
Questions
Questions for this IHW are by my presentations for Module 1: Lectures 1 – 3.
Problems
1
A 300 g object is attached to a horizontal spring. The spring is initially stretched by 3 dm, and the object is released from rest there. It proceeds to move without friction. The next time the speed of the object is zero at 0.5 min later.
(a) What is the angular frequency of oscillations of the object?
(b) What is the period of oscillations of the object?
(c) What is the frequency of oscillations of the object?
(d) What is the amplitude of oscillations of the object?
(e) What is the maximum speed of the object?
(f) What is the maximum acceleration of the object?
(g) What is the spring constant of the spring?
(h) What is the total mechanical energy of the oscillator?
2
Consider a damped oscillator as illustrated in Figures. Assume the mass is 400 g, the spring constant is 10 N/dm, and b=0.1 N/m.
(a) How long does it take for the amplitude to drop to half its initial value?
(b) How long does it take for the mechanical energy to drop to half its initial value?
(c) Show that, in general, the fractional rate at which the amplitude decreases in a damped harmonic oscillator is half the fractional rate at which the mechanical energy decreases.
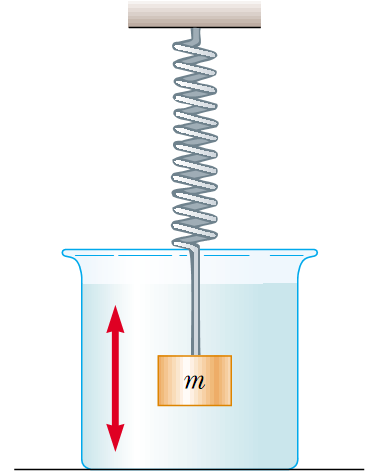

3
Ocean waves can be described by the wave function
y(x, t) = (8dm) sin[0.6x – 1.4t + /3]. (dm is decimeter, t is in seconds)
(a) Sketch y(x, t) at t = 0 and at t = 0.2 min in one picture.
(b) What is the direction of motion of waves?
(c) What is the speed of waves in the x direction?
(d) What is the acceleration of waves in the x direction?
(e) What is the wavelength, amplitude, period, frequency and angular frequency of waves?
(f) What is the wavenumber and the phase constant of the ocean waves?
(g) What means dy(x,t)/dt ?
(h) What means dy(x,t)/dx ?
(i) Calculate the maximum transverse speed of a point on the ocean surface.
(k) Calculate the maximum transverse acceleration of a point on the ocean surface.
4
A light string with a mass per unit length of 5 mg/cm has its ends tied to two walls separated by a distance equal to three fourths of the length of the string. An object of mass m is suspended from the center of the string, putting a tension in the string.
(a) Find an expression for the transverse wave speed in the string as a function of the mass of the hanging object.
(b) What should be the mass of the object suspended from the string in order to produce a wave speed of 60.0 m/s?
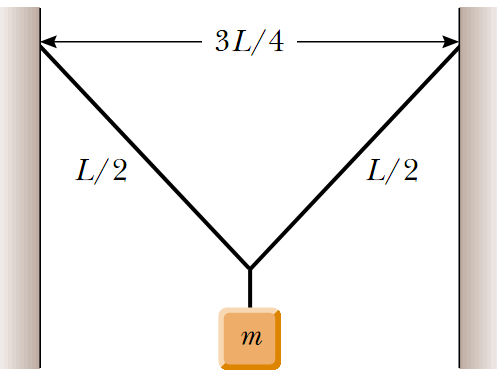
5
The wave function for a wave on a taut string is
y(x, t) = (0.35 m)sin(10t – 3x + /4)
where x is in meters and t in seconds.
(a) What is the average rate at which energy is transmitted along the string if the linear mass density is 5 g/dm?
(b) What is the energy contained in each cycle of the wave?
6
A horizontal string can transmit a maximum power P0 (without breaking) if a wave with amplitude A and angular frequency is traveling along it. In order to increase this maximum power, a student folds the string and uses this “double string” as a medium. Determine the maximum power that can be transmitted along the “double string,” assuming that the tension is constant.
7
Determine if the function y(x, t) is a solution to the wave equation
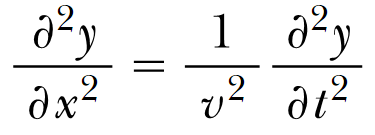
(a) y(x, t) = x2 -3v2t2
(b) y(x,t) = eb(x+vt), b=const
8
The speed of an electromagnetic wave traveling in
a transparent nonmagnetic substance is
![]() ,
where
is the dielectric constant of the substance. Determine the
speed of light in water, which has a dielectric constant at
optical frequencies of 1.7.
,
where
is the dielectric constant of the substance. Determine the
speed of light in water, which has a dielectric constant at
optical frequencies of 1.7.
9
There are three lamps connected to a 120 V AC (rms) household supply voltage. Lamps 1 and 2 have 150-W bulbs; lamp 3 has a 100-W bulb. Find the rms
current and resistance of each bulb.

10
An inductor has a 54 reactance at 60 Hz. What is the maximum current if this inductor is connected to a 50 Hz source that produces a 100 V rms voltage?
