) with a coil of wire around it. When the current in the coil is switched on the bar becomes magnetized; when it is off the bar loses its magnetism.
VIII Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, учитывая различные значения since; а)союз “так как”, “поскольку”, “с тех пор, как”, б) предлог “с”, “со времени”.
1. Since I9I8 electric bulbs have been filled, (наполнять) with gas, 2. Almost 300 years have passed (проходить) since the Newton laws have been discovered. 3. Electromagnetic induction is a process that causes (вызывать) current to flow without physical or electrical contact. Since there is no direct contact between the magnet, and the current-carrying wire we say that the electricity from a generator is produced by means of (посредством) electromagnetic induction.
IX. Прочтите текст, обращая внимание на первые предложения абзацев. Перечислите основные положения текста.
GENERATORS
I. One of the most important scientific discoveries was made by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday found that when a magnet is moved near a coil of wire, an electric current is produced in a coil. He also discovered that when a current is switched on and off in one coil a changing magnetic field is created around the coil and that this changing field will create another current in a second nearby coil (находящийся рядом). The current in the second coil is much greater if both coils are wound on the same iron core. This process of producing electricity from magnetism is called electromagnetic induction.
2 The electric generators, or dynamos, that supply us with the vast amounts of electric power needed today have all been developed from Faraday's discovery. A dynamo consists of many coils of wire wound on an Iron core (armature) which is rotated on a shaft between .the poles of an electromagnet. The current is generated in the coils when the armature is driven around. In a simple dynamo the current changes direction twice for each revolution of the coil. First it builds up to a positive peak. Then it returns to zero before building up to a positive peak again. This is called alternating current (a.c.) A graph showing how the current varies with time has the shape of a wave. To obtain direct current (d.c.) from a rotating generator requires a commutator with split rings (кольца с прорезью).
3. Once (как только) the principle of electromagnetic induction had been discovered there was rapid development in the design of more efficient generators.
(1,500)
X. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на различные значения подчеркнутых слов.
1. The lines in this figure show the refraction of light. 2. Many important figures relating to the growth of modern electronic industry are shown in the table. 3. The number of protons defines the mass number. 4. In this case a number of rules should be remembered. 5. Telephone and telegraph are important means of communication. 6. It is possible to translate from one language into another by means of computer. 7. The word “computer” comes from a Latin word which means, “to count”. 8. The mean value of power is given by the formula.
UNIT 5
I. Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
carry (v), stream (n), reverse (v), complete (a), measure (v), operate (v), advantage (n), depend (v), relative (a), step up (down) (v), link (v), case (n), breakdown (n), demand (n), cheap (a), reach (v), consumer (n).
II. Выпишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
surge (v)primary winding
cycle (n) secondary winding
frequency (n) input (n)
turn (n) output (n)
power station
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент:
constant (a), regular (a), interval (n), rhythmically (adv.), transformer (n), double (v), system (n), station (n), local (a), region (n), voltage (n), separate (a).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
carry (v) – carried – carrying – carrier;
reverse (v) – reversive;
complete (a) – incomplete – complete (v) – completeness;
measure (v) – measure (n) – measurement – measurable – measureless;
operate (v) – operator – operative – operation;
advantage (n) – disadvantage – advantageous;
depend (v) – dependent – dependence – independence;
relative (a) – relatively – relativity;
cheap (a) – cheapness – cheaply;
consume (v) – consumer – consumption.
V. Дайте исходную форму следующих слов:
wound, changed, stepped, supplied, carrying.
VI. Прочтите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на союзы as well as – так же как, either...or – или...или, both...and – и...и.
1. We shall assume (предполагать) here that you have a basic knowledge of such things as current and voltage as well as some familiarity (осведомлённость) with components such as resistors, capacitors and inductors. 2. The voltage of a transformer can be either stopped up or stepped down. 3. Until the middle (середина) of the 50s all our knowledge of the solar system came to us either by light waves or radio waves. 4. The semiconductor diode is made up of both p-type and n-type semiconductor material. 5. An electronic device is made up of both “active” circuit elements, such as transistor, and “passive” components, such as resistors, capacitors and inductors.
