
final_prep
.pdfFINAL EXAM TRAINING GROUND
GOOD LUCK!
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1) All economic questions arise because we |
1) _______ |
A)have limited wants that need to be satisfied.
B)want more than we need.
C)want more than we can get.
D)have an abundance of resources.
2) |
Scarcity is common to all economic systems because resources |
2) |
_______ |
|
|
A) are limited, but human desires and wants are unlimited. |
|
|
|
|
B) are unlimited due to constant technological advances. |
|
|
|
|
C) are unlimited, and so are human desires and wants. |
|
|
|
|
D) are limited, as are human material needs. |
|
|
|
3) |
People must make choices because |
|
3) |
_______ |
|
A) of scarcity. |
B) most people enjoy shopping. |
|
|
|
C) there are many goods available. |
D) None of the above answers is correct. |
|
|
4) |
Economics is best defined as the science of choice and how people cope with |
4) |
_______ |
|
|
A) differences in needs. |
B) scarcity. |
|
|
|
C) different economic systems. |
D) differences in wants. |
|
|
5) |
The term human capital refers to |
|
5) |
_______ |
A)people's knowledge and skill.
B)entrepreneurship and risk-taking.
C)labor resources used to make capital equipment.
D)buildings and machinery.
6) |
Suppose the cost of 5 pencils is $1.50. The cost of 6 pencils is $1.75. The marginal cost of the sixth |
6) |
_______ |
|||
|
pencil is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) $1.50. |
B) $1.75. |
C) $3.25. |
D) $ .25. |
|
|
7) |
If the marginal cost of an activity exceeds the marginal benefit, then |
|
7) |
_______ |
||
A)an alternative action will be selected.
B)the person must concentrate on the activity's total benefits.
C)the forgone alternatives' costs must be increased.
D)the activity will occur because of the high marginal cost.
8) To decide whether to go to the beach for spring break, you should |
8) _______ |
A)compare marginal cost to the marginal benefit of taking the trip.
B)unscramble cause and effect.
C)not make the fallacy of composition.
D)not make the post hoc fallacy.
9) Jed had a low exam score. There is an extra credit assignment that Jed can complete that will |
9) _______ |
raise his exam score by 20 percentage points. Jed has determined that the extra credit assignment |
|
will take 10 hours of his time. Jed will complete the assignment he values the |
|
A) 10 hours of his time more than the 20 percentage points. |
|
B) 20 percentage points more than the 10 hours of his time. |
|
C) 20 percentage points and 10 hours of his time equally. |
|
D) 20 percentage points less than the 10 hours of his time.
10) Normative economic statements |
10) ______ |
A)deal with economic hypotheses that are not well-established laws.
B)describe what is rather than what ought to be.
C)describe what ought to be.
D)describe the process of economic policy-making.
11) The statement that "peach ice cream is better than chocolate ice cream" |
11) ______ |
A)is a statement of fact.
B)is a normative statement.
C)can be tested using the scientific approach.
D)provides a basis for predicting which type of ice cream will exhibit the most sales.
12) |
The term ceteris paribus means |
12) |
______ |
|
A) the study of scarcity and choice. |
B) value free and testable. |
|
|
C) all other things remaining equal. |
D) the greatest good for all. |
|
13) |
The production possibilities frontier represents |
13) |
______ |
A)the maximum amount of labor and capital available to society.
B)combinations of goods and services among which consumers are indifferent.
C)the maximum rate of growth of capital and labor in a country.
D)the maximum levels of production that can be attained.
14) Which of the following is NOT true concerning a society's production possibilities frontier |
14) ______ |
(PPF)? |
|
A)It reveals the maximum amount of any two goods that can be produced from a given quantity of resources.
B)Consumers will receive equal benefits from the two goods.
C)Tradeoffs occur along a PPF.
D)Production efficiency occurs when production is on the frontier itself.
