

[116] |
|
|
[117]−[119] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
OH |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HN |
OH |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
NH |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
TlOH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
NH |
|
N |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
O |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OTBS |
|
OTBS |
|
|
|
O NH |
|
|||||
sameastheacid |
|
|
OAc OTBS OTBS |
OTBS |
OTBS |
OTBS TBSO |
|
OTBS |
HO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2 |
O |
OTBS O |
TBSO |
MeO |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TBSO O B(OH) TBS |
OTBSTBSO |
TBSOMe |
|
|
OTBS |
|
|
|
OTBS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
TBSO |
|
MeMe |
O |
|
|
O |
O |
O |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCOHN |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sanglifehrin A
TMS
palytoxin |
(cf.[116]) |
palytoxin carboxylicacid (cf.[119]) |
123 |
|
|
893

TABLE 4. Heteroaromatics (cf. Sect. III.2.7)
Catalyst Additive Yield (%) Reference
R′X
RM
Name
n C
82 [120]
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh
O
I
ZnBr
15 freelingyne THPO
|
|
[121] |
|
[122] |
|
|||
|
|
98 |
|
82 |
|
|||
|
|
K |
|
2 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Ba(OH) |
||||
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
4 |
|
|||
|
|
) |
|
) |
|
|||
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
|||
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
|
N |
|
F |
NH |
|
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
I |
I |
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
B(OH) |
|
NHCOtBu |
B(OH) |
|
NHCOtBu |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fascaplysin |
amphimedine |
18 |
19 |
[123] |
[123] |
19 |
15 |
4 |
|
|
4 |
|
||||
) |
|
|
|
) |
|
|||
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
||||
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|||
|
O |
O |
|
O |
O |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Br |
|
||
|
Br |
|
|
|
||||
|
ZnCl |
|
|
|
ZnCl O |
|||
|
|
O |
OMe |
OTBS |
|
|
OMe |
|
|
|
|
|
TBDPSO |
|
|||
TBDPSO |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
egonol |
|
|
(±machicendiol)- |
|
|||
19 |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
O |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
OMe |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
R |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
HO |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
O |
Me |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
||
|
|
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|||||||||
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
N H |
O |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
O
Hegonol |
OH(+)-machicendiol |
R= |
R= |
amphimedine
fascaplysin
freelingyne
894
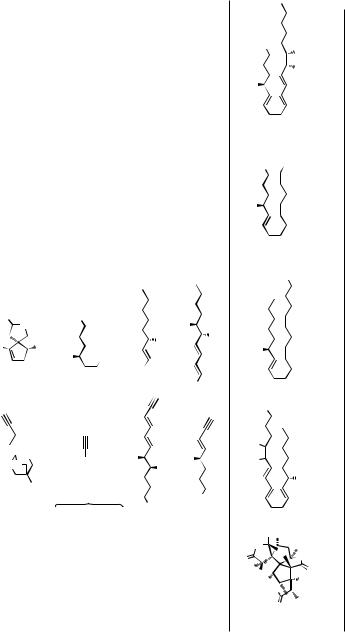
III.2.18 SYNTHESIS OF NATURAL PRODUCTS VIA CROSS-COUPLING |
895 |
protocol developed by Negishi[124] with Zn, B, and Sn as well as that involving the use of haloalkynes (Sect. III.2.8.2). Although not yet widely known, it should be noted that the scope of Sonogashira coupling is more limited than the latter. Thus, terminal alkynes cannot be directly and selectively synthesized without protection and deprotection of one of the acetylene carbon atoms. The reaction also is sluggish or it may altogether fail in cases where alkynes contain electron-withdrawing substituents. Despite these limitations, Sonogashira coupling has thus far been the much more widely employed of the two, probably because it is operationally somewhat simpler. It should also be recalled that there are other intricate differences between the two protocols, as discussed in Sect. III.2.8.
In cases where alkynylmetals are generated either in situ or in a separate step as discrete reagents, Mg, Zn, B, and Sn have been the four widely used metals. Comparative studies have shown that Zn is generally the most favorable among them (Sect. III.2.8.2). Here again, however, Sn has been the most frequently used metal. Similar comments on Sn as those made in Sect. D are also applicable to these cases. Particularly noteworthy are examples of the intramolecular cyclization of alkynyltins, as in the synthesis of neocarzinostatin, cyclization via double alkynylation with haloalkynes, as in the synthesis of calicheamicinone[129] and dynemicin A,[130]–[132] and the carbopalladation–cross-coupling tandem cyclization, as in the synthesis of neocarzinostatin.[133],[134]
F. SYNTHESIS OF NATURAL PRODUCTS VIA Pd-CATALYZED CROSS-COUPLING INVOLVING ALLYL, BENZYL,
AND PROPARGYL REAGENTS
Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling has been shown to be particularly well suited for the synthesis of diarylmethanes, allylated arenes, 1,4-dienes, 1,4-enynes, and related derivatives, as discussed in Sect. III.2.9. It should be recalled that this favorable characteristic does not extend to the coupling of two allylic, propargylic, and benzylic reagents to produce 1,5- dienes, 1,5-enynes, bibenzyl, and related compounds (Sect. III.2.10). Also to be recalled is that the use of propargyl reagents often leads to the formation of allenes, and this tendency of Pd is in contrast with that of Cu in dealing with propargyl(allenyl) reagents. As in many other cases of Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling, Zn, B, Al, and Sn have been used most frequently, although it is likely that Cu, Zr, and Si are also satisfactory in some cases.
Following a very satisfactory synthesis of -farnesene via alkenyl–allyl coupling[174] as the first example of natural product syntheses of this class, some other natural products containing 1,4-dienes and allylated arenes have been synthesized, as indicated by the results summarized in Table 7. The synthesis of humulene via intramolecular alkenyl–allyl coupling is noteworthy, even though the cyclization was achieved only in 32% yield.[175] Also noteworthy is the Nior Pd-catalyzed synthesis of allylated quinones, such as menaquinone-3 and coenzymes Qn (n 3 or 10).[176],[177],[194] Both Ni and Pd appear to be highly satisfactory and roughly comparative with each other[194] despite the claim that Ni is superior to Pd.[176] Many additional satisfactory examples may be expected. At present, however, no natural products appear to have been synthesized by using propargylic reagents in Pd-catalyzed crosscoupling.