VII. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, учитывая значение словосочетания “rather than” “а не”.
1. It is cheaper to transmit a low current at a high voltage rather than a high current at a low voltage. 2. If the anode is made negative it will repel rather than attract electrons and no current can pass through the valve (лампа).
VIII. Прочтите текст, скажите, в чем заключается прелиму|щество переменного тока по сравнению с постоянным.
ALTERNATING CURRENTS
1. In a wire carrying a direct current (produced, for instance, by a battery) there is a constant stream of electrons in one direction along the wire. An alternating current reverses its direction at regular intervals. In a wire carrying an alternating current the electrons surge rhythmically backwards and forwards. One complete forward and backward movement is a cycle and the number of cycles per second is the frequency of the alternating current. This is measured in hertz (one hertz – one cycle per second).
2. An alternating current operates lights, heaters and motors just as well as a direct current but it has the great advantage that the voltage of the supply can be easily changed up or down by using a transformer. A transformer consists essentially of two separate coils of wire wound onto the same iron core. Depending to the relative number of turns on the primary (input) and secondary (output) coils (windings) the voltage can be either stepped up or stepped down.
3. Large transformers are used In the grid system (единая энергосистема) which links all the power stations so that current from one station can be supplied to another region in the case of a breakdown or a greater demand for current than usual. The large power station generators produce electricity at 6000 V however, it is cheaper to transmit a low current at a high voltage, rather than a high current at a low voltage. The output of the power station is thus stepped up to 132000 V, before being fed (до поступления) into the grid system. It is stepped down again at local sub-stations and reaches the consumer at 240 V.
(1,500)
IX. Задания к тексту.
Прочтите и переведите 1 абзац текста.
Прочтите 2 абзац текста. Найдите в нем сложное предложение, скажите, сколько предложений входит в его состав, назовите союзы, с помощью которых осуществляется связь между этими предложениями. Переведите текст абзаца.
Прочтите 3 абзац текста, найдите в нем ответ на следующие вопросы:
What is the transformer used for? Why is the output of the power station stepped up to 130000 V before being fed to the grid system?
Еще раз прочтите текст, изложите кратко его содержание.
UNIT 6
I. Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
tiny (a), revolve (v), follow (v), lead (led, led), growth. (n), vast (a), rely on (v), invent (v), behaviour (n), light (a), equipment (n), restrict (v), exploration (n), perform (v), complicate (v).
II. Выпишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
valve
power supply
integrated circuit
chip
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент.
negative (a), atom (n), isolate (v), industry (n), revolutionize (v), miniaturize (v), radio (n), television (n), function (n), mathematical (a), operation (n), crystal (n), component (n).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
grow – growth;
rely (v) – reliable – unreliable – reliability;
invent (v) – inventor – invention – inventive – uninventive;
equip (v) – equipped – unequipped – equipment;
restrict – restricted – restricting – restriction;
explore (v) – explored – exploring – exploration;
perform (v) – performed – performing – performance;
complicate (v) – complication – complicated.
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания:
radio and television equipment, space exploration, semiconductor crystal, power supply.
VI. Прочтите текст, перечислите его основные положения.
ELECTRONICS – THE 20TH CENTURY SCIENCE
1. Electrons, the tiny particles of negative electricity that revolve around the nuclei of atoms, were discovered by J. J. Thomson in I897. It then appeared to be (казалось) an isolated discovery but in the following 75 years it has led to the growth of a vast industry that has changed our lives in many ways. At first all of these industries relied on the thermionic valve invented by J. A. Fleming in I904. The valve was the first electronic device to be invented and its development revolutionized methods of communication and entertainment (развлечение).
