
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgments
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •1.2 Forehead Augmentation
- •1.2.1 Discussion
- •1.3.1 Discussion
- •1.4 Rhinoplasty
- •1.4.1 Discussion
- •1.5 Lip Augmentation
- •1.5.1 Discussion
- •1.6 Chin and Jaw Augmentation
- •1.6.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Forehead Augmentation
- •Rhinoplasty
- •Lip Augmentation
- •Jaw Augmentation
- •2: Imaging the Postoperative Orbit
- •2.1 Eyelid Weights
- •2.1.1 Discussion
- •2.2 Palpebral Springs
- •2.2.1 Discussion
- •2.3.1 Discussion
- •2.4.1 Discussion
- •2.5.1 Discussion
- •2.6.1 Discussion
- •2.7 Strabismus Surgery
- •2.7.1 Discussion
- •2.8 Glaucoma Surgery
- •2.8.1 Discussion
- •2.9 Scleral Buckles
- •2.9.1 Discussion
- •2.10 Keratoprostheses
- •2.10.1 Discussion
- •2.11 Intraocular Lens Implants
- •2.11.1 Discussion
- •2.12 Surgical Aphakia
- •2.12.1 Discussion
- •2.13 Pneumatic Retinopexy
- •2.13.1 Discussion
- •2.14 Intraocular Silicone Oil
- •2.14.1 Discussion
- •2.15.1 Discussion
- •2.16 Orbital Tissue Expanders
- •2.16.1 Discussion
- •2.17 Orbital Exenteration
- •2.17.1 Discussion
- •2.18.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Eyelid Weights
- •Palpebral Spring
- •Frontalis Suspension Ptosis Repair
- •Strabismus Surgery
- •Glaucoma Surgery
- •Scleral Buckles
- •Keratoprostheses
- •Intraocular Lens Implants
- •Surgical Aphakia
- •Pneumatic Retinopexy
- •Intraocular Silicone Oil
- •Orbital Tissue Expanders
- •Orbital Exenteration
- •3.1.1 Discussion
- •3.2 Septoplasty
- •3.2.1 Discussion
- •3.3.1 Discussion
- •3.4.1 Discussion
- •3.5 Nasal Packing Material
- •3.5.1 Discussion
- •3.6 Rhinectomy
- •3.6.1 Discussion
- •3.7 Sinus Lift Procedure
- •3.7.1 Discussion
- •3.8 Caldwell-Luc Procedure
- •3.8.1 Discussion
- •3.9 External Ethmoidectomy
- •3.9.1 Discussion
- •3.10.1 Discussion
- •3.11 FESS Complications
- •3.11.1 Discussion
- •3.11.2 Discussion
- •3.11.3 Discussion
- •3.11.4 Discussion
- •3.11.5 Discussion
- •3.11.6 Discussion
- •3.11.7 Discussion
- •3.11.8 Discussion
- •3.11.9 Discussion
- •3.11.10 Discussion
- •3.11.11 Discussion
- •3.12 Osteoplastic Flap with Frontal Sinus Obliteration
- •3.12.1 Discussion
- •3.13 Frontal Sinus Cranialization
- •3.13.1 Discussion
- •3.14 Paranasal Sinus Stents
- •3.14.1 Discussion
- •3.15 Frontal Sinus Trephination
- •3.15.1 Discussion
- •3.16.1 Discussion
- •3.17.1 Discussion
- •3.18 Maxillary Swing
- •3.18.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Septoplasty
- •Nasal Septal Button Prosthesis
- •Nasal Packing Material
- •Rhinectomy
- •Sinus Lift
- •Caldwell-Luc Procedure
- •External Ethmoidectomy
- •Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- •FESS Complications
- •Osteoplastic Flap with Frontal Sinus Obliteration
- •Frontal Sinus Cranialization
- •Paranasal Sinus Stents
- •Frontal Sinus Trephination
- •Maxillectomy and Palatectomy
- •Maxillary Swing
- •4.1 Occipital Nerve Stimulator
- •4.1.1 Discussion
- •4.2 Tissue Expander
- •4.2.1 Discussion
- •4.3 Temporal Fossa Implants
