
2832
.pdf
2832 |
Министерство транспорта Российской Федерации |
|
|
|
Федеральное агентство железнодорожного транспорта |
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
«САМАРСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ ПУТЕЙ СООБЩЕНИЯ»
Кафедра иностранных языков
Л. В. Абдрахманова
АН Г Л И Й С К И Й Я З Ы К
Методические указания для студентов II курса специальности «Электроснабжение железных дорог»
Самара
2011
1
УДК 420
Абдрахманова Л.В.
Английский язык : методические указания для студентов II курса специальности «Электроснабжение железных дорог» / Л.В. Абдрахманова. – Самара : СамГУПС, 2011. – 72 с.
Утверждены на заседании кафедры 9 июня 2011 года, протокол № 9. Печатаются по решению редакционно-издательского совета университета.
Методические указания выполнены в соответствии с требованиями программы обучения иностранному языку студентов неязыковых специальностей, предполагающей профессионально ориентированную направленность учебного процесса. Методические указания ставят своей целью ознакомить студентов с основной терминологической лексикой по специальности «Электроснабжение железных дорог» и базовыми коммуникативными моделями.
Статьи из журналов Rail International, International Railway Journal, Railway Gazette, а также материалы, заимствованные из Encyclopedia Britannica, Chicago и Internet сайтов послужили основой для разработки уроков, каждый из которых освещает наиболее актуальные проблемы электрического транспорта и электроснабжения железных дорог. Кроме того, в методические указания включены частично адаптированные тексты познавательногохарактера.
Структура урока предполагает интеграцию всех видов учебной деятельности по иностранному языку, учитывает специфику технического вуза и обеспечивает индивидуальныйподходприпроведениизанятия.
Методические указания снабжены кратким терминологическим словарем, который призван восполнить недостаток лексикографических материалов по проблемам железнодорожноготранспорта.
Составитель: Любовь Вениаминовна Абдрахманова
Рецензенты: доцент кафедры «Иностранные языки», кандидат филологических наук С.Я. Никитина
(Самарский государственный университет путей сообщения);
доцент кафедры иностранных языков Т.А. Филоненко (Самарский государственный технический университет)
Под редакцией составителя
Подписано в печать 27.06.2011. Формат 60х90 1/16. Усл. печ. л. 4,5. Тираж 100 экз. Заказ № 180.
© Самарский государственный университет путей сообщения, 2011
2

C H A P T E R O N E E L E C T R I C P O W E R
U N I T 1
Ex. 1. Copy and memorize the following terms.
Glossary
charge – заряжать, заряд circuit – цепь, контур; схема conductor – проводник nucleus (мн.nuclei) – ядро
cross section – поперечное сечение particle – частица current – ток
drift – смещаться, смещение layer – слой
matter – вещество relative – относительный repulsion – отталкивание rod – стержень
SI (French: Système International) – Международная система единиц, СИ to attract – притягивать
attraction – притяжение value – значение, величина
wire – провод; подключать (при помощи проводов)
Ex. 2. Copy the following words and memorize their meanings:
9excess – избыток, избыточный
9force – сила
9fundamental – основной
9fundamentals – основы
9interaction – взаимодействие
9loose – свободный
9property – свойство, качество
9surface – поверхность
9thus – таким образом
9to bind (bound, bound) – связывать
9to determine – определять
9to exert – оказывать действие
9to experience – испытывать
9to involve – вовлекать, втягивать
Ex. 3. Translate the following sentences from English into Russian.
1. If one ball is charged by the glass rod, and the other by an amber rod, the two balls are found to attract each other. 2. The hydrogen molecule binds with the oxygen molecule. 3. The Moon exerts a force on the Earth. 4. Investigators are still trying to determine the cause of the fire. 5. Many old people will experience problems as the result of retirement. 6. This tooth feels very loose. 7. You may think you’re poor, but it's all relative. 8. Price is determined through the interaction of demand and supply. 9. Let x have the value 25. 10. Bags or cases that weigh more
3

than the legal limit that you can take on a plane are called excess baggage. 11. The walls are reinforced with steel rods. 12. Nearly 10 percent of the Earth's surface is covered by ice. 13. Leave the battery on charge all night. 14. Running your own business usually involves working long hours. 15. The roof beams were 50 centimetres square in cross section. 16.The metallic substances differ from all other materials by the fact that the outer shells of their atoms are bound rather loosely, and often let one of their electrons go free.