15) |
Suppose a country, when operating on its PPF, can produce 2 tons of butter and 200 cars OR 3 |
15) |
______ |
|||
|
tons of butter and 150 cars. The opportunity cost of 1 ton of butter is |
|
|
|
||
|
A) 300 cars. |
B) 0.75 cars. |
C) 200 cars. |
D) 50 cars. |
|
|
16) |
At one point along a PPF, 10 pizzas and 7 sandwiches can be produced. At another point along |
16) |
______ |
|||
|
the same PPF, 9 pizzas and 10 sandwiches can be produced. The opportunity cost of a pizza |
|
|
|||
|
between these points is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 7/10 of a sandwich. |
|
B) 3 sandwiches. |
|
|
|
|
C) 1/3 of a sandwich. |
|
D) 10/7 of a sandwich. |
|
|
|
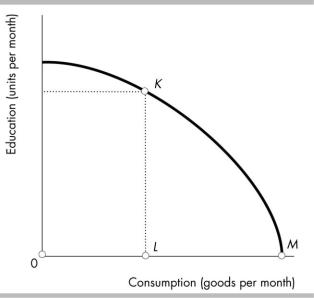
17) Molly just graduated from high school. The figure shows her possibilities frontier. If Molly goes |
17) |
______ |
|||||
|
to college, she will move from point M to point K. What is Molly's opportunity cost of going to |
|
|
||||
|
college? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) KL |
B) MK |
C) OL |
D) LM |
|
|
|
|
|
Production Possibilities |
|
|
|
|
|
Possibil |
Pizza |
Soda |
|
|
|
|
|
(per |
(cases per |
|
|
|
|
||
|
ity |
|
|
|
|
||
|
hour) |
hour) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
A |
|
0 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
B |
|
1 |
95 |
|
|
|
|
C |
|
2 |
80 |
|
|
|
|
D |
|
3 |
60 |
|
|
|
|
E |
|
4 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
F |
|
5 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
18) In the above table, the production of 3 pizzas and 80 cases of soda is |
|
18) |
______ |
||||
A)possible only if the economy produces with maximum efficiency.
B)possible only if there is inflation.
C)impossible unless more resources become available or technology improves.
D)feasible but would involve unemployed or misallocated resources.
19) The nation's production possibilities frontier is bowed outward. Suppose that the government |
19) ______ |
decides to increase the production of armaments by $20 billion, and that as a result the output of |
|
consumer goods falls by $20 billion. If a further $20 billion increase beyond the initial $20 billion |
|
increase in armaments output is sought, we can expect that the output of consumer goods and |
|
services will fall further by |
|
A) $20 billion. |
|
B) more than $20 billion. |
|
C) less than $20 billion. |
|
D) There is not enough information to determine the answer. |
|
20) A bowed outward production possibilities frontier occurs when |
20) ______ |
A) opportunity costs are constant.
B) the society is operating on the production possibilities frontier.
C) as more of a good is produced, producing additional units of it require increased reductions in the other good.
D) resources are not scarce. |
|
21) The fact of increasing opportunity costs means that a production possibilities frontier will |
21) ______ |
A) shift outward over time. |
|
B) bow outward. |
|
C) be a straight line. |
|
D) reach a maximum and then gradually decrease. |
|
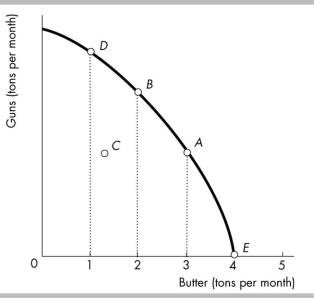
22) The country whose production possibilities frontier is illustrated above is currently at position A 22) ______
on the production possibilities frontier. If it wishes to move to position B, it will
A)have to employ all currently unemployed resources to accomplish this.
B)incur an opportunity cost of having to give up some butter in order to make the additional amount of guns desired.
C)find this change impossible to achieve given the resources it currently possesses.