- •4.3.1 Discussion
- •4.4.1 Discussion
- •4.5.1 Discussion
- •4.6.1 Discussion
- •4.7 Scalp Tumor Recurrence
- •4.7.1 Discussion
- •4.8 Burr Holes
- •4.8.1 Discussion
- •4.9 Craniotomy
- •4.9.1 Discussion
- •4.10 Cranioplasty
- •4.10.1 Discussion
- •4.11 Autocranioplasty
- •4.11.1 Discussion
- •4.12.1 Discussion
- •4.14.1 Discussion
- •4.15 Box Osteotomy
- •4.16.1 Discussion
- •4.17.1 Discussion
- •4.18.1 Discussion
- •4.19 Subdural Drainage Catheters
- •4.19.1 Discussion
- •4.20.1 Tension Pneumocephalus
- •4.20.5 Pseudomeningoceles
- •4.20.6 Pseudoaneurysm
- •4.20.7 Postoperative Infection
- •4.20.8 Textiloma
- •4.20.9 Sunken Skin Flap Syndrome
- •4.20.10 External Brain Herniation
- •4.20.11 Bone Flap Resorption
- •Further Reading
- •Occipital Nerve Stimulator
- •Tissue Expander
- •Temporal Fossa Implant
- •Scalp Tumor Recurrence
- •Box Osteotomy
- •Absorbable Hemostatic Agents
- •Duraplasty and Sealant Agents
- •Burr Holes
- •Craniotomy
- •Cranioplasty
- •Autocranioplasty
- •Cranial Vault Reconstruction for Craniosynostosis
- •Cranial Vault Encephalocele Repair
- •Subdural Drainage Catheters
- •Intracranial Pressure Monitor
- •Cranial Surgery Complications
- •5.1 Intraoperative MRI
- •5.1.1 Discussion
- •5.2.1 Stereotactic Biopsy
- •5.2.1.1 Discussion
- •5.2.2 Resection Cavities
- •5.2.2.1 Discussion
- •5.2.3 Ommaya Reservoirs
- •5.2.3.1 Discussion
- •5.2.4 Chemotherapy Wafers
- •5.2.4.1 Discussion
- •5.2.5 Brachytherapy Seeds
- •5.2.5.1 Discussion
- •5.2.6.1 Discussion
- •5.3.1 Prefrontal Lobotomy
- •5.3.1.1 Discussion
- •5.3.2 Pallidotomy
- •5.3.2.1 Discussion
- •5.3.3 Cingulotomy
- •5.3.3.1 Discussion
- •5.3.4.1 Discussion
- •5.3.4.2 Thalamotomy
- •5.3.5 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- •5.3.5.1 Discussion
- •5.3.6.1 Discussion
- •5.3.7.1 Discussion
- •5.3.8.1 Discussion
- •5.3.9.1 Discussion
- •5.3.10 Corticectomy
- •5.3.10.1 Discussion
- •5.3.11.1 Discussion
- •5.3.12.1 Discussion
- •5.3.13 Callosotomy
- •5.3.13.1 Discussion
- •5.3.14 Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
- •5.3.14.1 Discussion
- •5.3.15.1 Discussion
- •5.3.16 Hemispherectomy
- •5.3.16.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Intraoperative MRI
- •Brain Tumor Surgery
- •Stereotactic Biopsy
- •Resection Cavities
- •Postoperative Hemorrhagic Lesions
- •Ommaya Reservoirs
- •Chemotherapy Wafers
- •Brachytherapy Seeds
- •GliaSite Radiation Therapy System
- •Prefrontal Lobotomy
- •Pallidotomy
- •Cingulotomy
- •Thalamotomy
- •Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- •Epidural Motor Cortex Stimulator
- •Neural Interface System (BrainGate)
- •Corticectomy
- •Selective Disconnection
- •Callosotomy
- •Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
- •Hemispherectomy
- •6.1 Types of Procedures
- •6.1.1 External Ventricular Drainage
- •6.1.1.1 Discussion
- •6.1.2.1 Discussion
- •6.1.3 Atypical Ventricular Shunts
- •6.1.3.1 Discussion
- •6.1.4 Ventriculosubgaleal Shunts
- •6.1.4.1 Discussion
- •6.1.5.1 Discussion
- •6.1.6.1 Discussion