2. In 1948 the transistor was invented by William Shockley, an American physicist. It depends on the behaviour of electrons in semiconductors such as silicon and germanium. Transistors can do all that valves can do but they are much smaller, and therefore lighter, stronger, and work with much smaller power supplies than valves. This led to much smaller, or miniaturized, electronic equipment. Radio and television equipment can now fit in (помещаться) the restricted space of a satellite. In fact, the exploration of space would not have been possible without transistors. Integrated circuits – the smallest electronic devices – are made by designing semiconductor crystals in such a way that they perform functions of whole circuits. In these circuits, a chip of silicon may contain a large number of separate components, such as transistors, connected together. Computers also depend on electronic switches. The speed with which the electronic switches work allows the computer to carry out very complicated mathematical operations very quickly.
(1,600)
VII. Задания к тексту.
Прочтите 1 абзац текста, найдите в нем ключевые слова и их повторы. Раскройте значение местоимения it во втором предложении абзаца.
Отвегьте на следующие вопросы:
What is an electron? When were electrons discovered? What was the first electronic device to be invented?
Прочтите и переведите 2 абзац текста.
VIII. Замените подчеркнутые слова синонимами из текста.
1. Fleming developed the thermionic valve in 1904. This resulted in the growth of a vast industry that transformed our lives in many ways. 2. At first the development of electronics depended on the thermionic valve, which was called a tube in the USA. 3. The action of the transistor relies on the behaviour of electrons in semiconductors. 4. Transistors can perform with much smaller power supplies than valves. 5. In integrated circuits semiconductor crystals fulfil the functions of whole circuits. 6. The computer can do very complicated mathematical operations very rapidly.
UNIT 7
I. Найдите в Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, выучите их:
emit (v), cloud (n), seal (v), attract (v), repel (v), constitute (v), feed (fed, fed), several (a).
II. Найдите в Прил. 2 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
plate (n) terminal (n) rectifier record player filament (n) grid (n) amplifier gain (n)
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова, дайте их русский эквивалент:
ordinary (a), form (v,n), positive (a), negative (a), anode (n), cathode (n), regulator (n), distance (n), spiral (no), control (v), variation (n), modern (a).
IV. Прочтите следующие слова, определите по суффиксу, какой частью речи они являются, переведите их:
emit – emitter – emission – emitting – emitted;
attract – attraction – attracting – attracted – attractive;
repel (v) – repellant – repelling;
constitute – constitution – constituting – constituted;
amplify (v) – amplifier – amplification – amplified – amplifying;
rectify – rectifier – rectification.
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие пары, слов:
valve – value, tube – type, charge – change, around – surround, simple – signal, contain – obtain.
VI. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания:
lamp bulb, onе wау regulator, triode valve, radio and record-player amplifiers.
VII. Переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на сравнительную конструкцию: “the ...the” – “чем...чем”.
1. The longer and thinner a piece of wire the greater will be its resistance. 2. The more heat a gas contains the faster tne molecules move. The faster they move, the more frequent and powerful are their collisions. 3. Infrared waves are produced by the vibrating atoms and molecules of the source of radiation. The higher the temperature of the source, the mоrе rapidly the atoms vibrate and the greater the frequency of the waves.
(4000)
VIII. Прочтите текст, найдите абзац, где говорится об изобретении триода, опишите принцип действия триода.
THERMIONIC VALVES
1. In an ordinary electric lamp the electrons emitted by the filament form a cloud around it. If a metal plate is sealed inside the lamp bulb, a little distance from the filament, a simple diode valve is formed. If the positive terminal of a battery is connected to the plate (anode) and the negative terminal is connected to the filament (cathode), the negatively charged electrons will no longer collect around the filament but will be attracted towards the anode. Because a flow of electrons constitutes an electric current, a current flows through the valve from the cathode to the anode. If the anode is made negative it will repel rather than attract electrons and no current can pass through the valve. Thus the valve acts as one-way regulator for electrons. A valve operating in this way can be used as a rectifier.
