
- •СОВРЕМЕННЫЕ ДОСТИЖЕНИЯ И СПОРНЫЕ ПРОБЛЕМЫ В НЕЙРОРЕАНИМАТОЛОГИИ
- •УЧЕНЫЕ, КОТОРЫЕ ВНЕСЛИ ОГРОМНЫЙ ВКЛАД В РАЗВИТИЕ НЕЙРОРЕАНИМАТОЛОГИИ
- •ДОСТИЖЕНИЯ СОВРЕМЕННОЙ РЕАНИМАТОЛОГИИ
- •СЛОЖНЫЕ И СПОРНЫЕ ПРОБЛЕМЫ В СОВРЕМЕННОЙ НЕЙРОРЕАНИМАТОЛОГИИ
- ••Гипоксия Ишемия Инфекция
- •Our Brain – indispensible but most delicate and vulnerable
- •Specifics of the Brain
- •Specifics of the Brain (2)
- •Specifics of the Brain (3)
- •Cerebral
- •II. Cortical Spreading Depression
- •IV. Excitotoxicity
- •V. Lipid Peroxydation
- •Results of „Dysventilation“
- •CO2-Reactivity of cerebral vessels: Effects of paCO2 [ETpCO2] on ICP
- •Culprit vs. Victim: Specific
- •Culprit vs. Victim: Specific
- •How does the Lung damage the
- •Brain atrophy and cognitive impairment of ARDS
- •Effects of varying levels of positive end-expiratory pressure on intracranial pressure and cerebral
- •ФУНДАМЕНТ
- •Основы клинической физиологии мозга
- •ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТЬ МОЗГА ЗАВИСИТ ОТ ТРЕХ ГЛАВНЫХ ФАКТОРОВ
- •КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЕ МОЗГА
- •Ауторегуляция мозгового кровотока
- •Соотношение мозгового кровотока и РаСО2
- •РаСО2 и перфузия мозга
- •Доставка кислорода в
- •УНИКАЛЬНЫЙ ФЕНОМЕН ЗДОРОВОГО МОЗГА - СОХРАННЕНИЕ АУТОРЕГУЛЯЦИИ СВF
- •Вазодилатационный каскад мозга
- •Вазоконстрикторный каскад мозга
- •Стадийность мозговых сдвигов
- •Стадийность мозговых нарушений
- •ВНУТРИЧЕРЕПНОЕ ДАВЛЕНИЕ (ICP)
- •ГИПОКСИЧЕСКО-ИШЕМИЧЕСКИЕ ПОВРЕЖДЕНИЯ МОЗГА
- •Энергетический обмен мозга
- •Базисные основы диагностики характера и степени неврологического дефицита
- •АЛГОРИТМ ДИАГНОСТИКИ КОМАТОЗНЫХ СОСТОЯНИЙ
- •Оценка мозговых рефлексов
- •Зрачковые пути
- •Зрачковые пути