D)be able to make the desired switch only if there is a significant improvement in the technological base available to the nation.
23) In the figure above, moving from point B to point D |
23) ______ |
A)requires an increase in technology.
B)has an opportunity cost of one ton of butter per month.
C)is impossible.
D)has an opportunity cost of one ton of guns per month.
24) |
Economic growth means |
|
24) |
______ |
|
A) an expansion of production. |
B) an inward shift of the PPF. |
|
|
|
C) an outward shift of the PPF. |
D) Both answers A and C are correct. |
|
|
25) |
When an economist refers to choices made "at the margin" the economist is referring to |
25) |
______ |
|
A)decisions based on the marginal benefits and marginal costs of small changes in a particular activity.
B)an individual's all-or-nothing choice concerning a specific good or activity.
C)an individual's margin account with a stockbroker that allows part of a stock purchase to be made with borrowed money.
D)all of the above
26) Comparative advantage is |
26) ______ |
A)the ability to perform an activity at a higher opportunity cost than anyone else.
B)the ability to perform an activity at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else.
C)identical to absolute advantage.
D)the ability to perform an activity at a zero opportunity cost.
27) A person has a comparative advantage in an activity if that person can |
27) ______ |
A)perform that activity at a higher opportunity cost than anyone else.
B)produce fewer goods in a given amount of time than another person.
C)produce more goods in a given amount of time than another person.
D)perform the activity at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else.
|
U.S. production |
France's |
|
|
|
|
production |
|
|
|
|
|
possibilities |
|
|
|
|
|
possibilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Steel |
100 |
25 |
|
|
|
Concrete |
200 |
100 |
|
|
|
28) The above table shows the tons of steel and concrete that can be produced by the United States |
28) |
______ |
|||
and France in an hour. From the data in the table, |
|
|
|||
|
A) the United States has the comparative advantage in the production of both goods. |
|
|
||
|
B) France has the comparative advantage in the production of concrete. |
|
|
||
|
C) the United States has the comparative advantage in the production of concrete. |
|
|
||
|
D) France has the absolute advantage in the production of concrete. |
|
|
||
29) Suppose that a typical German factory can produce 20 cameras or 1 computer in an hour, and |
29) ______ |
||||
that a typical American factory can produce 10 cameras or one computer in an hour. If Germany |
|
|
|||
produces one less computer and switches resources to cameras, and the United States produces |
|
|
|||
one more computer and takes resources out of cameras, then the net change in camera |
|
|
|||
production in both countries taken together is |
|
|
|||
|
A) plus 20 cameras. |
|
B) plus 10 cameras. |
|
|
|
C) minus 10 cameras. |
|
D) 0. |
|
|
30) Gross domestic product is the total ________ produced within a country in a given time period. |
30) |
______ |
|||
|
A) market value of all final and intermediate goods and services |
|
|
||
|
B) market value of all final goods and services |
|
|
||
|
C) amount of final and intermediate goods and services |
|
|
||
|
D) market value of all goods and services |
|
|
||
31) National saving is defined as the amount of saving by |
31) |
______ |
|||
|
A) households. |
|
|
|
|
B) businesses and households.
C) businesses.
D) businesses and households and the government.
32) If national saving (S) is $100,000, net taxes (T) equal $100,000 and government purchases of |
goo ds and |
services 32) |
|
|
|
___ |
|
(G) are |
|
|
|
___ |
|
$25,000, |
|
|
|
|
|
how |
|
|
|
|
|
much are |
|
|
|
|
|
househol |
|
|
|
|
|
ds and |
|
|
|
|
|
business |
|
|
|
|
|
es |
|
|
|
|
|
saving? |
|
|
|
|
|
A) -$25,000. |
|
B) $225,000. |
|
|
|
C) $25,000. |
|
D) none of the above |
|
|
|
33) At the beginning of the year, your wealth is $10,000. During the year, you have an income of |
33) |
______ |
|||
$90,000 and you spend $80,000 on consumption. You pay no taxes. Your wealth at the end of the |
|
|
|||
year is |
|
|
|
|
|
A) $0. |
B) $90,000.00. |
C) $100,000.00. |
D) $20,000.00. |
|
|
34) The term capital, as used in macroeconomics, refers to |
|
34) |
______ |
||
A)the plant, equipment, buildings, and inventories of raw materials and semi-finished goods.
