
Testking_640-802_V13
.pdf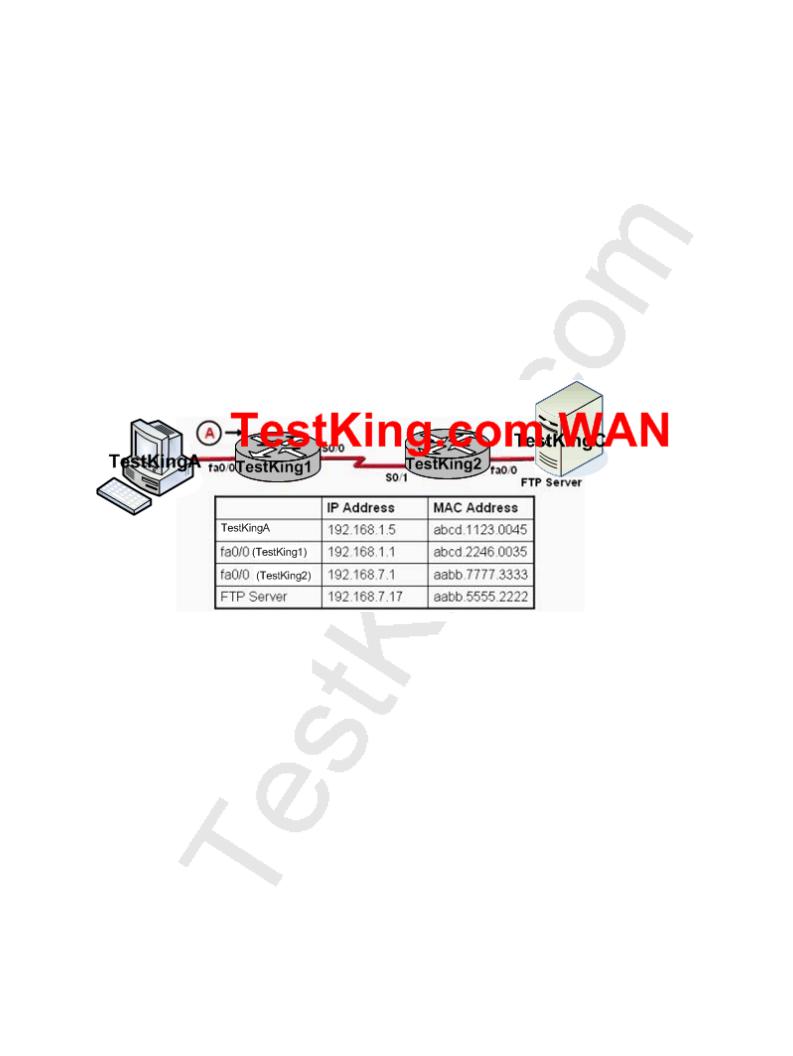
When packets transfer from one host to another across a routed segment, the source IP address always remains the same source IP address, and the source physical (MAC) address will be the existing router's interface address. Similarly, the destination IP address always remains the same and the destination physical (MAC) address is the destination router's interface address.
QUESTION NO: 13
In the network below, host TestKingA is transferring a file to the FTP server. Point A represents the frame as it goes toward the TestKing1 router. What will the Layer 2 destination address be at this point?
A.192.168.7.17
B.abcd.1123.0045
C.aabb.555.2222
D.192.168.1.1
E.abcd.2246.0035
Answer: E
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 71 -

For packets destined to a host on another IP network, the destination MAC address will be the LAN interface of the router. Since the FTP server lies on a different network, the host will know to send the frame to it's default gateway, which is TestKing1.
QUESTION NO: 14
Part of the TestKing network is shown below:
Host TestKing1 needs to communicate with the email server shown above. What address will be placed in the destination address field of the frame when it leaves Host TestKing1?
A.The MAC address of Host TestKing1
B.The MAC address of E0 of the router TestKingC
C.The MAC address of Switch TestKingB
D.The MAC address of E1 of the router TestKingC
E.The MAC address of Switch TestKingA
F.The MAC address of the email server TestKingD
G.None of the above
Answer: B
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 72 -

Since the email server resides on a different IP subnet than the host TestKing1, the host will send the frame to its default gateway. In this case, the router TestKingC is acting as the default gateway for all hosts on the LAN, so the frame will be sent to its Ethernet interface so that it can be routed to the email server.
QUESTION NO: 15
Part of the TestKing network is shown below:
In this TestKing network segment, host TestKingA needs to send data to Host TestKingB. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will be used in this session to send the data from Host TestKingA to Host TestKingB?
A.192.168.60.5 and 0007.0e56.ab2e
B.192.168.24.2 and 0007.0e84.acef
C.192.168.24.1 and 0007.0e56.ab2e
D.192.168.60.5 and 0011.43da.2c98
E.None of the above
Answer: A
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 73 -