TABLE 5. Alkyne Synthesis Via Sonogashira Cross-Coupling (cf. Sect. III.2.8.1)
Catalyst Additive Yield (%) Reference
R′X
RC CH
Name
n C
[135] |
|
|
|
||
52 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
NH |
|
|
|
CuI |
2 |
|
||
|
i-Pr |
|
|||
2 |
|
|
|||
) |
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
|
|||
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|||
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
O |
OTBS |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
11 (+)-harveynone
|
[136] |
|
|
|
[137] |
|
|
|||
|
62 |
|
|
|
55 |
|
|
|||
|
CuI |
N |
CuI |
N |
3 |
|||||
|
Et |
Et |
PPh |
|||||||
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
||
|
2 |
|
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|||
|
Pd(OAc) |
|
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
||
OMe |
|
O |
|
|
O |
|
|
COOH |
|
|
MeO I |
|
|
|
|
|
Br |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
OTBS |
OTBS |
|
|
|
|
(±)-harveynone |
goniobutenolideA |
11 |
13 |
[120] |
|
50 |
|
CuI |
N |
Et |
|
|
3 |
4 |
|
) |
|
3 |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
COOH |
|
I |
|
|
|
O
15 freelingyne
[138]
76
2 CuI BuNH -n
2 Pd(OAc)
TMS
Cl
N 18 (−)-calicheamicinone TBSO O
O O
3 PPh
|
O |
NHCO |
HO |
|
|
OH |
SSSMe |
calicheamicinone-)(− |
||||||
|
|
|
Me |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
O |
freelingyne |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
A |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
goniobutenolide |
||||
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
OH |
|
||||||
OTBS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
harveynone |
|||
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(+)- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
896

