
Mini-course 1 Decision Analysis (Dr. Mariya Sodenkamp) / Class 1 / Paderborn_ITB_L1_ 2015_04_13 Instructor
.pdf
(Advanced) IT in Business: Decision Analysis
13 April, 2015
Lecture 1: Making trade-o s with Even Swaps
Dr. Mariya Sodenkamp
Energy E cient Systems Group
Department of InformaCon Systems

Dominance and Even Swaps
Ø Even Swaps is a method of qualitative decision analysis
Ø It is aimed to simplify complexity of decisions
Ø It is based on the idea of logical and practical dominance to reduce number of alternatives and even swaps to eliminate not relevant criteria
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
2 |
|

Sahid’s Problem
The only child of a widower, Vincent Sahid plans to take time o from college, where he’s majoring in business, to help his father recover from a serious illness. To make ends while away from school, he will need to take a job. He wants a position that pays adequately, has good benefits and vacation allowances, and involves enjoyable work, but he’d also like to gain some experience that will be useful when he returns to school. And, given his dad’s frail condition, it is very important that the job give him a flexibility to deal with emergencies. After a lot of work, Vincent identifies five possible jobs. Each has very di erent consequences and he charts those consequences in a consequences table.
* This case is adopted from:
Hommond J. S, Keeney R.L. and Raiffa H.: Ewen Swaps: A Rational Method for Making Trade-offs, Harward Business Review, MarchApril 1998, pp.137-148.
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
3 |
|
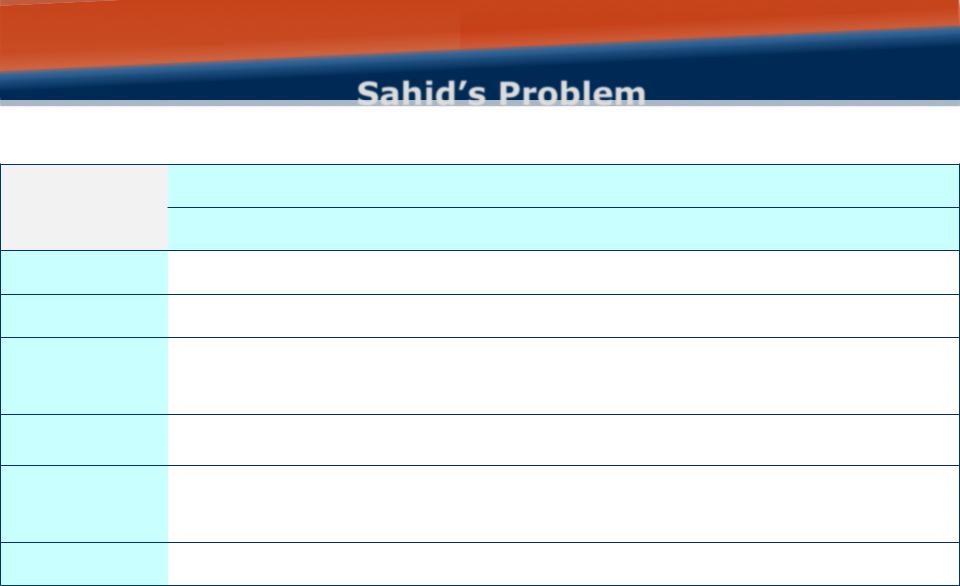
Sahid’s Problem
Consequences Table
