МР СРС 1 курс.Болонский процесс
.docUNIT 1
Educational systems
Ukraine and Bologna process

Read and memorize the following words, words combinations and word-groups:
Purpose - мета
quality assurance standards – стандарти гарантії якості
compatible - сумісний
signatory – сторона, що підписує документ
Magna Charta Universitatum – Велика університетська хартія
framework- структура
commit – зобов’язатися
ECTS - Європейска система переводу й накопичення кредитів
response – дія у відповідь, реакція, відгук
issue- питання, проблема
governance – управління, керування
implementation - впровадження
further - подальший
to benefit – отримувати вигоду, користь
employment – зайнятість, (тут) – влаштування на роботу
cutting-edge – надсучасний, передовий
convergence – зближення, взаємодія
eligible- той, що має право на
stipulate – обумовлювати, ставити за умову
expansion - розширення
curriculum – навчальний план
provision - забезпечення
approach - підхід
elimination - видалення
 1.
The purpose of the Bologna Process (or Bologna Accords) is the
creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic
degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and
compatible throughout Europe. It is named after the place it was
proposed, the University of Bologna, with the signing in 1999 of the
Bologna declaration by Education Ministers from 29 European
countries. It was opened up to other countries signatory to the
European Cultural Convention of the Council of Europe; further
governmental meetings have been held in Prague (2001), Berlin (2003),
Bergen (2005), London (2007), and Leuven (2009).
1.
The purpose of the Bologna Process (or Bologna Accords) is the
creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic
degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and
compatible throughout Europe. It is named after the place it was
proposed, the University of Bologna, with the signing in 1999 of the
Bologna declaration by Education Ministers from 29 European
countries. It was opened up to other countries signatory to the
European Cultural Convention of the Council of Europe; further
governmental meetings have been held in Prague (2001), Berlin (2003),
Bergen (2005), London (2007), and Leuven (2009).
2. Before the signing of the Bologna declaration, the Magna Charta Universitatum (MCU) had been issued at a meeting of university rectors celebrating the 900th anniversary of the University of Bologna – and thus of (Western) European universities – in 1988. One year before the Bologna declaration, education ministers signed the Sorbonne declaration in Paris 1998, committing themselves to "harmonising the architecture of the European Higher Education system".
Timeline: The Bologna Process
The Bologna Zone
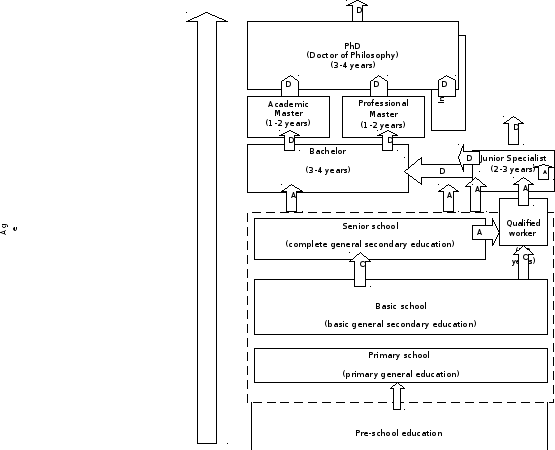
3. The basic framework adopted is of three cycles of higher education qualification. As outlined in the Bergen Declaration of 2005, the cycles are defined in terms of qualifications and European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) credits:
-
1st cycle: typically 180–240 ECTS credits, usually awarding a Bachelor's degree.
-
2nd cycle: typically 90–120 ECTS credits (a minimum of 60 on 2nd-cycle level). Usually awarding a Master's degree.
-
3rd cycle: Doctoral degree. No ECTS range given.
In most cases, these will take 3, 2, and 3 years respectively to complete. The actual naming of the degrees may vary from country to country.
One academic year corresponds to 60 ECTS-credits that are equivalent to 1,500–1,800 hours of study. The new model comes closer to the North American and Japanese systems. It gives greater weight to practical training and to intensive research projects. The way credits are measured reflects how hard a student has worked. The new evaluation methods reflect not only a student's performance on exams, but also his or her lab experiments, presentations, hours spent on study, innovation capacities, and so forth.