- •Зрачковые реакции
- •Прямая и содружественная реакция зрачков на свет
- •Околовестибулярный
- •Глазодвигательные пути
- •Прогностическая значимость глазодвигательных рефлексов
- •Прогностическая значимость глазодвигательных рефлексов
- •Прогностическая значимость глазодвигательных рефлексов
- •Глазодвигательные
- •Оценка двигательной сферы Сохранность сенсорных и двигательных путей
- •Декортикационная
- •Децебрационная
- •Дислокационные
- •Транстенториальное
- •Дислокационный синдром
- •Транстенториальное вклинение Ранняя диэнцефальная стадия
- •Транстенториальное вклинение Поздняя диэнцефальная стадия
- •Транстенториальное вклинение Стадия среднего мозга-верхних отделов моста
- •Транстенториальное вклинение, стадия нижних отделов моста-верхних отделов прдолговатого мозга
- •Боковое вклинение мозга Ранняя стадия 111 нерва
- •Боковое вклинение мозга Поздняя стадия 111 нерва
- •Транскраниальная допплерография
- •Оценка кровотока с СМА
- •Оценка ауторегуляции мозгового кровотока по данным ТКДГ
- •Коэффициент реактивности на гипокапнию
- •Коэффициент овершута
- •Коэффициент овершута (КО)
- •• Мониторинг ОЦН
- •ТЯЖЕСТЬ КОМ АТОЗНЫХ СОСТОЯНИЙ (W.Jenett, J.Bozza-Maarrubini, Лондон, 1995)
- •ИНТЕНСИВНАЯ ТЕРАПИЯ ОЦН
- •СТАРТОВАЯ ТЕРАПИЯ КОМ НЕЯСНОЙ ЭТИОЛОГИИ
- •Постреанимационн ая болезнь
- •ПЕРВОЕ СООБЩЕНИЕ О РЕАНИМАЦИИ
- •ОСНОВОПОЛОЖНИК
- •ФАКТОРЫ, ВЛИЯЮЩИЕ НА ПРОГНОЗ
- •СИЭТТЛ и НЬЮ-ЙОРК
- •РЕКОМЕНДАЦИИ АМЕРИКАНСКОЙ АССОЦИАЦИИ КАРДИОЛОГОВ И МЕЖДУНАРОДНОГО СОГЛАСИТЕЛЬНОГО КОМИТЕТА ПО РЕАНИМАЦИИ
- •ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЙ КОМИТЕТ ПО АВИАЦИИ США
- •АЭРОПОРТЫ И КРУПНЫЕ КАЗИНО г. ЧИКАГО
- •ПЯТЬ КЛЮЧЕВЫХ АСПЕКТОВ УСПЕШНОЙ СЛР
- •РАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ СЛР