- •6.1.7 Subdural-Peritoneal Shunts
- •6.1.7.1 Discussion
- •6.1.8.1 Discussion
- •6.1.9.1 Discussion
- •6.1.10 Lumboperitoneal Shunts
- •6.1.10.1 Discussion
- •6.1.11 Third Ventriculocisternostomy
- •6.1.11.1 Discussion
- •6.1.12.1 Discussion
- •6.1.13 Aqueductoplasty
- •6.1.13.1 Discussion
- •6.1.14.1 Discussion
- •6.2.1.1 Discussion
- •6.2.2.1 Discussion
- •6.2.3 Intraventricular Fat Migration
- •6.2.3.1 Discussion
- •6.2.4.1 Discussion
- •6.2.5.1 Discussion
- •6.2.6 Slit Ventricle Syndrome
- •6.2.6.1 Discussion
- •6.2.7.1 Discussion
- •6.2.8 Shunt-Associated Infections
- •6.2.8.1 Discussion
- •6.2.9.1 Discussion
- •6.2.10.1 Discussion
- •6.2.11.1 Discussion
- •6.2.12 Peritoneal Pseudocysts
- •6.2.12.1 Discussion
- •6.2.13.1 Discussion
- •6.2.14 Tumor Seeding
- •6.2.14.1 Discussion
- •6.2.15 Shunt Catheter Calcification
- •6.2.15.1 Discussion
- •6.2.16.1 Discussion
- •6.2.17.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Types of Procedures
- •External Ventricular Drainage
- •Ventriculoperitoneal Shunts
- •Atypical Ventricular Shunts
- •Ventriculosubgaleal Shunts
- •Subdural-Peritoneal Shunts
- •Lumboperitoneal Shunt
- •Third Ventriculostomy
- •Aqueductoplasty
- •Fourth Ventricular Stenting
- •Complications
- •Intraventricular Fat Migration
- •Slit Ventricle Syndrome
- •Shunt-Associated Infections
- •Shunt Malposition and Migration
- •Pseudocysts
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Syndrome
- •Tumor Seeding
- •Shunt Catheter Calcifications
- •7.1.1 Discussion
- •7.2.1 Discussion
- •7.3.1 Discussion
- •7.4.1 Discussion
- •7.5.1 Discussion
- •7.6.1 Discussion
- •7.7 Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannomas
- •7.7.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Anterior Craniofacial Resection
- •Transsphenoidal Resection
- •Middle Cranial Fossa Reconstruction
- •Surgical Approaches for Vestibular Schwannoma Resection
- •8.1.1 Discussion
- •8.2 Auriculectomy
- •8.2.1 Discussion
- •8.3 Auricular Reconstruction
- •8.3.1 Discussion
- •8.4.1 Discussion
- •8.5 Atresiaplasty
- •8.5.1 Discussion
- •8.6.1 Discussion
- •8.7.1 Discussion
- •8.8 Ossicular Interposition
- •8.8.1 Discussion
- •8.9.1 Discussion
- •8.10.1 Discussion
- •8.11.1 Discussion
- •8.12 Atticotomy
- •8.12.1 Discussion
- •8.13.1 Discussion
- •8.14.1 Discussion
- •8.15.1 Discussion
- •8.16 Temporal Bone Resection
- •8.16.1 Discussion
- •8.17 Cochlear Implants
- •8.17.1 Discussion
- •8.18.1 Discussion
- •8.19.1 Discussion
- •8.20.1 Discussion
- •8.21.1 Discussion
- •8.22 Labyrinthectomy
- •8.22.1 Discussion
- •8.23 Vestibular Nerve Section
- •8.23.1 Discussion
- •8.24.1 Discussion
- •8.25.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •BAHA Device
- •Auriculectomy
- •Auricular Reconstruction
- •Canaloplasty and Meatoplasty
- •Atresiaplasty
- •Myringoplasty and Tympanoplasty
- •Incus Interposition
- •Ossicular Prosthesis Complications
- •Transcanal Atticotomy
- •Mastoidectomy Complications
- •Lateral Temporal Bone Resection
- •Cochlear Implants
- •Cochlear Implant Complications
- •Auditory Brainstem Stimulator
