
- •Moist adiabatic processes
- •From the above reasoning it follows:
- •First law of thermodynamics for the moist, saturated air
- •For adiabatic process
- •Values of the moist adiabatic lapse rate at different temperature and pressure
- •Criterion of instability for the moist air
- •Some additional information
- •Some additional information
- •• If we have a convergence in an area with relatively high tpspot

Moist adiabatic processes
An adiabatic process in moist, saturated air is called
MOIST ADIABATIC PROCESS
This process is significantly different form that in the dry or non-saturated air
1
P |
Dry adiabat |
|
dTi |
1 /100m |
|
Moist adiabat |
|
0 |
|||
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
Pk |
|
Lifting |
|
|
|
|
dSi |
0 |
|
||
|
|
Condensation level |
|
||
|
|
dz |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
d RH |
|
|
|
S0=Sm, Tk, |
So, Ti0, |
0 |
||
|
dz |
|
|||
|
RH=100% |
RH<100% |
|
||
RH 100%
Sm S0 ;Ti Tk
RH 100%
S0 Sm ;Ti Tk
So, Ti0, RH<100%
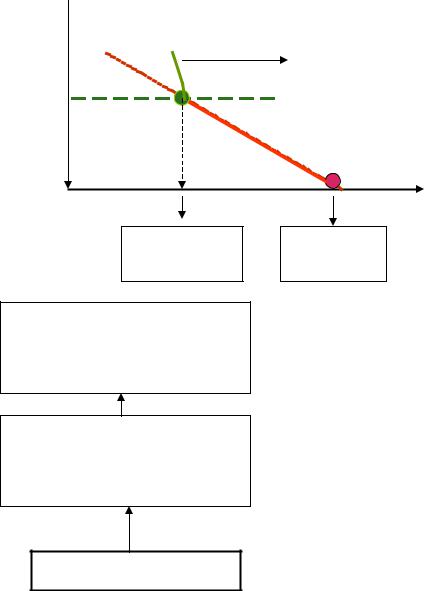
Continuous ascent results in further temperature fall and water vapor condensation that makes the rate of the temperature fall less than 1°/100 m.
Lifting Condensation level
Initial level
The rate of temperature variation of the ascending saturated air without heat influx or outflow is called MOIST ADIABATIC LAPSE
RATE 2
From the above reasoning it follows:
Temperature of an ascending parcel of air decreases with height, |
|
• |
m.a. a ). |
but slower that at dry adiabatic process ( |
|
•Due to condensation, the particle specific humidity Sm decreases with height
•Relative humidity remains equal to 100%.
Adiabatic ascent of the moist air till attaining saturated state is called DRY STAGE.
Further ascending of the saturated air above the condensation level is called MOIST STAGE
PDry adiabat
Moist stage




































 Condensation level Dry stage
Condensation level Dry stage 






T
3
First law of thermodynamics for the moist, saturated air
Suppose a parcel of the saturated air has got some amount of heat dq. This heat will be laid out for:
•Inner energy increase
•Expansion work
•Evaporation of some amount of water
Reason for evaporation
dq 0 |
dTi 0 |
RH 100% RH 100% |
|
RH 100% |
|
|
|
The parcel becomes non-saturated + |
dSm evaporation |
||
dq cvdTi pdvi LdSm |
As we know, pdv RT |
dP |
|||
|
|
|
i |
i |
P |
dq c |
dT |
RT |
dP LdS |
m |
|
|
p i |
i |
P |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

For adiabatic process
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cpdTi |
RTi |
dP LdSm 0 |
|
||||||||
|
|
c dT pdv |
|
LdS |
m |
0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
v i |
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Accounting for static equation, |
cpdTi gTi |
dz LdSm 0 |
c dz |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
we get: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Te |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
p |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
dT |
gT |
|
L |
dS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dTi |
|
|
|
g |
Ti |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
i |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m |
0 |
|
Since |
|
|
m.a.; |
|
|
a ; T 1 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dz |
c |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
cp |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
dz |
cpTe |
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
p |
|
e |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dSm |
0 |
|
|
m.a a |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L dSm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
m.a a |
|
|
|
|
dz |
|
|
Value of the moist adiabatic |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cp |
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
a |
const |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lapse rate depends on pressure |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m.a const |
and temperature only and does |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
not depend on humidity |
5 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sm 0,622 E |
ln Sm ln 0,622 ln E ln P |
P |
|
1 |
dSm |
1 dE |
|
1 dP |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Sm |
E dz |
P dz |
|||||
dz |
|
||||||
E E T
1 |
dSm |
1 dE dTi |
|
1 dP |
|
1 dP |
|
|
|
g |
dT |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
; |
i |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
dTi |
|
dz |
|
|
dz |
|
|
|
dz m.a |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Sm |
E |
P |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P |
|
RT |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
dSm |
Sm dE |
|
|
Sm g |
|
E |
|
|
g |
|
m.a dE |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
dz |
E dTi |
m.a |
RTe |
0,622 P |
|
|
|
|
|
dT |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
RT |
E |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|
i |
|
|||||
m.a a |
L dSm |
|
m.a |
a 0,622 |
L E |
g |
m.a |
1 dE |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
dT |
|
|||||||||||||||||
c |
|
dz |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
p |
|
c |
p |
RT |
E |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
i |
|
|||
6