B)investment.
C)the sum of investment and government purchases of goods.
D)financial wealth.
35) Depreciation |
35) ______ |
A)does not change the amount of capital in the economy.
B)is the decrease in the capital stock because of wear and tear.
C)is also known as capital consumption.
D)Both answers B and C are correct.
36) |
Investment, as defined in the text, refers to the purchase of |
36) |
______ |
|
|
A) stocks and bonds. |
B) durable goods by consumers. |
|
|
|
C) new capital. |
D) All of the above answers are correct. |
|
|
37) |
Economists define depreciation as |
|
37) |
______ |
A)the drop in the price of a company's product.
B)the loss in stock market of a company's value.
C)the decrease in the capital stock from wear and tear and obsolescence.
D)All of the above answers are correct.
38) |
At the beginning of the year, Tom's Tubes had a capital stock of 5 tube inflating machines. |
38) |
______ |
|||
|
During the year, Tom scrapped 2 old machines and purchased 3 new machines. Tom's net |
|
|
|||
|
investment for the year totaled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 6 machines. |
B) 3 machines. |
C) 1 machine. |
D) 2 machines. |
|
|
39) |
Which of the following is NOT a final good? |
|
|
39) |
______ |
|
A)a purse sold to a foreign visitor
B)a new computer sold to an NYU student
C)a hot dog sold to a spectator at a Chicago Bears football game
D)a new car sold to Avis for use in their fleet of rental cars
40) GDP equals |
40) ______ |
A) aggregate income.
B) the value of the aggregate production in a country during a given time period.
C) aggregate expenditure.
D) all of the above |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Million |
|
Item |
s of |
|
|
dollars |
|
Personal consumption |
80 |
|
expenditure |
||
|
||
Government purchases of goods |
30 |
|
and services |
||
|
||
Net taxes |
35 |
|
Gross private domestic investment |
20 |
|
Imports of goods and services |
10 |
|
Exports of goods and services |
20 |
41) |
Use the information in the table above to calculate the value of private saving. |
|
41) |
______ |
||
|
A) $20 million |
B) -$15 million |
C) $25 million |
D) $40 million |
|
|
42) |
Use the information in the table above to calculate the value of government saving. |
42) |
______ |
|||
|
A) $15 million |
B) $45 million |
C) $5 million |
D) -$5 million |
|
|
43) |
GDP can be computed as the sum of |
|
|
43) |
______ |
|
A)the total expenditures of consumers and business over a period of time.
B)the total expenditures of consumption, investment, government expenditure on goods and services, and net exports over a period of time.
C)all sales that have taken place in an economy over a period of time.
D)the total expenditures of consumption, investment, and government expenditure on goods and services over a period of time.
44) |
In the expenditure approach to GDP, the largest component is |
|
44) |
______ |
||
|
A) gross private domestic investment. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B) personal consumption expenditures. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C) net exports. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D) government expenditure on goods and services. |
|
|
|
||
45) |
Let C represent consumption expenditure, S saving, I gross private domestic investment, G |
45) |
______ |
|||
|
government expenditure on goods and services, and NX net exports of goods and services. Then |
|
|
|||
|
GDP equals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) C + I + G + NX. |
B) C + S + G - NX. |
C) C + S + G + NX. |
D) C + I + G - NX. |
|
|
46) |
Personal consumption expenditures include |
|
|
46) |
______ |
|
A)the purchase of used goods and new goods.