|
|
|
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
|
|
|
Job A |
|
Job B |
|
Job C |
|
Job D |
|
Job E |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Monthly Salary($) |
2000 |
|
2400 |
|
1800 |
|
1900 |
|
2200 |
Flexibility |
Moderate |
|
Low |
|
High |
|
Moderate |
|
None |
Business Skills |
Computer |
|
People |
|
Operations, |
|
Organization |
|
Time |
Development |
|
|
management, |
|
Computer |
|
|
|
management, |
|
|
|
Computer |
|
|
|
|
|
Multitasking |
Annual Vacation |
14 |
|
12 |
|
10 |
|
15 |
|
12 |
Days |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benefits |
Health |
|
Health |
|
Health |
|
Health |
|
Health |
|
Dental |
|
Dental |
|
|
|
Retirement |
|
Dental |
|
Retirement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enjoyment |
Great |
|
Good |
|
Good |
|
Great |
|
Boring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A consequences table puts a lot of information into a concise and orderly format that allows you to compare alternatives easily, objective by objective. It gives a clear framework for making trade-o s, imposes a discipline, focusing you to define all
 alternatives, objectives and all the relevant consequences at the outset of decision process. 4
alternatives, objectives and all the relevant consequences at the outset of decision process. 4
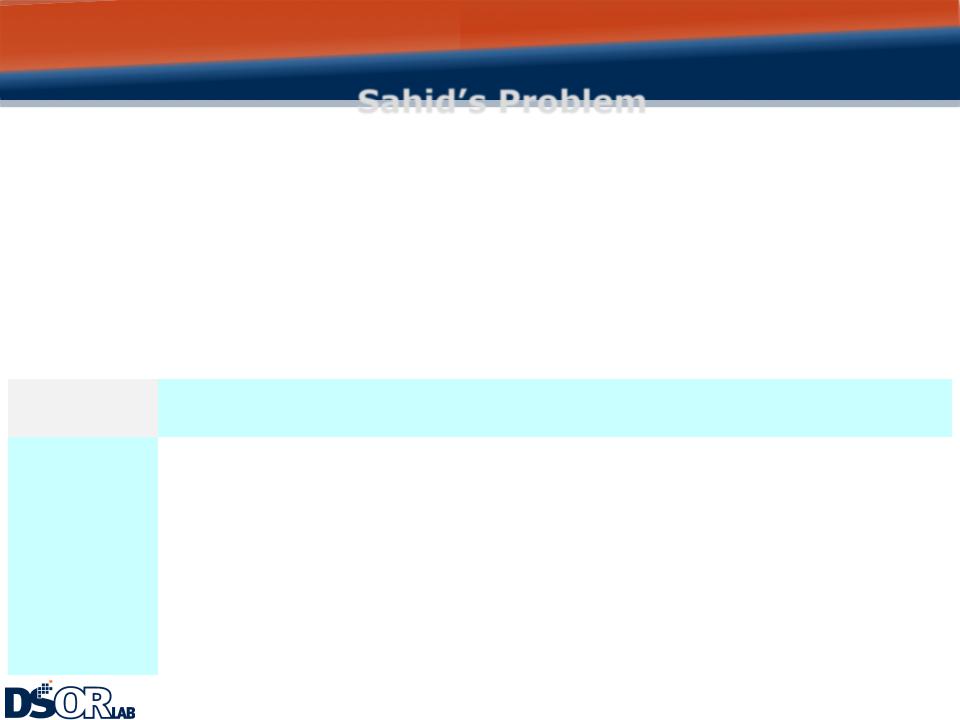
Sahid’s Problem
Ranking Table
v Once you‘ve defined and mapped the consequences for each alternative, you should always look for opportunities to eliminate one or more of the alternatives.
v If a consequences table contains many objectives and alternatives, it gets hard to compare consequences.