Ex.3. Fill in the blanks with the words given in the box. Translate the sentences.
charged |
attract |
value |
excess |
current |
SI |
forces |
wire |
thus |
charges |
surface |
circuit |
determines |
conductor |
interactions |
|
experienced |
|
cross section |
|
1. He … severe hardships as a child. 2. Wood is a poor … of heat. 3.Electric … is measured using an ammeter. 4. Gravitation is a natural phenomenon by which objects with mass … one another. 5. All conductors contain electric … which will move when an electric potential difference is applied across separate points on the material. 6. The terrorists … the bomb with an explosive substance. 7. The car reached speeds in … of 100 miles per hour. 8. In mathematics, the absolute … of a real number is its numerical one without regard to its sign. 9. It only … the action of chemical force. 10. The … was developed in 1960 from the old metre-kilogram-second system, rather than the centimetre-gram-second system. 11. ... we have man modifying nature, and nature modifying man. 12. … has many different applications in modern technology and in household use. 13. All the known … of nature can be traced to these fundamental … 14. Nearly 10 percent of the Earth’s … is covered by ice. 15. An electrical ….is a network that has a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. 16. The … of an octahedron is a square.
Ex. 4. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the tense form of the predicates in the Passive Voice. Put general questions and special questions to the sentences.
1.One in every five homes with television are wired to a cable system (How many?).
2.A crowd was attracted to the scene of the accident (Where?). 3. The taxpayer was determined by the court that he was not entitled to a refund (What?). 4. A body which is positively charged and a body which is negatively charged experience an attractive force (What kind of force?).
5.The electric charge that flows is carried by mobile electrons in a conductor (Where?). 6. The track is surfaced with cement (What …with?). 7. A great increase in the national debt was involved by the war (What … by?). 8. Parcels must be properly bound up for posting to other countries (What … for?). 9. The interview was conducted in English (What language…in?).
10.The gravitational force was described systematically by Isaac Newton in the 17th century (When?). 11. One of the basic physical forces, the electric force is named after a French physicist, Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (Who …after?). 12. In SI system, the unit of force (newton), the unit of charge (coulomb), and the unit of distance (metre), are all defined independently of Coulomb’s law (How?). 13. In many contexts the direction of the current in electric circuits is taken as the direction of positive charge flow, the direction opposite to the actual electron drift (How?). 14. When so defined the current is called conventional current (What?). 15. When an electric current flows in an external magnetic field, a magnetic force is experienced (When?). 16. The magnetic field can be visualized as a pattern of circular field lines surrounding the wire (How?).
4

Ex. 5. Practice the reading and translate the following word combinations. You are to copy them and memorize their meanings.
Subatomic particles, electromagnetic interaction, electrically charged, positively charged, negatively charged, electrically neutral, a force of repulsion, a force of attraction, a fundamental physical constant, a drift of electrons, net amount of electric charge, electric circuit, cross section of a conductor.
Ex. 6. Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right.
1. |
value |
a) |
quality or power that a substance has |
2. |
repulsion |
b) |
to make someone or something move towards another thing |
3. |
to determine |
c) |
to tie someone so that they cannot move or escape |
4. |
interaction |
d) |
mathematical quantity shown by a letter of the alphabet or sign |
5. |
nucleus |
e) |
force by which one object pushes another one away from it |
6. |
property |
f) |
to find out the facts about something |
7. |
force |
g) |
very slow movement |
8. |
circuit |
h) |
flow of electricity through a wire |
9. |
to exert |
i) |
the complete circle that an electric current travels |
10.to attract |
j) |
to influence in order to make something happen |
|
11.current |
k) |
process by which two or more things affect each other |
|
12.drift |
l) |
the positively charged central core of an atom |
|
13.to bind |
m) influence changing the motion of a body or producing motion |
||
Read the text and translate it using a dictionary if necessary.
