
- •Radiation balance (budget) of the Earth surface and the atmosphere
- •Radiation balance of the Earth surface
- •Radiation balance of the surface influences:
- •Annual and diurnal variations of the radiation balance of the Earth surface.
- •Some particularities of the radiation balance annual variation
- •Radiation balance depends on Sun altitude, albedo and cloudiness.
- •Radiation balance of the atmosphere
- •Radiation balance of the Earth as a whole planet
- •Cloudiness impact on RE value

Radiation balance (budget) of the Earth surface and the atmosphere
B
Definition
R I B
I
Difference between absorbed and emitted by a body radiation is called balance of radiative energy (radiation balance – R) of the body.
We know sufficiently well about the R of the Earth surface and R of the Earth as a whole planet. However, we know a little about the radiation balance of separate layers of the atmosphere.
1
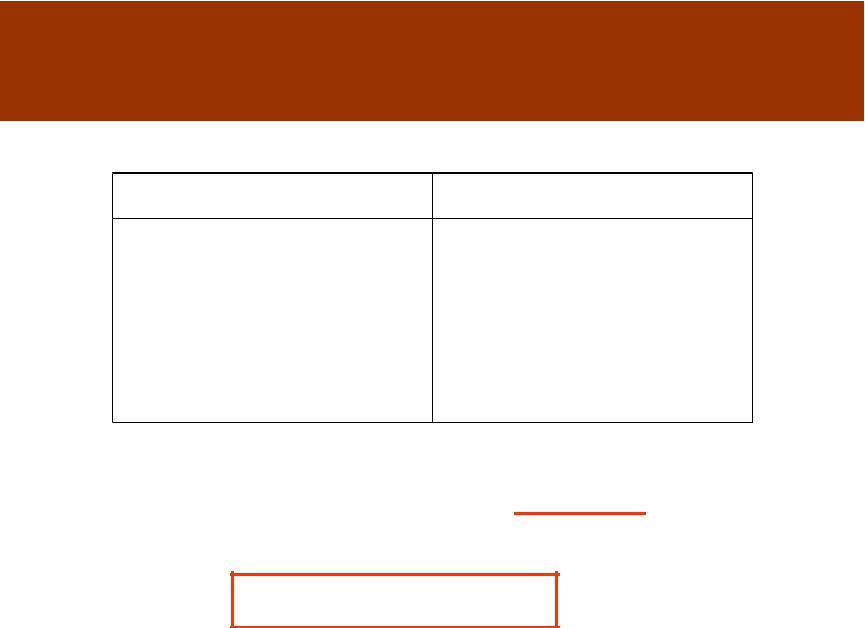
Radiation balance of the Earth surface
Income part |
Outlay part |
|
•Absorbed fraction of the |
The Earth surface |
|
direct SR |
1 r I ' |
radiation B0 |
•Absorbed fraction of the scattered SR 1 r i
•A fraction of atmospheric radiation BA
R 1 r I ' 1 r i BA B0
B *
R 1 r I' i B *
2
Radiation balance of the surface influences:
• Temperature regime in the soil and the surface layer of the atmosphere.
•Processes of fog and frost formation.
•Air mass transformation.
Radiation balance varies depending on latitude, time of the year and day, and weather conditions.
Radiation balance can be calculated for various time intervals: minutes, hours, days, weeks etc.
It can be positive ( income exceeds outlay) and negative (the body emits more energy than absorbs)
Radiation balance is subject for annual and diurnal variations.
3
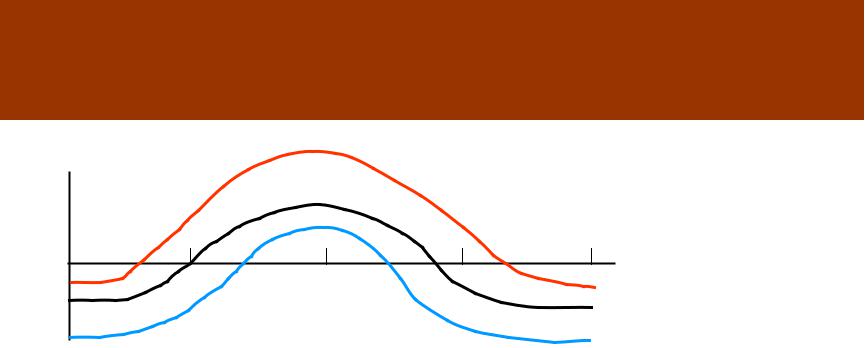
Annual and diurnal variations of the radiation balance of the Earth surface.
R |
|
|
For a location at |
|
|
|
60°N latitude |
|
|
|
June |
6 |
noon |
18 |
t |
|
|||
|
|
|
April |
|
|
|
October |
An important feature of the radiation balance is its transfer via 0. Usually, it happens at the time when Sun altitude reaches 10 -15°. In case of snow cover existence it occurs at the Sun altitude 20 - 25°. This means that the time interval with positive radiation balance becomes much shorter.
4
Some particularities of the radiation balance annual variation
Annual variation of the radiation balance depends on latitude and type of underlying surface.
Tropical area: radiation balance is always positive.
Antarctic area: radiation balance is always negative due to large value of the surface albedo.
At 60° latitude: radiation balance is positive 6 – 8 months a year.
In arctic area there are some places where radiation balance (average for a year) is positive. It is valid for the places with snow and ice free surfaces for at least 2 months. The Sun shines here 24 hours at summer months.
Question: Where radiation balance is larger on ocean or on land at the same altitude and weather conditions?
Answer: On ocean, since water surface albedo is less than that of land
5