- •Repair of Perilymphatic Fistula
- •Labyrinthectomy
- •Vestibular Nerve Sectioning
- •Tube Drainage of Cholesterol Cysts
- •9.1 Vertical Ramus Osteotomy
- •9.1.1 Discussion
- •9.2 Sagittal Split Osteotomy
- •9.2.1 Discussion
- •9.3 Genioplasty
- •9.3.1 Discussion
- •9.4.1 Discussion
- •9.5 Mandibular Distraction
- •9.5.1 Discussion
- •9.6 LeFort I Osteotomy
- •9.6.1 Discussion
- •9.7 LeFort III Osteotomy
- •9.7.1 Discussion
- •9.8.1 Discussion
- •9.9 Mandibulotomy
- •9.9.1 Discussion
- •9.10 Enucleation
- •9.10.1 Discussion
- •9.11 Cyst Decompression
- •9.11.1 Discussion
- •9.12 Coronoidectomy
- •9.12.1 Discussion
- •9.13.1 Discussion
- •9.14.1 Discussion
- •9.15.1 Discussion
- •9.16.1 Discussion
- •9.17.1 Discussion
- •9.18.1 Discussion
- •9.19.1 Discussion
- •9.20.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Vertical Ramus Osteotomy
- •Sagittal Split Osteotomy
- •Genioplasty
- •Mandibular Angle Augmentation
- •Mandibular Distraction
- •Lefort I Surgery
- •Lefort III Surgery
- •Fixation of Mandible Fractures
- •Mandibulotomy
- •Enucleation
- •Cyst Decompression
- •Coronoidectomy
- •Eminectomy and Meniscal Plication
- •10: Imaging the Postoperative Neck
- •10.1 Reconstruction Flaps
- •10.1.1 Discussion
- •10.2 Neck Dissection
- •10.2.1 Discussion
- •10.3 Parotidectomy
- •10.3.1 Discussion
- •10.4.1 Discussion
- •10.5 Facial Reanimation
- •10.5.1 Discussion
- •10.6.1 Discussion
- •10.7.1 Discussion
- •10.8 Transoral Robotic Surgery
- •10.8.1 Discussion
- •10.9 Sistrunk Procedure
- •10.9.1 Discussion
- •10.10 Laryngectomy
- •10.10.1 Discussion
- •10.11.1 Discussion
- •10.12 Montgomery T-Tubes
- •10.12.1 Discussion
- •10.13 Salivary Bypass Stent
- •10.13.1 Discussion
- •10.14 Laryngeal Stents
- •10.14.1 Discussion
- •10.15.1 Discussion
- •10.16 Arytenoid Adduction
- •10.16.1 Discussion
- •10.17 Arytenoidectomy
- •10.17.1 Discussion
- •10.18 Laryngeal Cartilage Remodeling
- •10.18.1 Discussion
- •10.19 Tracheotomy
- •10.19.1 Discussion
- •10.20 Thyroidectomy
- •10.20.1 Discussion
- •10.21.1 Discussion
- •10.22 Brachytherapy
- •10.22.1 Discussion
- •10.23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- •10.23.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Reconstruction Flaps
- •Facial Reanimation
- •Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
- •Transoral Robotic Surgery
- •Neck Dissection
- •Parotidectomy
- •Salivary Duct Stenting
- •Laryngectomy
- •Montgomery T-Tubes
- •Salivary Bypass Stents
- •Laryngeal Stents
- •Arytenoid Adduction
- •Arytenoidectomy
- •Laryngeal Cartilage Remodeling
- •Tracheotomy
- •Thyroidectomy
- •Neck Exploration and Parathyroidectomy
- •Sistrunk Procedure
- •Brachytherapy
- •Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- •11: Imaging of Postoperative Spine
- •11.1 Overview
- •11.2 Spine Decompression
- •11.2.1.1 Discussion
- •11.2.2 Laminectomy
- •11.2.2.1 Discussion
- •11.2.3 Facetectomy
- •11.2.3.1 Discussion
- •11.2.4 Microdiscectomy
- •11.2.4.1 Discussion
- •11.2.5 Laminoplasty
- •11.2.5.1 Discussion