E L E C T R I C C H A R G E
Electric charge is a fundamental conserved of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. Electricity consists of charges carried by electrons, protons, and other particles. Electric charge comes in two forms: positive and negative. Electrons and protons both carry exactly the same amount of electric charge, but the positive charge of the proton is exactly opposite the negative charge of the electron. If an object has more protons than electrons, it is said to be positively charged; if it has more electrons than protons, it is said to be negatively charged. If an object contains as many protons as electrons, the charges will cancel each other and the object is said to be uncharged, or electrically neutral.
Two objects that have an excess of one type of charge exert a force of repulsion on each other when relatively close together. Two objects that have excess opposite charges, one positively charged and the other negatively charged, each other when relatively near.
Many fundamental, or subatomic, particles of matter have the property of electric charge. For example, electrons have negative charge and protons have positive charge, but neutrons have zero charge. The negative charge of each electron is found by experiment to have the same value, which is also equal to that of the positive charge of each proton. Charge thus exists in natural units equal to the charge of an electron or a proton, a fundamental physical constant.
Atoms of matter are electrically neutral because their nuclei contain the same number of protons as there are electrons surrounding the nuclei. Electric current and charged objects involve the separation of some of the negative charge of neutral atoms. Current in metal wires
5
consists of a drift of electrons of which one or two from each atom are more loosely bound than the rest. Some of the atoms in the surface layer of a glass rod positively charged by rubbing it with a silk cloth have lost electrons, leaving a net positive charge because of the unneutralized protons of their nuclei. A negatively charged object has an excess of electrons on its surface.
Electric charge is conserved: in any isolated system, in any chemical or nuclear reaction, the net electric charge is constant. The unit of electric charge in the metre-kilogram-second and SI systems is the coulomb, equivalent to the net amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a conductor in an electric circuit during each second when the current has a value of one ampere.
Ex. 7. Match the halves of the sentences together.
|
A |
|
B |
1. |
Electrically charged matter … |
a) |
as the positive charge of each proton |
2. |
Two objects that have an excess of |
b) |
the net electric charge is constant |
|
one type of charge … |
|
|
3. |
Two objects that have excess |
c) |
have the property of electric charge. |
|
opposite charges … |
|
|
4. |
Atoms of matter are electrically |
d) |
exert a force of repulsion. |
|
neutral because… |
|
|
5. |
Electricity consists of charges … |
e) |
a drift of electrons. |
6. |
Electric charge … |
f) |
loose electrons by rubbing it with a silk cloth |
7. |
The negative charge of each |
g) |
equals to the amount of electric charge that |
|
electron has the same value … |
|
flows through a conductor when the current has |
|
|
|
a value of one ampere. |
8. |
In any isolated system, in any |
h) |
produces electromagnetic fields |
|
chemical or nuclear reaction … |
|
|
9. |
Subatomic particles of matter … |
i) |
the separation of some of the negative charge of |
|
|
|
neutral atoms. |
10. Current in metal wires consists |
j) |
exert a force of attraction. |
|
|
of … |
|
|
11. The atoms in the surface layer of a |
k) |
carried by electrons, protons, and other particles. |
|
|
glass rod … |
|
|
12. The unit of electric charge … |
l) |
because their nuclei contain the same number of |
|
|
|
|
protons as electrons. |
Ex. 8. Choose the best alternative and answer the questions.