2. An American inventor, Lee de Forest, added a third electrode in the form of a wire spiral between the cathode and the anode and produced the triode valve. This third electrode (grid) can control the number of electrons reaching the anode. The more positive the voltage of the grid compared to the cathode, the more electrons pass through it to reach the anode and so the anode current is increased. The less positive the grid, the fewer number of electrons reach the anodes. The important point is that a small variation in the voltage of the grid can produce a large variation in the anode current. So if a weak signal is fed to the grid a much stronger signal can be taken from the anode. The valve therefore acts as an amplifier. Modern valves have several grids and are more sensitive than the triode. Until the invention of the transistor, all radio and record-player amplifiers were based on thermionic valves.
(1,7ОО)
IX. Задания к тексту.
Прочтите 1 абзац текста, найдите в нем сложные предложения, назовите союзы, с помощью которых осуществляется связь внутри сложных предлжений. В каждом предложении найдитe сказуемое, определите его время и залог. Переведите текст абзаца.
Прочтите 2 абзац текста. Найдите предложения со сравнительной конструкцией, переведите их. Ответьте на следующие вопросы:
Who invented the triode valve? What is the function of the grid in a triode? What makes possible the amplification of a signal in the triode?
X. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на различные значения подчёркнутых слов:
1. A diode is not capable of gain, so it cannot serve as an active circuit element. 2. One must work hard in order to gain experience in the field of modern electronics. 3. It is known that wires carrying current in a magnetic field have forces on them. 4. Reading scientific papers we obtain information on current developments in the field of science and technology. 5. The above definition states that there is a close connection between the phenomena described. 6. Plasma is the fourth state of matter. 7.For an electric current to flow we must have a closed circuit. 8. During the experiment the temperature rode above the calculated value.
UNIT 8
I. Выпишите из Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомниве их:
straight (a), hole (n), glow (n), narrow (a), similar (a), enormous (a), widen (v), coat (v), strike (struck, stricken) (v), spot (n), screen (n), amount (n), set (n), pair (n), point (n).
II. Выпишите из Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их:
cathode ray tube
electron gun
deflector plate
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент:
electrode (n), gas (n), line (n), modern (a), opposite (a), lens (n), vertical (a), horizontal a), chemicals (n).
IV. Образуйте существительные от следующих глаголов, используя суффиксы: -ment, -ion (-tion), -у, -ity, -age, -er (-or)
develop, discover, deflect, heat, pass, act, attract, apply, move, produce, similar.
V. Прочтите текст, замените местоименными повторами подчеркнутые слова. Раскройте логико-смысловую функцию слов-гидов. Переведите текст.
The cathode ray tube (crt) is used in oscilloscopes, radar receivers and television sets. By means of a crt, an oscilloscope not only shows the size of a signal, but also how the signal varies with time. In other words an oscilloscope shows the waveform of the signal.
The crt operates as follows. First electrons are emitted from a heated cathode. Then these electrons are accelerated to give them some velocity (скорость). Next these electrons are formed into a beam which can be deflected vertically and horizontally. Finally these electrons are made to strike a screen coated on screen's inner surface with a phosphor.
VI. Прочтите текст, разделите его на логико-смысловые единства, озаглавьте их.
CATHODE RAYS AMD CATHODE RAY TUBE
1. When a voltage is applied between two electrodes sealed into a tube from which most of the gas has been removed, a stream of electrons passes from the negative electrode (cathode) to the positive electrode (anode). Because the stream travels in straight lines, like light rays, they are called cathode rays. If the anode has a hole in it, the cathode rays will pass through it and strike the end of the glass tube producing a greenish glow. It was from the study of cathode rays that J. J. Thomson discovered electrons in 1897. This discovery led to the development of the whole field of electronics.
2. The modern cathode ray tube uses a narrow beam of electrons produced by heating the filament similar to the one in a thermionic valve. The beam is focused by a system of cylindrical electrodes, which act in the same way as a lens acts on a beam of light. The system of electrodes together with the filament is called an electron gun. The electrons travel at the enormous speed of about 80 000 km per second. The widened end of the tube opposite the electron gun is coated with chemicals (phosphor) which glow when struck by the electron beam and produce a green spot on the screen.