- •11.2.6 Vertebrectomy
- •11.2.6.1 Discussion
- •11.2.7 Cordectomy
- •11.2.7.1 Discussion
- •11.3.1 Halo and Traction Devices
- •11.3.1.1 Discussion
- •11.3.2 Bone Graft Materials
- •11.3.2.1 Discussion
- •11.3.3 Implantable Bone Stimulators
- •11.3.3.1 Discussion
- •11.3.4 Odontoid Screw Fixation
- •11.3.4.1 Discussion
- •11.3.5 Occipitocervical Fusion
- •11.3.5.1 Discussion
- •11.3.6 Anterior Cervical Fusion
- •11.3.6.1 Discussion
- •11.3.7.1 Discussion
- •11.3.8 Posterior Fusion
- •11.3.8.1 Discussion
- •11.3.9 Scoliosis Rods
- •11.3.9.1 Discussion
- •11.3.10 Vertebral Stapling
- •11.3.10.1 Discussion
- •11.3.11 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib (VEPTR)
- •11.3.11.1 Discussion
- •11.3.12 Interbody Fusion
- •11.3.12.1 Discussion
- •11.4.1 Total Disc Replacement
- •11.4.1.1 Discussion
- •11.4.2.1 Discussion
- •11.4.3.1 Discussion
- •11.4.4 Dynamic Facet Replacement
- •11.4.4.1 Discussion
- •11.4.5 Dynamic Rods
- •11.4.5.1 Discussion
- •11.5.1 Overview
- •11.5.2.1 Discussion
- •11.5.3.1 Discussion
- •11.5.4.1 Discussion
- •11.5.5 Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
- •11.5.5.1 Discussion
- •11.5.6.1 Discussion
- •11.5.7 Surgical Site Infections
- •11.5.7.1 Discussion
- •11.5.8 Postoperative Neuritis
- •11.5.8.1 Discussion
- •11.5.9 Arachnoiditis
- •11.5.9.1 Discussion
- •11.5.10.1 Discussion
- •11.5.11 Postoperative Synovial Cyst
- •11.5.11.1 Discussion
- •11.5.12 Residual/Recurrent Tumors
- •11.5.12.1 Discussion
- •11.5.13 Inclusion Cysts
- •11.5.13.1 Discussion
- •11.5.14.1 Discussion
- •11.5.15 Retained Surgical Tools
- •11.5.15.1 Discussion
- •11.5.16 Gossypiboma
- •11.5.16.1 Discussion
- •11.5.17.1 Discussion
- •11.5.18 Postoperative Deformity
- •11.5.18.1 Discussion
- •11.6.1 Discussion
- •11.7 Spinal Cord Stimulators
- •11.7.1 Discussion
- •11.8 Filum Terminale Sectioning
- •11.8.1 Discussion
- •11.9.1 Vertebral Augmentation
- •11.9.1.1 Discussion
- •11.9.2 Kiva Device
- •11.9.2.1 Discussion
- •11.9.3 Sacroplasty
- •11.9.3.1 Discussion
- •11.9.4.1 Discussion
- •11.9.5.1 Discussion
- •11.9.6.1 Discussion
- •Further Reading
- •Overview
- •Laminectomy
- •Facetectomy
- •Microdiscectomy
- •Laminoplasty
- •Vertebrectomy
- •Cordectomy
- •Bone Graft Materials
- •Implantable Bone Stimulators
- •Odontoid Screw Fixation
- •Anterior Cervical Fusion
- •Posterior Fusion
- •Occiptiocervical Fusion
- •Scoliosis Rods
- •Vertebral Stapling
- •Interbody Fusion
- •Nucleus Pulposus Replacement
- •Dynamic Facet Replacement
- •Dynamic Rods
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
- •Seromas and Hematomas
- •Postoperative Infection
- •Postoperative Neuritis
- •Arachnoiditis
- •Postoperative Synovial Cyst
- •Residual/Recurrent Tumors
- •Inclusion Cysts
- •Retained Surgical Tools
- •Gossypiboma
- •Postoperative Deformity
- •Intrathecal Spinal Infusion Pump
- •Spinal Cord Stimulators
- •Filum Terminale Sectioning
- •Kiva Device
- •Sacroplasty
- •Percutaneous Spine Fusion
- •CT-Guided Epidural Blood Patch
- •12.1 Vascular Surgery
- •12.1.1.1 Discussion
- •12.1.2.1 Discussion