- •РАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ СЛР
- •РАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ СЛР
- •ИЗМЕНЕНИЯ 2005 года
- •ПЕРФУЗИОННОЕ ДАВЛЕНИЕ В КОРОНАРНЫХ АРТЕРИЯХ
- •ИЗМЕНЕНИЯ 2005 года
- •ДЛИТЕЛЬНОСТЬ ВДОХА
- •РАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ
- •РАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ
- •ИЗМЕНЕНИЯ 2005 года
- •СТАДИИ И ЭТАПЫ СЛР по П. Сафару [1997]
- •СТАДИИ И ЭТАПЫ СЛР по П. Сафару [1997]
- •СТАДИИ И ЭТАПЫ СЛР по П. Сафару [1997]
- •ВИДЫ ОСТАНОВКИ КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЯ
- •ТАХИКАРДИЯ
- •ФИБРИЛЛЯЦИЯ
- •БРАДИКАРДИЯ
- •СССУ
- •ПОЛНАЯ АВ-БЛОКАДА
- •ЭЛЕКТРОМЕХАНИЧЕСКАЯ
- •НЕЦЕЛЕСООБРАЗНОСТЬ СЛР (приказ №73 МЗ РФ)
- •НЕЦЕЛЕСООБРАЗНОСТЬ СЛР (приказ №73 МЗ РФ)
- •СТАДИИ ПОСТРЕАНИМАЦИОННОЙ БОЛЕЗНИ МОЗГА
- •Реперфузионный синдром мозга
- •СИНДРОМ
- •МощнымиМощнымиэкстрацеллюлярнымиэкстрацеллюлярнымиингибиторамиингибиторамиапоптозаапоптозаввнервнойнервной системе являются нейтрофилы (цитокины), такие как
- •СТАНДАРТНЫЙ ПРОТОКОЛ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ПРБМ
- •ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНЫЕ МЕТОДЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ПРБМ
- •ВИДЫ ОТЕКА (НАБУХАНИЯ) МОЗГА
- •Патогенез отека мозга
- •Транскапиллярный жидкостный
- •Механизмы развития отека- набухания мозга
- •КРИТИЧЕКСКИЙ ОТЕК МОЗГА -
- •Тактика инфузионной
- •Механизм действия маннитола
- •ДИНАМИКА ГИДРАТАЦИИ ТКАНИ МОЗГА ПОСЛЕ ОЧМТ
- •ВЛИЯНИЕ МАННИТОЛА НА ОТЕК- НАБУХАНИЕ МОЗГА ПРИ ОЧМТ
- •ПОКАЗАНИЯ ДЛЯ ПРИМЕНЕНИЯ МАННИТОЛА
- •Синдром
- •ЭДИНБУРГСКИЙ ПРОТОКОЛ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ВЧГ
- •Влияние гипервентиляции