Radiation balance depends on Sun altitude, albedo and cloudiness.
R...a ho b |
Parameters “a” and “b” depends on albedo of |
||||
|
|
the underlying surface. |
|
|
|
r% |
10 - 20 |
20 - 30 |
50 - 60 |
60 - 70 |
80 - 90 |
a W/m² |
9,1 |
8,4 |
6,3 |
4,9 |
2,8 |
b° |
10,0 |
9,8 |
7,4 |
7,4 |
8,5 |
Cloudiness impact
When R>0, cloudiness causes the net and effective radiation decrease. But the net radiation decrease is much stronger. Therefore, the radiation balance decreases at cloudiness condition.
When R<0, cloudiness causes the effective radiation decease and, hence, decrease of radiation balance absolute value.
Conclusion: cloudiness always decreases the radiation balance |
6 |
|
absolute value |
||
|
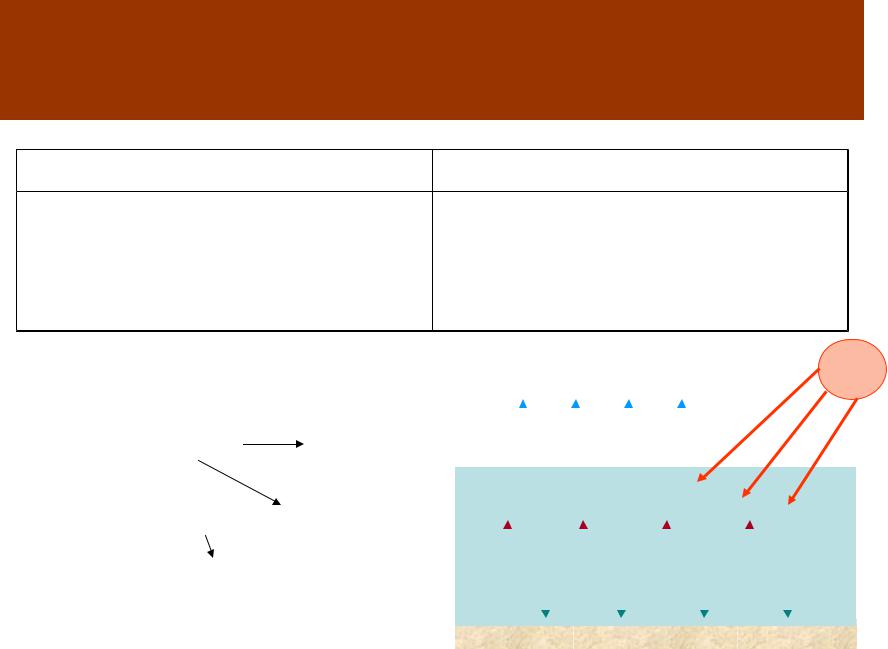
Radiation balance of the atmosphere
Income part |
Outlay part |
•The Earth surface radiation |
•Radiation directed toward the |
absorbed by the atmosphere Ua |
Earth surface BA |
•Direct and scattered SR absorbed |
•Radiation into space B |
by the atmosphere Qa |
|
|
|
RA Ua Qa BA B |
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
Ua 1 |
P B0 |
|
Surface |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
radiation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Qa |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Ua B0 |
PB0 |
|
Transmission |
|
|
|
Ua |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Part of the surface radiation that goes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
into the space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
B* B0 BA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BA |
||||||||
|
BA B0 B * |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
RA Ua Qa BA B
|
Ua B0 PB0 |
|
|
|
|
BA B0 B * |
|
|
|||
|
RA B0 PB0 B Qa B0 B * |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
|
Calculations done with this formula |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
RA B * Qa U |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
have shown that the RA values are |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
negative over whole globe. |
||||
|
φ° |
0 - 10 |
|
20 - 30 |
40 - 50 |
60 - 70 |
|||||
|
RA W/m² |
-101 |
|
-109 |
-80 |
|
-93 |
||||
8

Radiation balance of the Earth as a whole planet
We’ll discuss the balance of radiative energy in a vertical column including active layer of soil ( water) and the atmosphere.
Incoming part RE I0! 1 rE  U
U 
 Outgoing part
Outgoing part
Every unit of time the Earth receives the amount of SR equal to the |
|||
product of the solar constant |
I0* by the area of the Earth cross |
||
section |
R2 |
i. e. R2 I0* |
|
Due to Earth rotation this energy is distributed over the all surface of the globe that is 4 R2
R |
2 |
* |
* |
|
|
Near equator RE>0 over the whole |
|
|
I0 |
|
I0 |
0,343 kW |
m2 |
year. In the middle latitudes RE>0 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
4 R2 |
4 |
|
is observed only in summer. |
||||
9

Cloudiness impact on RE value
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
E |
I! |
1 r U |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Cloudiness increases albedo rE . |
U |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
rE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Cloudiness diminishes U∞ value |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
U∞ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RE |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
At nights, when I0! 0 , RE U |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
At clear sky RE 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At cloudy weather |
RE 0 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
RE |
|
Clear |
|
|
|
RE |
|
Cloudy |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
10