- •12.1.3.1 Discussion
- •12.1.4.1 Discussion
- •12.1.6.1 Discussion
- •12.1.7 Carotid Endarterectomy
- •12.1.7.1 Discussion
- •12.1.8 Carotid Body Stimulation
- •12.1.8.1 Discussion
- •12.1.9 Adjustable Vascular Clamp
- •12.1.9.1 Discussion
- •12.1.10.1 Discussion
- •12.2 Endovascular Surgery
- •12.2.7 Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Intra-arterial Thrombolysis or Embolectomy
- •12.2.10 Endovascular Stent Reconstructive Treatment for Extracranial Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- •12.2.11 Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Active Extracranial Hemorrhage or Pseudoaneurysm
- •Further Reading
- •Vascular Surgery
- •Aneurysm and Hemostatic Ligation Clips
- •Intracranial Aneurysm Muscle Wrap
- •Vascular Malformation Surgery
- •Carotid Endarterectomy
- •Carotid Body Stimulation
- •Adjustable Vascular Clamp
- •Reconstruction of the Great Vessels
- •Endovascular Surgery
- •General Imaging Considerations Following Endovascular Cerebrovascular Procedures
- •Endovascular Treatment for Aneurysms
- •Endovascular Stent Reconstructive Treatment for Extracranial Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- •Endovascular Reconstructive Treatment for Active Extracranial Hemorrhage or Pseudoaneurysm
- •Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Venous Stenosis and Occlusion
- •Index
110 |
D.T. Ginat et al. |
|
|
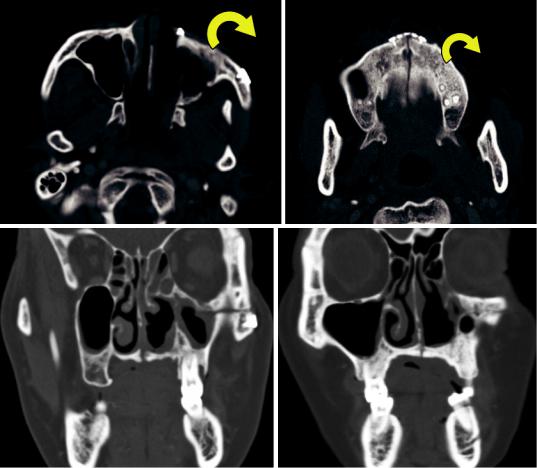
3.18\ Maxillary Swing
3.18.1\ Discussion
The maxillary swing approach is sometimes used to resect nasopharyngeal and pterygopalatine fossa tumors. The technique includes several
a
c
osteotomies through and around the maxillary sinus in order to free the structure and rotate it laterally and expose the underlying lesions (Fig. 3.58). The infraorbital nerve is often sacrificed during the procedure. Recurrent tumors can spread through the osteotomy sites (Figs. 3.58 and 3.59).
b
d
Fig. 3.58 Maxillary swing. The patient has a history of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which was resected via the maxillary swing approach. Axial (a, b) and coronal (c, d) CT images show multiple osteotomy sites, most of which are secured by microfixation plates, including the left
nasal process of the maxillary bone, the posterior maxillary wall, the zygomatic process, and the midline hard palate, in order to allow the maxillary sinus to rotate laterally (curved yellow arrows). The left infraorbital nerve was sacrificed by the osteotomy
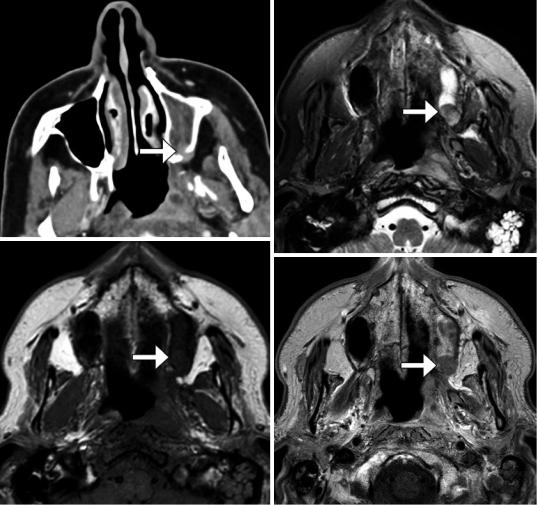
3 Imaging the Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity |
111 |
|
|
a |
b |
c
d
Fig. 3.59 Recurrent tumor. The patient has a history of nasopharyngeal carcinoma resected via a maxillary swing approach. Axial CT image (a) demonstrates a nodular lesion (arrows) that insinuates across the left posterior
maxillary wall osteotomy defect. The corresponding axial T2-weighted (b), T1-weighted (c), and post-contrast T1-weighted (d) MR images show that the intermediate T2 signal lesion enhances (arrows)