When packets leave from the host, the packets contains the source MAC and IP of the host address. The source and destination IP address will not change. Because the host knows that the destination is on another subnet, it will forward the packet to the default gateway device, so the destination MAC address will be of the default gateway, which is the FA0/0 interface of router TestKing2.
QUESTION NO: 16
Part of the TestKing network is shown below:
In this network segment, host TestKingA sends data to Host TestKingB. As packets travel from host TestKingA to host TestKingB, which three devices will use the destination MAC address of the packet to determine a forwarding path? (Choose three)
A.Hub TestKing0
B.Switch TestKing1
C.Router TestKing5
D.Router TestKing4
E.Switch TestKing2
F.Switch TestKing3
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 74 -

Answer: B, E, F Explanation:
Switches use the destination MAC address information for forwarding traffic, while routers use the destination IP address information.
Local Area Networks employ Layer 2 Switches and Bridges to forward and filter network traffic. Switches and Bridges operate at the Data Link Layer of the Open System Interconnect Model (OSI). Since Switches and Bridges operate at the Layer 2 they operate more intelligently than hubs, which work at Layer 1 (Physical Layer) of the OSI. Because the switches and bridges are able to listen to the traffic on the wire to examine the source and destination MAC address. Being able to listen to the traffic also allows the switches and bridges to compile a MAC address table to better filter and forward network traffic. To accomplish the above functions switches and bridges carry out the following tasks:
1.MAC address learning by a switch or a bridge is accomplished by the same method. The switch or bridge listens to each device connected to each of its ports and scan the incoming frame for the source MAC address. This creates a MAC address to port map that is cataloged in the switches/bridge MAC database. Another name for the MAC address table is content addressable memory or
CAM table.
2.When a switch or bridge is listening o the network traffic, it receives each frame and compares it to the MAC address table. By checking the MAC table the switch/ bridge are able o determine which port the frame came in on. If the frame is on the MAC table the frame is filtered or transmitted on only that port. If the switch determines that the frame is not on the MAC table, the frame is forwarded out to all ports except the incoming port.
Section 9: Describe the components required for network and Internet communications (5 questions)
QUESTION NO: 1
The TestKing network is displayed in the diagram shown below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 75 -