- •ВАРИАНТЫ ИНТЕНСИВНОЙ ТЕРАПИИ ОЦН ПРИ РАЗЛИЧНЫХ СОСТОЯНИЯХ МОЗГОВОГО КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЯ
- •Инфузионная терапия при ЧМТ
- •Влияние крахмалсодержащих коллоидов на сдвиги гемостаза на различных коагуляционных каскадах (данные за последние
- •2. Безопасность
- •Влияние ГЭК на гемостаз
- •Острые нарушения мозгового кровообращения
- •Концепция Rosner
- •Triple – H ( Hypertension,
- •Критерии проведения triple-H терапии
- •ГЭК при triple-H терапии
- •Продолжение
- •Продолжение
- •Крахмалсодержащие коллоиды при остром ишемическом церебральном инсульте
- •Осложнения triple-H терапии
- •Протокол интенсивной терапии ОЧМТ
- •Продолжение 1
- •Продолжение 2
- •Продолжение 3 ( Выбор анестезии)
- •Интенсивная терапия ОЧМТ
- •Продолжение 1 ( Снижение ВЧД )
- •Продолжение 2
- •За и против интенсивной терапии при ОЧМТ
- •Шкала ком Глазго
- •Прогноз ПРБМ по
- •ПРОГНОЗ КОМАТОЗНЫХ СОСТОЯНИЙ
- •КРИТЕРИИ СМЕРТИ МОЗГА
- •«Трагедия нерешительности»
- •«Ты должен лечить и не должен
II. Cortical Spreading Depression
Intracortical spreading depression following local application of K+Cl-. The signal is spreading in a wave pattern at a speed of 3,5 mm/min over the whole Cortex (Vilagi, Klapka & Luhmann, 2001).

IV. Excitotoxicity
Energy depletion shuts down Glutamate-Portersystems and produces Lactacidosis.
Extracellular Glutamate concentration rises; Acidosis removes the Mg++-lock from the NMDA-Receptor (Ca-channel)
Intracellular Ca++-overload
„Misuse“ of Mitochondria
Further Energy depletion, Cell death

V. Lipid Peroxydation
•Oxygen free radicals [Reactive oxygen species (ROS)] attack the cell membrane and organelles
•Arachidonic acid is oxydized to eicosanoids plus further ROS