B)expenditures by households on goods and services produced only in the United States.
C)the purchase of new homes.
D)expenditures by households on goods and services produced in the United States and the rest of the world.
47) An example of "investment" in computing real GDP using the expenditure approach is the |
47) ______ |
purchase of |
|
A) a new set of tools by an auto mechanic, for use in repairing cars.
B) 100 shares of IBM stock.
C)computer chips by Dell to put in their personal computers.
D)a 100 year old house by a married couple.
Government purchases of goods and |
|
|
$24 |
|
|
|
|
||
services |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation |
|
240 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gross private domestic investment |
|
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Personal income taxes |
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net taxes |
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net exports of goods and services |
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Personal consumption expenditures |
|
640 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net interest |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
48) From the data in the above table, GDP equals |
|
|
|
48) ______ |
|||||
A) $1,290. |
B) $1,280. |
|
C) $1,360. |
D) $1,120. |
|
|
|||
49) Using the data in the above table, net domestic product equals |
|
49) |
______ |
||||||
A) $1,280. |
B) $1,120. |
|
C) $1,290. |
D) $1,360. |
|
|
|||
50) The approach to GDP that sums compensation of employees, rental income, corporate profits, |
50) ______ |
||||||||
net interest, proprietors' income, depreciation, and indirect taxes and subtracts subsidies is the |
|
|
|||||||
A) expenditure approach. |
|
B) opportunity cost approach. |
|
|
|||||
C) income approach. |
|
|
|
|
D) added cost approach. |
|
|
|
|
51) Government expenditures included in the expenditures approach to GDP include ________. |
51) ______ |
||||||||
A) buying a new bomber |
|
|
|
|
B) social security and education |
|
|
||
C) net exports |
|
|
|
|
D) Both answers A and C are correct |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Million |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
|
s of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dollars |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Personal consumption |
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
expenditure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government purchases of goods |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net taxes |
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross private domestic investment |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Imports of goods and services |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exports of goods and services |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52) Using the information in the table above, calculate the value of GDP. |
|
52) |
______ |
||||||
A) $145 million |
B) $140 million |
|
C) $185 million |
D) $195 million |
|
|
|||
53) In the country of Darrowby, net domestic income at factor cost is $2.0 million. Gross domestic |
53) |
______ |
|||||||
product is $3.0 million, and depreciation is $0.5 million. Indirect taxes less subsidies ________. |
|
|
|||||||
A) are $1 million |
|
|
|
|
B) cannot be calculated |
|
|
|
|
C) are $0.5 million |
|
|
|
|
D) are -$0.5 million |
|
|
|
|
54) Real GDP measures the |
54) ______ |
A)value of total production linked to prices of a single year.
B)changes in the prices of output measured in dollars.
C)total profits earned by all businesses valued using prices from a single year.
D)general upward drift in prices.