1.What determines electromagnetic interaction of subatomic particles?
a)protons and electrons
b)electric charge
c)electromagnetic field
2.What do electromagnetic fields influence?
a)protons and electrons
b)metals
c)electrically charged matter
4.What is the amount of electric charge carried by electrons and protons?
a)the same amount
b)protons carry bigger value of electric charge
6

c)protons carry smaller value of electric charge
5.Which two objects exert a force of repulsion on each other?
a)that have excess opposite charges
b)that have an excess of one type of charge
c)that have the same amount of charges
6.Which two objects exert a force of attraction on each other?
a)that have excess opposite charges
b)that have an excess of one type of charge
c)that have the same amount of charges
7.When do the two objects exert a force of attraction or repulsion?
a)when they are close to each other
b)when they are far from each other
c)when they contain as many protons as electrons
8.Why are atoms of matter electrically neutral?
a)because their nuclei contain more protons than electrons surrounding the nuclei
b)because their nuclei contain fewer protons as there are electrons surrounding the nuclei
c)because their nuclei contain the same number of protons than electrons surrounding the nuclei
9.How are electrons bound in metals?
a) loosely |
b) tightly |
c) they are unbound |
10.What does “electric charge is conserved” mean?
a)electric charge is different
b)electric charge is the same
c)electric charge is variable
Ex. 9. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
1. Электрический заряд – это источник электромагнитного поля, связанный с материальным носителем; Электрический заряд - это также внутренняя характеристика элементарной частицы, определяющая её электромагнитные взаимодействия. 2. Существует два вида электрического заряда - положительный заряд и отрицательный заряд; при этом одноимённо заряженные тела (частицы) отталкиваются, а разноимённо заряженные притягиваются. 3. Электроны имеют отрицательный заряд, а протоны имеют такой же положительный заряд. 4. Единицей измерения заряда в СИ является кулон.
U N I T 2
Ex. 1. Copy and memorize the following terms.
Glossary
bulb – лампочка
incandescent bulb – лампочка накаливания capacitance – ёмкость, ёмкостное сопротивление device – устройство, прибор
electric battery – гальванический элемент, аккумулятор electric power – электроэнергия
7

electromotive force (emf) – электродвижущая сила equation – уравнение
friction – трение measure – измерять,
to measure - единица измерения outlet – розетка
resistance – сопротивление
Ex. 1. Copy the following words and memorize the meanings.
9alternating – переменный
9direct – прямой, постоянный
9direction – направление
9flow – течение
to flow – течь
9glow – свет
to glow - светиться
9law – закон
9movement – движение
9passage – прохождение
9relation – отношение; зависимость
9supply – снабжение to supply – снабжать
9to distribute – распределять
9to plug in – включать в сеть
9to quantify – определять количество, измерять
9to state – формулировать
Translate the following sentences into Russian
1. Make sure the weight of the load is evenly distributed. 2. An alternating current is an electric current that continually changes direction as it flows. 3. The streets are in a direct line, and of a convenient breadth. 4. The bridge isn’t strong enough to allow the passage of heavy vehicles. 4. Is your printer working? Wait a minute – it’s not plugged in. 5. The price the meat is sold has no relation to the price the farmer receives. 6. If you fail to pay your bill, you run the risk of having your electricity supply cut off. 7. A new road system to improve traffic flow through the city centre is being introduced now. 8. Tell me in what direction to look. 9. The damage caused to the tourist industry is difficult to quantify. 10. When electrical currents flow they produce magnetic fields 11. When the pilot switched on his flight systems, a red warning light glowed. 12. There’s been no movement in the peace talks since Thursday. 13. Women's earnings are still low in relation to men's. 14. A problem must be stated in order to be solved. 15. An informer supplied the police with the names of those involved in the crime. 16. He saw the green glow of the computer monitor at a distance.
Ex. 2. Practice the reading and translate the following word combinations. You are to copy them and memorize their meanings.
Direct current (DC), alternating current (AC), power supply, Ohm’s law, battery-powered devices light bulb, charge movement, copper wire, plugged in to electrical outlets, passage of current, potential difference, directly proportional, inversely proportional
8
Ex. 3. Cardinal numbers, or cardinals for short, are a generalization of the natural numbers used to measure the cardinality (size) of sets.
Ordinal numbers or ordinals are the order type of numbers. The decimal numeral system has ten as its base.
A fraction is a number that can represent part of a whole.
A percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100.