•Thromboxane disrupts the blood-brain- barrier, producing vasogenic oedema
•Excess Calcium binds to phosphate, limiting phosphorylation of ADP to ATP

Results of „Dysventilation“
•Hypoxia: Brain damage
•Hyperoxia: Convulsions
•Hypocapnia: Cerebral ischaemia
•Hypercapnia: Brain swelling (venous
congestion resulting in intracranial hypertension)
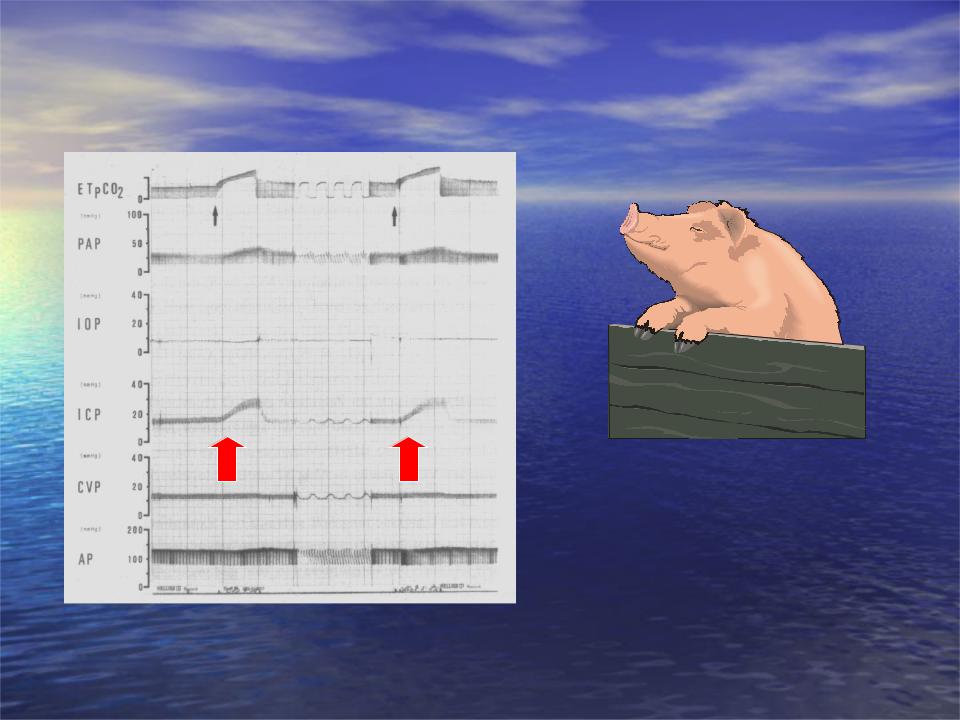
CO2-Reactivity of cerebral vessels: Effects of paCO2 [ETpCO2] on ICP
Removing / reintegrating soda lime absorbers of the breathing system.

Culprit vs. Victim: Specific
(1)
Brain Lung: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
TBI Neurogenic Pulmonary Oedema
•Frequency: 50%
•Mechanism: Catecholamine surge
TBI Acute Lung Injury (ALI)
• Frequency: 30%
J Trauma (2003) 55:106-11

Culprit vs. Victim: Specific
(2)
Brain Lung: Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
(SAH)
SAH Neurogenic Pulmonary Oedema
•Frequency: 25%
•Mechanism: Catecholamine surge
SAH ARDS
• Frequency: 20%
Intensive Care Med (2002) 28:1012-23

How does the Lung damage the
Brain ?
•Pulmonary liberation of Cytokines Brain
•Pneumonia Sepsis Septic Encephalopathy
•Pneumonia Fever Cerebral Hyperthermia Excitotoxicity
•ARDS Pulmonary compliance AWP ICP
•ARDS Permissive Hypercapnia ICP
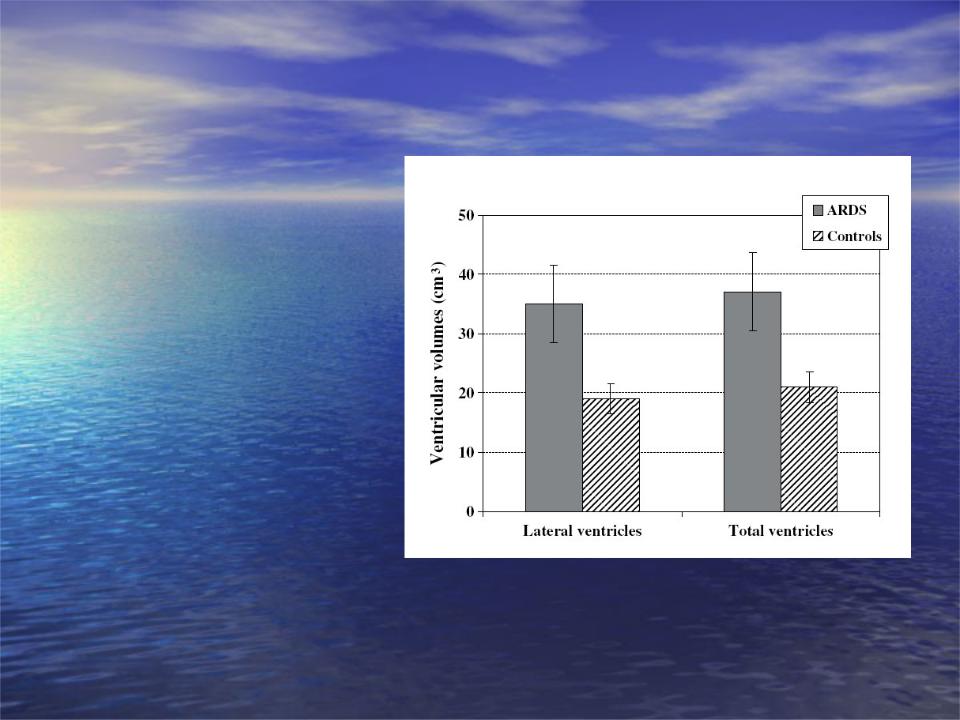
Brain atrophy and cognitive impairment of ARDS
Sharshar et al. 2007
Intensive Care Med 33 798-806
(Brain lesions in septic shock: a MRI study) Hopkins et al. 2006 Brain Injury 20 263-271
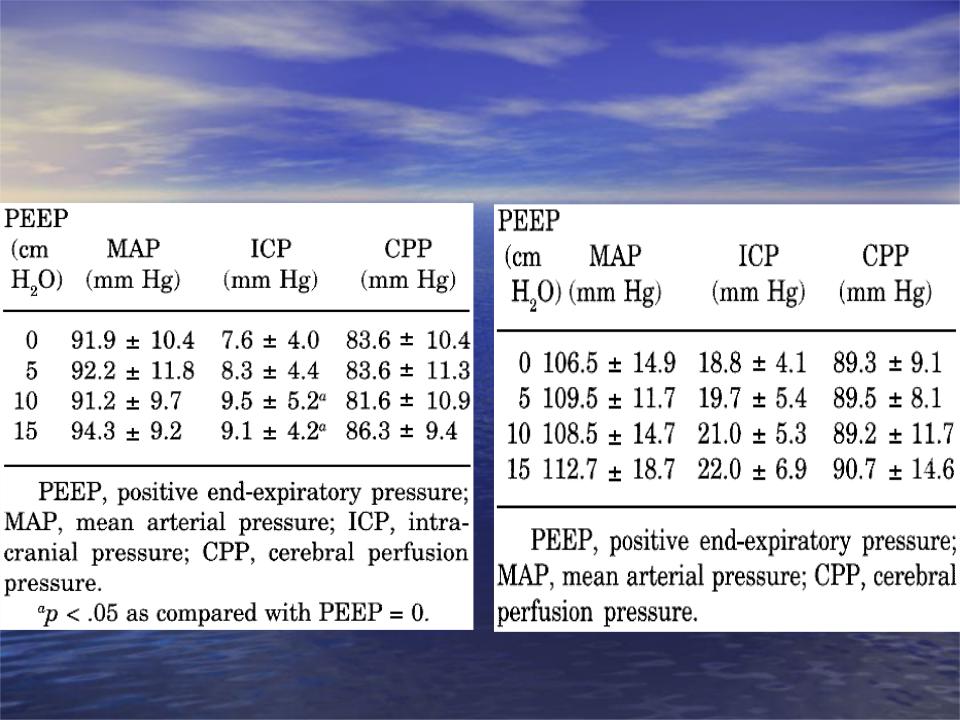
Effects of varying levels of positive end-expiratory pressure on intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure
McGuire et al. Crit Care Med 1997