55) In years with inflation, nominal GDP increases ________ real GDP. |
55) ______ |
A)slower than
B)at the same rate as
C)faster than
D)sometimes faster, sometimes slower, and sometimes at the same rate as
56) If nominal GDP is $5 trillion and the GDP deflator is 125, what is real GDP? |
|
56) |
______ |
||||||
|
|
A) $6.25 trillion |
B) $4 trillion |
|
C) $.04 trillion |
D) $625 trillion |
|
|
|
57) The GDP deflator equals ________. |
|
|
|
57) ______ |
|||||
|
|
A) (Nominal GDP ÷ 100) × Real GDP |
|
B) (Real GDP ÷ Nominal GDP) × 100 |
|
|
|||
|
|
C) (Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP) × 100 |
|
D) nominal GDP |
|
|
|
||
58) A measure of the price level that is an average of current year prices expressed as a percentage of |
58) |
______ |
|||||||
|
base-year prices is the ________. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
A) Urban GDP Price Level |
|
B) GDP deflator |
|
|
|
||
|
|
C) inflation rate |
|
|
|
D) GDP inflator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nomin |
Real |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
al GDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yea |
(billion |
|
GDP |
|
|
|
|
||
(billion |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
r |
s of |
|
deflator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
s of |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dollars) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dollars) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2003 |
|
|
90 |
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
2004 |
|
125 |
|
|
125 |
|
|
|
|
59) Use the information in the table above to calculate nominal GDP in 2003. |
|
59) |
______ |
||||||
|
|
A) $108 billion |
B) $75 billion |
|
C) $10,800 billion |
D) $0.75 billion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nomin |
Real |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yea |
al GDP |
GDP |
|
GDP |
|
|
|
|
|
(billion |
(billion |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
r |
|
deflator |
|
|
|
|
||
|
s of |
s of |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
dollars) |
dollars) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2004 |
|
2500 |
________ |
|
105 |
|
|
|
|
2005 |
|
________ |
2400 |
|
117 |
|
|
|
|
60) Using the data in the above table, what is real GDP in 2004? |
|
60) |
______ |
||||||
|
|
A) $2137 billion |
B) $2381 billion |
C) $2520 billion |
D) $2051 billion |
|
|
||
61) Real GDP in 2006 is $10 trillion. Between 2006 and 2007, using 2006 prices, GDP grew 3 percent |
61) ______ |
||||||||
|
and using 2007 prices real GDP grew 7 percent. Using the chain-weighted output index method, |
|
|
||||||
|
real GDP in 2007 is ________ trillion. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
A) $11 |
B) $12.72 |
C) $10.1 |
D) $10.5 |
62) Which of the following is NOT included in real GDP? |
62) ______ |
||
A)production that takes place in the underground economy
B)production of goods that last more than a year, such as a pair of roller blades
C)production of services, such as the services of hair dressers
D)production of goods that last less than a year, such as production of hot dogs
63) Because pollution reduces economic welfare, on this count real GDP |
63) ______ |
A)increases to take into account the expenditures that will be made in the future to clean up the pollution.
B)decreases as pollution increases.
C)understates economic welfare.
D)overstates economic welfare.
64) Which of the following would lead GDP to overstate economic welfare? |
64) ______ |
A)restaurant workers that under-report tip income
B)the existence of home-cooked meals
C)a self-employed CPA who takes a longer than normal vacation
D)electric utilities that switch to burning coal because of higher natural gas prices and thereby create more acid rain pollution
65) Pollution is a by-product of some production processes, so on this count real GDP as measured |
65) ______ |
A)tends to understate economic welfare.
B)is adjusted downward to take into account the pollution.
C)tends to overstate economic welfare.
D)is adjusted upward to take into account the expenditures that will be made in the future to clean up the pollution.
66) |
Real GDP fluctuations tend to ________ fluctuations in total production because household |
66) |
______ |
|
production ________. |
|
|
|
A) understate; decreases during a recession and increases during an expansion |
|
|
|
B) overstate; decreases during a recession and increases during an expansion |
|
|
|
C) understate; increases during a recession and decreases during an expansion |
|
|
|
D) overstate; increases during a recession and decreases during an expansion |
|
|
67) |
The labor force is the sum of the |
67) |
______ |
A)number of employed people and the number of unemployed people.
B)total population and the number of unemployed people.
C)number of employed people and the working-age population.
D)working-age population and the number of unemployed people.
68) The labor force is defined as the number of people who |
68) ______ |
A)would like to have a job but have stopped seeking work.
B)would like to have a full-time job but are working part-time.
C)are employed plus the number of people who are unemployed.
D)are available and looking for work but are unable to find employment.
69) The unemployment rate is calculated as 100 times |
69) ______ |
A) *(labor force) ÷ (unemployment)+. |
B) [(unemployment) ÷ (labor force)+. |
C) *(labor force) ÷ (population)+. |
D) *(unemployment) ÷ (population)+. |