3. As electrons are negatively charged they are attracted by a positive charge and repelled by a negative charge. Inside the tube there are two sets of deflector plates. One set is vertical and the other horizontal. When voltages are applied to the deflector plates the electron beam, and thus the spot of light on the screen, can be moved up and down from side to side. The amount of deflection is in proportion to the voltage applied to the plates. By applying voltages to both pairs of plates at the same time the spot can be moved to any point on the screen.
UNIT 9
I. Найдите в Прил. 1 значения следующих слов, запомните их:
remove (v), reason (n), solid (a), layer (n), piece (n), slice (n), correspond (v), involve (v), conceive (v), quantity (n).
II. Найдите в Прил. 2 значения следующих терминов, запомните их.
oscillation emitter
tube (n) junction transistor
solid state bipolar transistor
base (n) field-effect transistor
collector charge carrier
III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и дайте их русский эквивалент.
detect (v), signal (n), central (a), polarity (n), fabrication (n), practical (a), diameter (n), modern (a).
IV. Дайте исходнув форму следующих слов:
moving, called, known, less, smaller
V. Прочтите и переведите следующие словосочетания:
glass-tube, solid-state device, n-type germanium, warming-up time.
VI. Назовите глаголы, от которых образованы следующие существительные:
detection, amplification, rectifier, production, carrier, passage, introduction, correspondence, operation, fabrication, involvement, collector, emitter.
VII. Прочтите следующий текст, замените подчеркнутые существительные соответствующими местоимениями. Переведите текст.
In recent years the transistor – an entirely (совершенно) new type of electron device – has replaced the electron tubes in most, if not all applications. Transistors are much smaller than tubes. Transistors have no filament and hence need no heating power, and may be operated in any position. Transistors are mechanically rugged (прочный) and transistors' life is practically unlimited. In contrast to electron tubes, which utilize (использовать ) the flow of free electrons through a vacuum or gas, the transistor relies (основываться ) for transistor's operation on the movement of charge carriers through a solid substance, a semiconductor.
VIII. Прочтите текст, скажите, какие типы транзисторов в нем упоминаотся. Назовите основные элементы транзистора.
TRANSISTORS
1. Valves are used in electronics to control the flow of currents in circuits, to detect and amplify radio signals and to produce oscillations in transmitters. Transistor can also perform these functions. In valves, the current is carried by electrons passing from the cathode to the anode in a glass tube from which the air has been removed. Transistors are completely solid, the electrons moving between the atoms of certain semiconducting crystals. For this reason they are called solid-state devices.
2. A transistor is made by sandwiching a thin layer of n-type germanium between two small pieces of p-type germanium. This is a p-n-p-transistor (n-p-n-translators are also used). The central n-slice is the base and corresponds to the grid of a valve. One of the two outer p-type layers is the emitter and the other is the collector: they correspond to the cathode and the anode of a valve respectively. The n-p-n and p-n-p-transistors make up the class of devices called junction transistors. They are also known as bipolar transistors because charge carriers of both polarities are involved in their operation. It is the bipolar transistor that was invented in 1948. A second basic kind of transistor was conceived almost 25 years before the bipolar devices, but its fabrication in quantity became practical only in the early 1960’s. This is the field-effect transistor.
3. Transistors are very small and light. A typical transistors is less than one centimetre long and three millimetres in diameter. There is no filament to heat up in order to emit electrons and so there is no warming-up time. Modern radio and television sets and computers use transistors instead of valves.
(1.700)
IX. Ответьте на следующие вопросы:
How is a p-n-p-transistor manufactured? What are the main elements of a transistor? What are the main elements of а valve? Why can we compare these two devices? What kind of transistor was the first to be invented?
Переведите текст абзаца.
Прочтите 3 абзац текста, расскажите о преимуществах транзисторов по сравнению с лампами.
X. Прочтите и переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на различные значения подчеркнутых слов.
1.Transistors are the main functional units of microelectronic devices. 2. Ohm is a unit of resistance. 3. Heat causes many chemical changes in substances. 4. This phenomenon takes place due to several causes. 5. There is only one paper devoted to the subject discussed. 6. Electronic computers are the only kind of machine with which one hopes to translate from one language to another.