4. The Bologna Process was a major reform created with the goal of providing responses to issues such as the public responsibility for higher education and research, higher education governance, the social dimension of higher education and research, and the values and roles of higher education and research in modern, globalized, and increasingly complex societies with the most demanding qualification needs.
 With
the Bologna Process implementation, higher education systems in
European countries are to be organized in such a way that:
With
the Bologna Process implementation, higher education systems in
European countries are to be organized in such a way that:
-
it is easy to move from one country to the other (within the European Higher Education Area) – for the purpose of further study or employment;
-
the attractiveness of European higher education has increased, so that many people from non-European countries also come to study and/or work in Europe;
-
the European Higher Education Area provides Europe with a broad, high-quality advanced knowledge base, and ensures the further development of Europe as a stable, peaceful and tolerant community benefiting from a cutting-edge European Research Area;
-
there will also be a greater convergence between the U.S. and Europe as European higher education adopts aspects of the American system.
5. Since the mid-90s, Ukraine took steps to reform its education frameworks in consistence with the Bologna Process. Ukraine joined the Bologna process in 2005. By mid-2000s, most Universities grant lower Bachelor's degree (about 4 years) and higher Master's degree (about 6 years). In the Soviet times the only degree was Specialist, which is discontinued by now. Masters are eligible for post-graduate courses. The post-graduate system (Aspirantura) has not been reformed, with Candidate of Sciences and Doktor nauk degrees being granted.
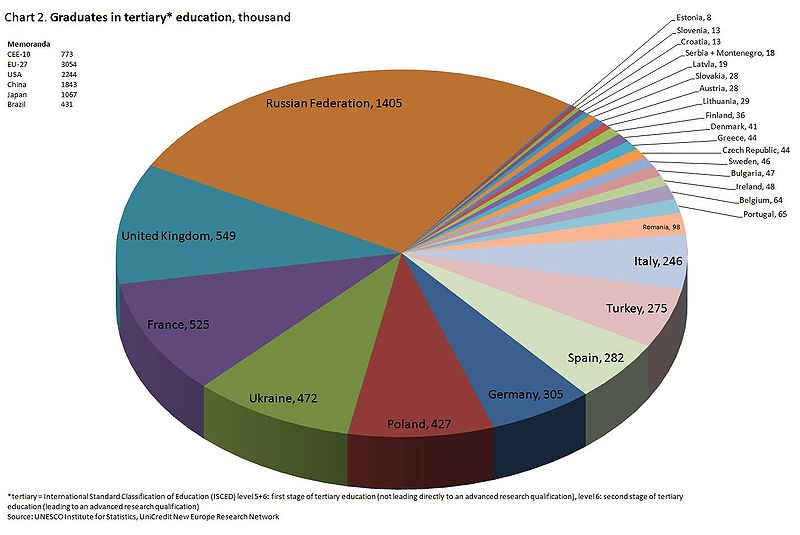
Ukraine produces the fourth largest number of academic graduates in Europe.
6. For Ukraine participation in the Bologna process is a chance of realizing Eurointegration strategy, assisting to improving education quality, solving the problem of recognition of the Ukrainian diplomas abroad. The primary goal is to introduce the system of academic credits stipulated by the Bologna declaration which is similar to ЕСТS (European credit- transfer system). It is considered as a means of students' mobility increase for transition from one curriculum to another, including programs of postgraduate education, as well as reforming curriculums and transfer of credits to higher educational establishments of other countries. An important point of introducing accumulative credit system is the possibility to take into account all student's achievements, not just an academic load, for example, participation in researches, conferences, subject Olympiads, etc.
7. The further actions for achievement of the Bologna process purposes are as follows: adoption of clear and adequate degrees system; inclusion of the two-cyclic education system (two-stage and subsequent training); introduction of the credits' system, i.e. system of credits accruing (ECTS) or its other joint systems which are capable to provide both differential-distinctive and accruing functions; contribution to students and teachers' mobility (elimination of barriers to free students and teachers' moving); provision of higher education high-quality standards; assistance to the European higher education approach (introduction of curricula, courses, modules with the "European" contents); long life training; common work of higher educational establishments and students as competent, active and constructive partners in establishment and formation of the European higher education area.
|
|
30 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
27 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
25 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
18 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
Modernization of the structure of the system of education in Ukraine in accordance with the Bologna requirements
Exercises
Ex.1. Find where in the text it is said about the points given below. Put down the number of the paragraph.