|
|
0,622 |
L E |
g |
|
1 dE |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
c |
|
P RT |
|
|
|||||
m.a |
a |
|
p |
m.a E dT |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
i |
|
Opening brackets we obtain
m.a
L 2,5 106 J kg
and solving the equation with respect to m.a ,
|
|
0,622 |
L |
E |
g |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
a |
|
|
cp P RTe |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
1 0,622 |
|
L |
|
1 dE |
|
|||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
c |
p |
|
P dT |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
||
dE |
|
L |
|
E |
|
dT |
R |
T 2 |
|||
|
|||||
|
|
w |
|
|
|
|
P 0,622 |
LE |
|
|
||
RT |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
m.a a |
|
|
|
e |
|
|
P 0,622 |
|
|
L2 E |
|
||
|
c |
|
R T 2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
p w i |
|
||
7
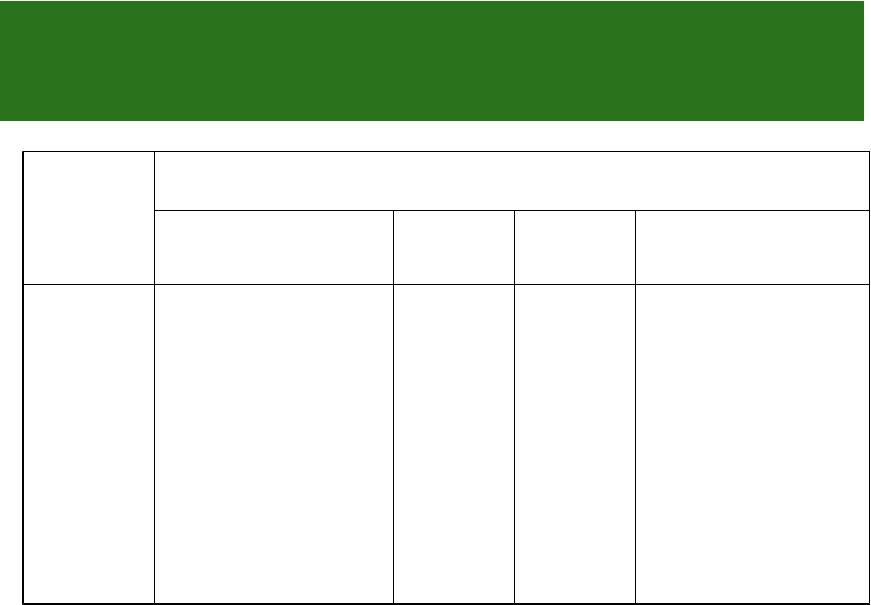
Values of the moist adiabatic lapse rate at different temperature and pressure
Pressure |
|
|
|
T°C |
|
|
hPa |
-50 |
-20 |
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
|
||||||
1000 |
0,966 |
0,856 |
0,658 |
0,532 |
0,435 |
0,363 |
800 |
0,964 |
0,831 |
0,614 |
0,489 |
0,398 |
0,335 |
600 |
0,960 |
0,793 |
0,557 |
0,436 |
0,356 |
0,303 |
400 |
0,952 |
0,730 |
0,478 |
0,371 |
0,307 |
0,267 |
200 |
0,928 |
0,597 |
0,361 |
0,286 |
0,247 |
0,223 |
8
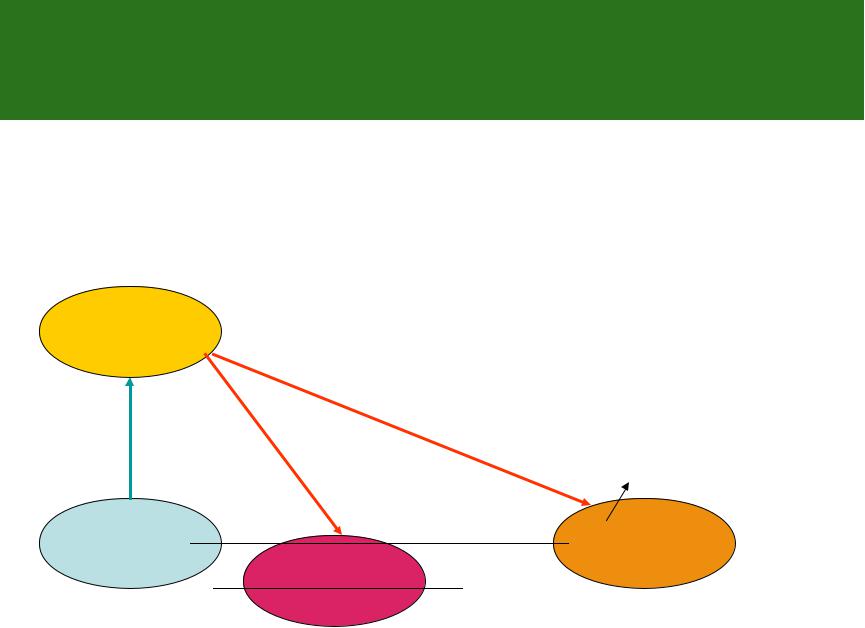
Criterion of instability for the moist air
aaa
m.am.am.a
Unstable atmosphere
Stable atmosphere Dry, non-saturated air
Neutral atmosphere
a m.a
Unstable atmosphere
Stable atmosphere Moist, saturated air
Neutral atmosphere
.a m.a |
Absolute instability |
|
Combine criterion of instability |
||
|
|||||
m.a a |
Absolute stability |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
a m.a |
Conditional instability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The air is unstable, it is saturated |
9 |
|||
Some additional information
Equivalent-potential temperature is the potential
temperature of an air parcel, the water vapor containing in it had been condensed due to adiabatic ascent and the heat obtained has been laid out to rise up the air parcel temperature,
Θ+dθ, e=0
|
|
Pseudo-potential |
|
|
temperature |
Θ, e |
Initial level |
Θp.p, e=0 |
|
Θe, e=0 |
1000 hPa |
|
|
|
|
Equivalent-potential temperature |
10 |
|
|
||