The TestKing network consists of a small office with twenty-five employees that has one connection to the Internet through the TK1 router. What routing configurations are recommended on the TK1 and ISP routers?
A.BGP on both the routers.
B.RIP on both the routers.
C.Default routes on both routers.
D.BGP on the ISP router and a static route on TK1.
E.A default route on TK1 and a static route on the ISP router.
F.None of the above
Answer: E Explanation:
Since private network use RFC 1918 IP address ranges internally, and because of security reasons, it is generally not possible to use an interior routing protocol with the ISP. This eliminates choice B. When connecting to an ISP, usually only BGP or static routes are supported. In this case, since there is only one connection to the Internet, BGP is not needed so choices A and D can be eliminated. A static default route would be needed on router TK1 to route to the Internet. In turn, the ISP only needs a specific static route to reach the LAN of the TestKing network.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D: BGP is not needed on networks that contain only a single link to the Internet.
B.Interior routing protocols are generally not supported with an ISP.
C.A default route on the ISP router would send all of their customers Internet traffic to the TestKing network, and not the Internet.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 76 -
QUESTION NO: 2
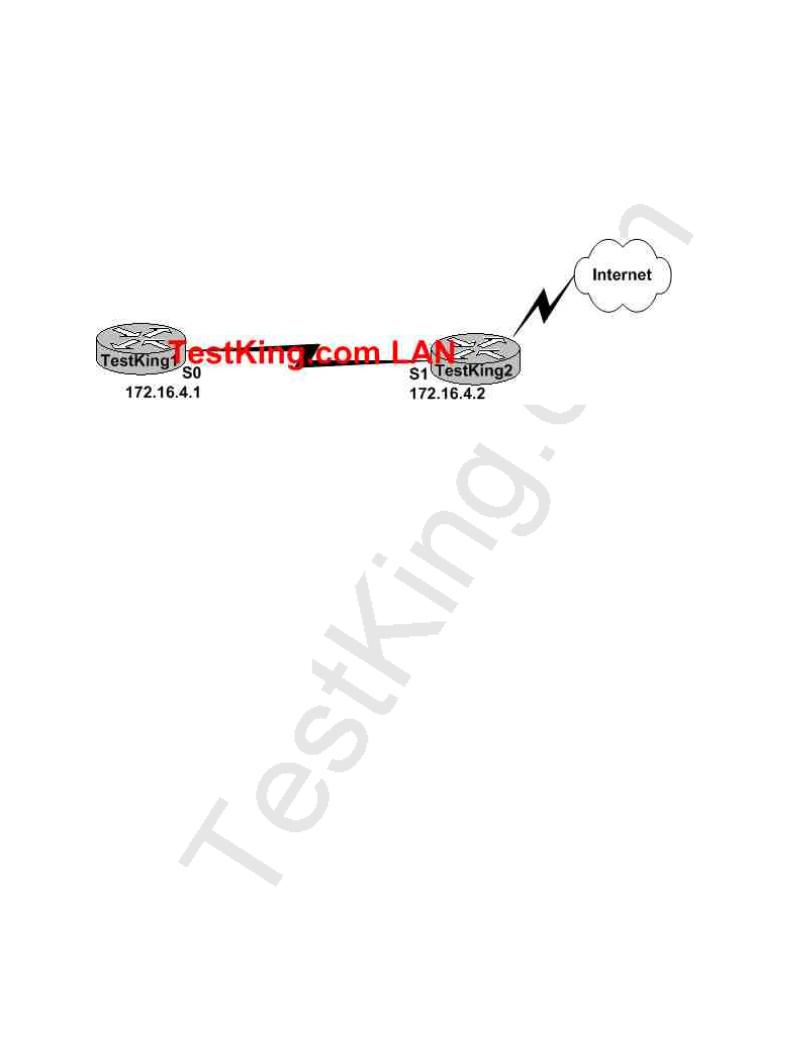
A new point to point circuit is installed, connecting Testking 1 to Testking 2 as shown below:
Users at Testking 1 wish to utilize the existing Internet connection at Testking 2. To do this, a gateway of last resort needs to be set. What is the command to do this?
A.TestKing1(config)# ip route 172.16.4.2 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
B.TestKing1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S1
C.TestKing1(config)# ip route 172.16.4.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
D.TestKing1(config)# ip route S0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
E.TestKing1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.4.2
F.None of the above
Answer: E Explanation:
Setting the default gateway is done by issuing either the "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0" or the "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.4.2" command. The following excerpt provides some additional information:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 77 -

Incorrect Answers:
A, C. The IP address of the next hop needs to go after the route, not before.
B.This would have been acceptable if the interface specified was S0, not S1.
C.The interface used to forward packets for the route should be placed after the route, not before.
QUESTION NO: 3
The network associate is configuring OSPF on the Core router shown below. All the connections to the branches should be participating in OSPF. The link to the ISP should NOT participate in OSPF and should only be advertised as the default route. What set of commands will properly configure the Core router?
A. Core(config-router)# default-information originate
Core(config-router)# network 10.0.0.00.255.255.255 area 0
Core(config-router)# exit
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 78 -

Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.00.0.0.010.10.2.14
B.Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0 Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.00.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
C.Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.13 0.0.0.242 area 0 Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.00.0.0.010.10.2.14
D.Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 area 0 Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.00.0.0.010.10.2.14
Answer: D
Explanation:
There are two ways to inject a default route into a normal area.
1.If the ASBR already has the default route in its routing table, you can advertise the existing 0.0.0.0/0 into the OSPF domain with the default-information originate router configuration command.
2.If the ASBR doesn't have a default route, you can add the keyword always to the default-information originate command (default-information originate always).
This command will advertise a default route into the OSPF domain, regardless of whether it has a route to 0.0.0.0. Another benefit of adding always keyword is that it can add stability to the internetwork. For example, if the ASBR is learning a default route from another routing domain such as RIP and this route is flapping, then without the always keyword, each time the route flaps, the ASBR will send a new Type 5 LSA into the OSPF domain causing some instability inside the OSPF domain. With the always keyword, the ASBR will advertise the default inside the OSPF domain always, and thus the flapping of the default route from the RIP domain will not cause any instability inside the OSPF domain.
In the example shown here, only choice D is correct as the wildcard mask correctly specifies the 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 networks, which include all IP addresses in the 10.10.2.16-10.10.2.31 range.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/104/21.html
QUESTION NO: 4
A new Internet T1 is being added to the TestKing network as shown:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 79 -

The ISP assigned you the class CIP address 207.134.6.0/30 for this Internet connection. A default route to the Internet should be set up. Which of the following are acceptable ways to configure this on the Gateway router? (Select all that apply)
A. Gateway(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 207.134.6.1.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 80 -