Ex. 4. Match the words with the examples below |
||||
|
|
A |
|
B |
|
1. |
cardinal numbers |
a) |
⅓: ⅔ ⅜ |
|
2. |
ordinal numbers |
b) |
first, second, third |
|
3. |
decimals |
c) |
1, 2, 3, ... |
|
4. |
fractions |
d) |
25%, 50% |
|
5. |
percentages |
e) |
2.5, 3.14 |
Remember how to read fractions and decimals: |
|
|
|
|||
⅓ – one third |
|
|
1.1 – one point one |
|
|
|
⅔ – two thirds |
|
|
0.002 |
– zero point two zeros two |
|
|
3 ⅞ – three and seven thirds |
|
3.576 |
– three point five seven six |
|
||
Ex. 5. Read the following fractions and decimals. |
|
|
||||
2/5 |
7 2/7 |
15 8/9 |
0.009 |
205.35 |
0. 0003 |
|
5/8 |
9 5/7 |
0.23 |
10.01 |
79.31 |
3.14 |
|
Ex. 6. Match the numbers with the way they are said:
|
A |
|
B |
1. |
240 |
a) |
two hundred and sixty-five thousand |
2. |
2,750 |
b) |
two thousand seven hundred and fifty |
3. |
265,000 |
c) |
two billion |
4. |
2,500,000 |
d) |
two hundred and forty |
5. |
2,000,000,000 |
e) |
two million, five hundred thousand |
Ex. 7. Match the written numbers with the way they are said. Practice their reading.
|
|
|
A |
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
50% |
a) |
four point six percent |
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
2 ½ |
b) |
one point two three |
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
2.5 |
c) |
two point five |
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
4.6% |
d) |
two thirds |
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
1/4 |
e) |
two and a half |
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
1.23 |
f) |
three quarters |
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
3/4 |
g) |
a quarter |
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
2/3 |
h) |
fifty percent |
|
|
|
Ex. 8. Fill in the blanks with the words from the box. |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
times |
|
divided by |
minus |
plus |
|
1.Six … six equals twelve.
2.Ten… six equals four.
9

3.Ten …six equals sixty.
4.Ten … two equals five.
5.Twenty four ... six equals four.
6.Ten ... ten equals one hundred.
7.Seventy eight ... thirty six equals fourty two.
8.Eighty eight ... twenty five equals one hundred and thirteen.
Now match the following words with the four patterns above: multiplication, addition division, subtraction.
Remember how to read powering:
¾32 – three squared; three raised to the second power; the second power of three;
¾52 = 25 – the second power of five is twenty five;
¾53 – five cubed; five raised to the third power; the third power of five;
¾8 = 23 – eight is the third power of two;
¾107 – ten to the seventh power;
¾10-7 – ten to the minus seven power.
Ex. 9. Match the numbers with the way they are said. Practice their reading.
|
|
A |
|
B |
|
|
1. |
23 |
a) |
six to the second power |
|
|
2. |
64 |
b) |
six to the six power |
|
|
3. |
2-6 |
c) |
six squared |
|
|
4. |
66 |
d) |
the third power of two |
|
|
5. |
62 |
e) |
the third power of twelve |
|
|
6. |
123 |
f) |
the minus sixth power of two |
|
Remember how to read formulas: |
|||||
¾ |
|
2= 10 – Two plus x the square root of four plus x squared is equal to ten; |
|||
¾M = R1x - P1 (x - a1) – P2 (x – a2) – M is equal to R sub one multiplied by x minus P sub one round brackets opened, x minus a sub one, round brackets closed, minus P sub two, round brackets opened, x minus a sub two, round brackets closed;
¾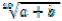 – the tenth root out of a plus b.
– the tenth root out of a plus b.
Ex.10. Read the formulas given below.
|
; |
; |
; a =
=  .
.
Ex. 11. Many words in English can be both nouns, adjectives and verbs. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the part of speech of the highlighted words.
1.A. The streets are in a direct line, and of a convenient breadth.
B.Our efforts were directed towards the elimination of poverty.
2.A. He saw the dim glow of the light bulb in her window.
B.The bedside lamp glowed dimly.
3.A. Things were in an untidy state.
B.A problem must be stated in order to be solved.
4.A. We can measure the energy that food provides in calories.
10