[52]
96
2 CuI PrNH -n
2 ) 3 Pd(PPh 2 Cl
OTHP
Br


 OH
OH
18 coriolic acid
[135]
54
NH 2 CuI Pr -i
2 ) 3 Pd(PPh 2 Cl
O |
|
|
|
O |
OTBS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
I |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 (−)-tricholomenyn A
[54] |
|
|
[139] |
[139] |
|
70 |
|
|
98 |
80 |
|
CuI Et |
BHT |
2 |
2 |
||
|
CuI BuNH-n |
CuI BuNH-n |
|||
|
N |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
4 |
4 |
||
) |
|
|
) |
) |
|
3 |
|
3 |
3 |
||
Pd(PPh |
|
|
Pd(PPh |
Pd(PPh |
|
|
COOH |
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Cl |
xerulin |
eleostearate |
MeOOC |
methyl |
|
|
18 |
19 |
|
COOMe |
7 |
|
eleostearate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
methyl |
9 |
|
||
|
|
||
H |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
xerulin |
|
|
|
|
|
O |
OAc |
|
|
O |
|
|
tricholomenynA |
|||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
−)- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
COOH |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
coriolicacid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Continued )
897

TABLE 5. (Continued )
Catalyst Additive Yield (%) Reference
R′X
RC CH
Name
n C
[140]
CuIpiperidine 85
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh
Cl
Cl
11 H 5  C
C
HO
(5S,12S)-DiHETE
20
[140]
CuIpiperidine 62
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh
Me 2 CO
OH
I
11 H 5 C
HO
[141] |
[141] |
82 |
80 |
2 |
2 |
CuI n-PrNH |
CuI n-PrNH |
4 |
4 |
) |
) |
3 |
3 |
Pd(PPh |
Pd(PPh |
OTBS |
OTBS |
Br |
Br |
|
|
|
|
Me |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
OH |
CO |
|
|
|
||
|
TMS |
|
||
5,15-DiHETE |
8,15-DiHETE |
|||
20 |
|
|
20 |
|
[142] |
|
|
[142] |
|
70 |
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
CuI |
n-BuNH |
CuI |
n-BuNH |
|
4 |
|
|
4 |
|
) |
|
|
) |
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
Cl |
OH |
C |
|
|
|
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cl |
|
|
OH |
OTBS |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
C |
|
C |
||
n- |
|
MeO |
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
14,15-dihydro |
4 |
|
|
|
leukotrieneB |
|
|
||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
COOH |
|
|
|||||
OH |
|
dihydro |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
14,15- |
||||||
|
|
|||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|||
8 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|||
COOH |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
8,15-DiHETE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
OH |
OH |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
COOH |
|
|
||||||
OH |
OH |
DiHETE |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,15- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COOH |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
DiHETE |
||
11 |
|
S)- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
C |
|
,12S(5 |
||
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
||
|
5 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
|
||||||
4 Bleukotriene
898
84-76 [143]
2 CuI PrNH -n
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh
|
OMe |
|
O |
OTf |
t-Bu |
 O
O
O
O
Me
20 (+)-ginkgolide B
[60] |
[69] |
|
94 |
100 |
|
2 |
|
|
CuI n-PrNH |
|
above |
4 |
|
as |
|
same |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
Me |
|
|
2 |
|
|
CO |
|
|
OTBS |
|
Br |
|
|
|
TMS
4 |
4 |
||
leukotrieneB |
(cf.Table3) |
leukotrieneB |
(cf.Table3) |
20 |
|
20 |
|
[144] |
[61] |
96 |
70 |
2 |
2 |
CuI n-PrNH |
CuI n-PrNH |
4 |
4 |
) |
) |
3 |
3 |
Pd(PPh |
Pd(PPh |
|
OTBS |
OH |
OH |
|
Br |
|
|
|
|
Cl |
|
OTBS |
OTBS |
OTBS |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
MeOOC |
2 |
|
|
MeO |
) |
|
|
lipoxinA |
lipoxinB |
(cf.Table3 |
|
20 |
20 |
|
|
COOMe |
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
HO |
|
lipoxin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
COOMe |
|
|
|
C |
|
HETE |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(S)- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
COOH |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15-(S)-HETE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
COOH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
HO |
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
lipoxin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H tBu |
|
H |
|
B |
|||||
H HO HO |
O |
|
O |
ginkgolide-(+) |
||||||
H Me |
||||||||||
O |
O |
|
O |
|
O |
|
||||
|
|
|
O |
|
OH |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
(Continued )
899