-
The purpose of the Bologna Process.
-
The history of the process
-
The basic framework.
-
Themain goals of the Bologna Process.
-
Ukraine participation in the Bologna process.
Ex.2. Give the meaning of the following abbreviations:
ECTS
EHEA
MCU
PhD
Ex.3. Say if the following statements are true or false:
-
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe..
-
The basic framework adopted is of two cycles of higher education qualification.
-
Before the signing of the Bologna declaration, the Magna Charta Universitatum had been issued in 1988.
-
Ukraine joined the Bologna process in 2008.
-
For Ukraine participation in the Bologna process is a chance of realizing Eurointegration strategy.
-
The post-graduate system (Aspirantura) has been reformed.
Ex. 4. Answer the following questions:
-
What is the main aim of Bologna process?
-
What is the origin of this name?
-
How must higher education systems in European countries be organized in accordance with the Bologna process?
-
What are the main benefits for Ukraine in participating the Bologna process?
-
What are the actions for achievement of the Bologna process purposes?
Ex. 5. Describe the development of the Bologna process.
Ex. 6. Explain the way in which the structure of the system of education in Ukraine must be modernized.
Ex. 7. Prove the necessity and importance of the implementation of the Bologna process.
Ex. 8. Make up a plan covering the main ideas. Discuss the text according to the plan.
Ex. 9. Discussion points:
-
Think over the prospectives of globalization and European integration in the sphere of education. Give your reasons and ideas.
-
What elements of Bologna process are introduced at our University?
Great Universities









The Ivy League is an athletic conference comprising eight private institutions of higher education in the Northeastern United States. The conference name is also commonly used to refer to those eight schools as a group. The eight institutions are Brown University, Columbia University, Cornell University, Dartmouth College, Harvard University, Princeton University, the University of Pennsylvania, and Yale University. The term Ivy League also has connotations of academic excellence, selectivity in admissions, and social elitism. The Ivy League universities are also called the "Ancient Eight" or simply the Ivies.
Brown University is a private, Ivy League university located in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. Founded in 1764 prior to American independence from the British Empire as the College in the English Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations early in the reign of King George III (1760–1820), Brown is the third oldest institution of higher education in New England and seventh oldest in the United States.
Brown was the first college in the nation to accept students regardless of religious affiliation. Academically, Brown consists of The College, Graduate School, Alpert Medical School, and the School of Engineering. Brown's international programs are organized through the Watson Institute for International Studies. The New Curriculum, instituted in 1969, eliminated distribution requirements and allows any course to be taken on a satisfactory/no credit basis. The school has the oldest undergraduate engineering program in the Ivy League (1847).
Columbia University in the City of New York (Columbia University) is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. Today the University operates seven Columbia Global Centers overseas in Amman, Beijing, Istanbul, Paris, Mumbai, Santiago, and Nairobi.
Columbia annually administers the Pulitzer Prize and has been affiliated with more Nobel Prize laureates than any other academic institution in the world. The University is one of the fourteen founding members of the prestigious Association of American Universities, and was the first school in the United States to grant the M.D. degree. Notable students of the University include nine Justices of the United States Supreme Court; 20 living billionaires; 25 Academy Award winners; and 29 Heads of State, including three United States Presidents. The University encompasses twenty schools and is affiliated with numerous institutions.
Cornell University is located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, the university was intended to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences and from the theoretical to the applied. Since its founding, Cornell has also been a co-educational, non-sectarian institution where admission is offered irrespective of religion or race. Cornell counts more than 255,000 living alumni, 31 Marshall Scholars, 28 Rhodes Scholars and 41 Nobel laureates as affiliated with the university. The student body consists of nearly 14,000 undergraduate and 7,000 graduate students from all 50 states and 122 countries.
Dartmouth College is a private, Ivy League university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. The institution comprises a liberal arts college, Dartmouth Medical School, Thayer School of Engineering, and the Tuck School of Business, as well as 19 graduate programs in the arts and sciences. Incorporated as "Trustees of Dartmouth College," it is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. With an undergraduate enrollment of 4,196 and a total student enrollment of 5,987, Dartmouth is the smallest school in the Ivy League