
ИДЗ 5 англ
.docxIndividual Task. LESSON 5. By
Answer the following questions:
-
What is the equivalent scheme for capacitor in steady-state condition?
-
What is the equivalent scheme for inductor in steady-state condition?
-
List the procedure for calculating transients in a first-order circuit.
-
What law was used in the video to find the current in the circuit for t=0-?
-
What transients are?
-
How to calculate the root of characteristic equation, time constant, and the total time of transients for the circuit.
-
How many roots do the equation describing the free component in a circuit with only one inductor or capacitor includes only one exponential function and characteristic equation has?
-
What does coefficient A_k mean?
-
What two components of a circuit to describing the transient regime do you know?
-
Where transients are usually developed?
Answers:
-
In steady-state condition capacitor changes to a break circuit.
-
In steady-state condition inductor changes to a short circuit.
-
The first stage is to analyze the circuit for t = 0 (steady-state condition). Then analyze the circuit for t = ∞. The next stage is to find Thevenin resistance from the terminals of the capacitor or inductor. The fourth stage is to find the time constant. Аfter all this, need to substitute your values into the final equation.
-
To find the current, the author of the video used the Ohm’s law.
-
A transient event is a short-lived burst of energy in a system caused by a sudden change of state, for example, opening / closing of a switch. It is a momentary event preceding the steady state during a sudden change of a circuit.
-
Root of characteristic equation (p) can be found if we write down an equation according to KVL and take derivatives of it from both sides of equation and we must substitute differential with any variable. Solution of the equation for this variable will give us root of characteristic equation.
Time
constant ( )
can be found using this formulas:
)
can be found using this formulas:
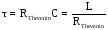 .
.
it can also be found from the relation:
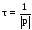 .
.
-
This equation has only one root of characteristic equation.
-
This is the integration constant, their number is equal to the order of the differential equation.
-
This forced component and free component.
-
An electrical transient occurs on a power system each time an abrupt circuit change occurs. This circuit change is usually the result of a normal switching operation, such as breaker opening or closing or simply turning a light switch on or off. Bus transfers witching operations along with abnormal conditions, such as inception and clearing of system faults, also cause transients.
Most power system transients are oscillatory in nature and are characterized by their transient period of oscillation. Despite the fact that these transient periods are usually very short when compared with the power frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz, they are extremely important because at such times, the circuit components and electrical equipment are subjected to the greatest stresses resulting from abnormal transient voltages and currents. While over voltages may result in flashovers or insulation breakdown, overcurrent may damage power equipment due to electromagnetic forces and excessive heat generation. Flashovers usually cause temporary power outages due to tripping of the protective devices, but insulation breakdown usually leads to permanent equipment damage. For this reason, a clear understanding of the circuit during transientperiods is essential in the formulation of steps required to minimize and prevent the damaging effects of switching transients