TABLE 5. (Continued )
Catalyst Additive Yield (%) Reference
R′X
RC CH
Name
n C
[145]
92
2 CuI PrNH -n
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh



 OTBS
OTBS
Br
Me 2 CO
15-(S)-HETE |
(cf.above) |
20 |
|
[146] |
[147] |
[148] |
[148] |
[148] |
[148] |
83 |
75 |
70 |
54 |
54 |
50 |
CuI piperidine |
CuI piperidine |
CuI Et |
CuI Et |
CuI Et |
CuI Et |
|
|
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
Pd(PPh |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Pd(PhCN) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
) |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pd(PPh |
Cl |
|
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
Cl |
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Me |
TMS |
Cl |
Br |
|
|
|
|
COOH |
I |
|
|
|
COOH I |
Br |
|
|
|
COOH I |
|||
OTBS CO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AcO |
|
|
|
Br |
||
|
|
|
|
|
AcO |
|
Br |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AcO |
|
||||||||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
OH |
OH |
Br |
|
|
|
|
Br |
Br |
|
|
|
Br |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
C |
|
AcO |
|
AcO |
|
AcO |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-)S(-5HETE above)(cf. |
lipoxinB |
above)(cf. |
|
|
rubrolideA |
below)(cf. |
|
|
rubrolideC |
below)(cf. |
rubrolideD |
below)(cf. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
21 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2 ) 3 Pd(PPh 2 Cl
I
COOH
AcO
rubrolide E AcO (cf. below)
900

[149] |
[150] |
98 |
|
|
|
|
CuI |
|
NH |
3 |
|
|
Et |
PPh |
||
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
Pd(OAc) |
|
|
|
|
OBn |
3 |
OCH |
||
|
OCH |
|||
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
MeO |
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TBSO |
|
81
CuIpiperidine
2 Pd(PhCN) 2 Cl
I |
N |
|
Boc |
OH
furaquinoneA |
furaquinoneB |
furaquinoneH |
himbacine |
22 |
22 |
22 |
22 |
HO |
O |
Me |
Me |
himbacine |
H |
|
H |
H |
|
|
|
H |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
OH H OH |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
H OH OH |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
3 |
|
R |
|
R |
|
OH OH OH |
|||||||
|
R |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A B H |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
furaquinone |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
MeO |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Z |
|
|
|
H H H H |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Y |
|
|
|
Br H Br H |
|||||||||
|
X |
|
|
|
Br Br H H |
|||||||||
|
R |
|
|
|
Ac Ac Ac Ac |
|||||||||
|
Rubrolides diacetates |
|
|
|
A C D E |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
X |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
RO |
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
RO |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
(Continued )
901

TABLE 5. (Continued )
Catalyst Additive Yield (%) Reference
R′X
RC CH
Name
n C
[151] |
[152] |
||
88 |
86 |
||
2 |
2 |
||
|
|
CuI PrNH-n PPh |
CuI BuNH-n |
3 |
|
||
2 |
2 |
||
|
|
Pd(OAc) |
Pd(OAc) |
TMS |
|
||
|
|
Cl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 O
O
 O
O

O 30 dynemicin A models PhO N
|
[153] |
|
25 |
3 |
|
PPh |
CuI |
|
4 |
|
) |
|
3 |
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
OMe |
||
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
N |
|||||
MeO H |
|
|
|
|
Me |
|
|
|
|
O |
|||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Br |
|||
|
dynemicinA |
related |
||||
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
[86]
91
2 CuI PrNH -n
4 ) 3 Pd(PPh
I
TBSO


31 (−)-pateamine A HO
12 [154]
|
CuI |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
||
) |
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
|
|
||
|
Pd(PPh |
|
|
|
|
Me |
|
|
|
||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
CO |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Br |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
||
|
|
N |
|||
CO |
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
A |
|
|
CO |
|
|
dynemicin |
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
3 |
||
|
tri-O-methyl |
methylester |
|||
32 |
|
|
|
||
2 NMe
S |
N |
|
|
O Me |
pateamine- A |
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
−) |
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
Me |
N |
|
||
|
H |
|
|||
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
COOH |
OMe |
|
|||||||
Me |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OOH |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
HNO |
|
|
|
|
dynemicin |
||||
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|
|
|
OH |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
902