v To make it easier to uncover dominance you should create a second table in which descriptions of consequences are replaced with simple rankings:
|
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
|
|
Job A |
Job B |
Job C |
Job D |
Job E |
|
Monthly Salary |
3 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
|
Flexibility |
2 (tie) |
4 |
1 |
2 (tie) |
5 |
|
Business Skills |
4 |
1 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
|
Development |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Annual Vacation |
2 |
3 (tie) |
5 |
1 |
3 (tie) |
|
Days |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Benefits |
1 |
2 (tie) |
5 |
4 |
2 (tie) |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enjoyment |
1 (tie) |
3 (tie) |
3 (tie) |
1 (tie) |
5 |
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
5 |
|
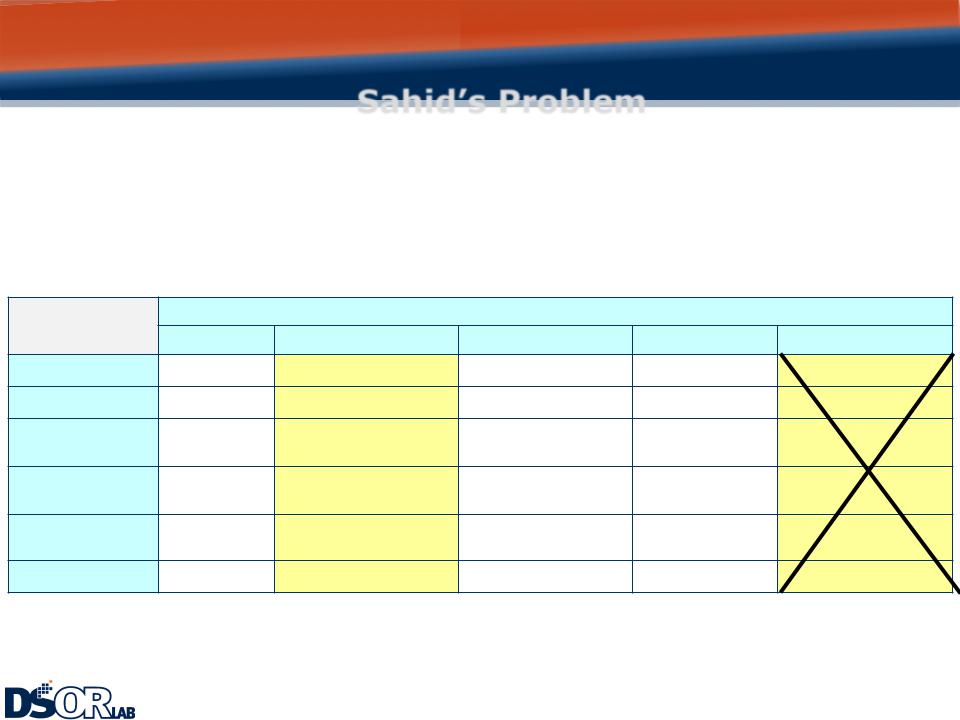
Sahid’s Problem
Logical Dominance
If alternative A is better than alternative B on some objectives and no worse than B on all other objectives, B can be eliminated from consideration. In such cases B is said to be logically dominated by A – it has disadvantages without any advantage.
|
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
|
|
Job A |
Job B |
Job C |
Job D |
Job E |
|
Monthly Salary |
3 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
|
Flexibility |
2 (tie) |
4 |
1 |
2 (tie) |
5 |
|
Business Skills |
4 |
1 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
|
Development |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Annual Vacation |
2 |
3 (tie) |
5 |
1 |
3 (tie) |
|
Days |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Benefits |
1 |
2 (tie) |
5 |
4 |
2 (tie) |
|
|
||||||
Enjoyment |
1 (tie) |
3 (tie) |
3 (tie) |
1 (tie) |
5 |
Job B logically dominates Job E since B is better than E on four objectives and equivalent on two.
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
6 |
|
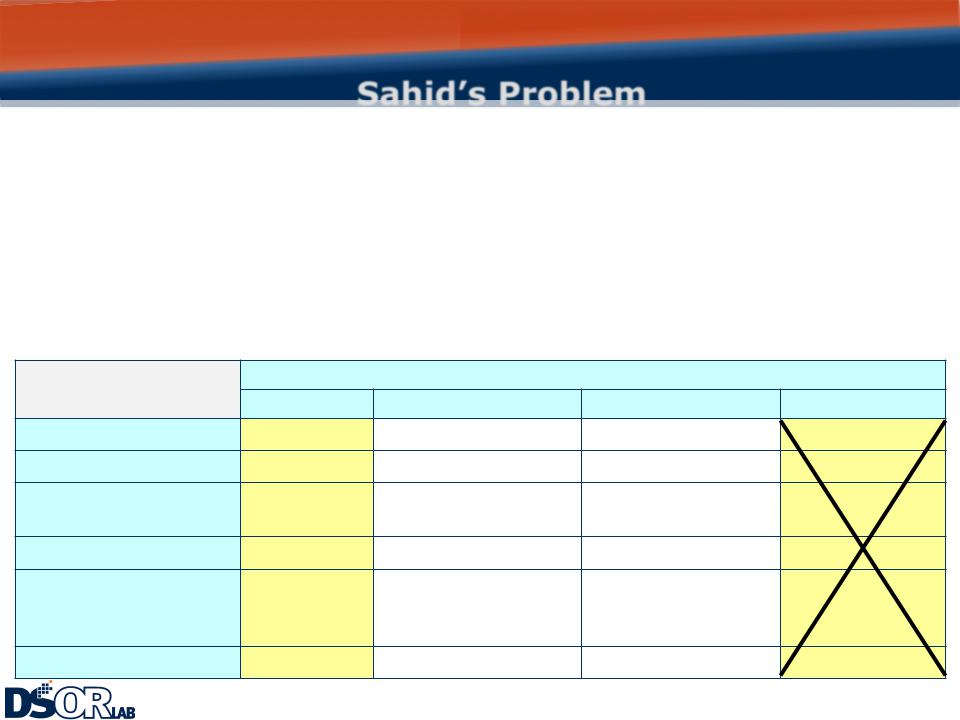
Sahid’s Problem
Practical Dominance
When an alternative has only one advantage over another, it is a candidate for elimination due to practical dominance.
Comparing Job A and Job D Vincent sees that Job A is better on three objectives, tied on two and is worse on one (vacation), However, one-day advantage of Job D is far outweighed by its disadvantages in salary and benefits. Hence, Job D is practically dominated by Job A and can be eliminated.
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
|
Job A |
Job B |
Job C |
Job D |
Monthly Salary ($) |
2000 |
2400 |
1800 |
1900 |
Flexibility |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
Moderate |
Business Skills |
Computer |
People management, |
Operations, |
Organization |
Development |
(rank 4) |
Computer |
Computer |
(rank 5) |
Annual Vacation Days |
14 |
12 |
10 |
15 |
Benefits |
Health |
Health |
Health |
Health |
|
Dental |
Dental |
|
Retirement |
|
Retirement |
|
|
|
Enjoyment |
Great |
Good |
Good |
Great |
|
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
||

Making Even Swaps
• Even swap is used to reduce the number of objectives.
• An even swap increases the value of an alternative in terms of one objective while decreasing its value in terms of another objective.
• Steps of even-swap: 1. Determine the change necessary to cancel out an objective;
2. Assess what change in another objective would compensate for the needed change; 3. Make an even-swap. 4. Cancel irrelevant objective
Let’s assume that Vincent can purchase retirement insurance for $150 per month and dental insurance for $75 per month:
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
Job A |
Job B |
Job C |
Monthly Salary ($) |
2000 |
2400-150=2250 |
1800-150-75=1575 |
Flexibility |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
Business Skills |
Computer |
People management, |
Operations, |
Development |
|
Computer |
Computer |
Annual Vacation Days |
14 |
12 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
Benefits |
Health |
Health |
Health |
|
Dental |
Dental |
Dental |
|
Retirement |
Retirement |
Retirement |
Enjoyment |
Great |
Good |
Good |

Sahid’s Problem
Final Consequences Table
|
|
Alternatives |
|
|
Job A |
Job B |
Job C |
Monthly Salary ($) |
2000 |
2250 |
1575 |
Flexibility |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
Business Skills |
Computer |
People management, |
Operations, |
Development |
|
Computer |
Computer |
Annual Vacation Days |
14 |
12 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
Enjoyment |
Great |
Good |
Good |
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp

Rolling Dice Expansion
Rolling Dice is a distributing company mainly dealing with kitchen appliances. Currently it is looking to expand its presence in several geographic areas. The franchise manager has identified six key towns where Rolling Dice does not operate. These towns are: Kerket, Bertstat, Blueport, Warsburg, Telyxt and Feldburg.
These locations o er varying degrees of growth in the areas of population and consumer spending. To evaluate these sites the franchise manager has collected a series of statistic descriptions.
(Advanced) IT in Business | © Sodenkamp |
10 |
|
