
- •Price and output determination under the perfect competition. Profit maximization under perfect competition. Firms behavior under perfect competition.
- •Basic characteristics of perfect competition.
- •T otal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •A verage and marginal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Last week was said!!!
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •Oligopoly.
- •The basic characteristics of an oligopoly:
- •Explicit collusions:
- •Rules of thumb models.
- •Kinked d-curve. Assumptions:
- •Maximax strategy (optimistic approach). Ex:
- •Cournot model / duopoly (2 firms in industry) 1830s.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Market equilibrium in different market structures.
- •Algebraic explanation of the Cournot model.
- •Stackelberg model (quantity leadership model).
- •Contestable markets model.
- •Oligopoly and public.
- •Monopolistic competition.
- •Major characteristics:
- •Lr equilibrium
- •Minuses”-”.
- •Derived dem. For ec. Resources.
- •Equilibrium of the firm on the resource market.
- •Sr equilibrium:
- •Lr equilibrium(all factors are variable):
- •Wage determination under Perfect competition.
- •Wage determination under imperfect competition.
- •The theory of distribution of income II. Capital(k) and Land.
- •Concepts of capital.
- •Measuring k.
- •How does the firm invest?
- •Sell bills/bonds to the households.
- •Sr rentals include:
- •Demand and Supply for k purchase.
- •Fairness and effectiveness
- •Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- •Distr. Of income and wealth characteristics:
- •Pareto efficiency and Edgeworth box.
- •Edgeworth box
- •Pareto efficiency allocation:
- •P rinciple possibility of losses compensation.Icks
- •There are positive and negative external effects, divided into 4 groups:
- •Taxes (Pigourian taxes)
- •Sell the right to pollute for example.
- •Public goods –
Oligopoly and public.
Minuses:
No allocative efficiency as Price>MC.
No productive efficiency.
Underproduction.
Overpricing.
Deadweight loss of welfare.
Pluses:
They are big =>they have resources to modernize production, R/D and innovate.
Competition is limited. Though encourages to innovate.
Monopolistic competition.
Major characteristics:
Very many firms in an industry
A firm can’t influence the price by means of its individual supply, it can influence price because:
Product is differentiated
The entry to the market is rather free
Dem. curve for the product is sloping down, but it’s rather flat, as there are many rivals on the market.
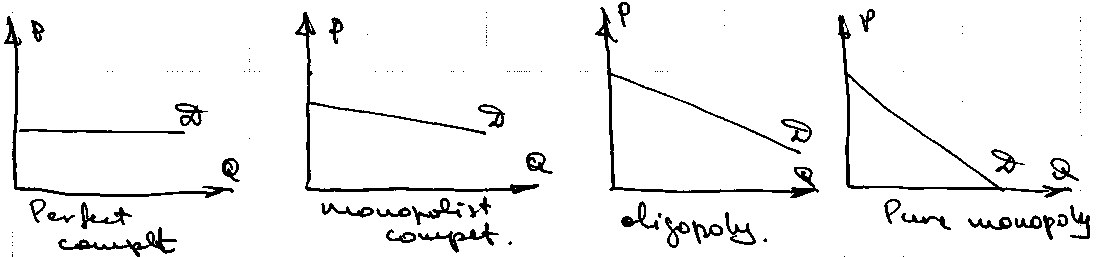 !!!
As the product is differentiated, it’s important to tell about it
to customer by means of advertising.
!!!
As the product is differentiated, it’s important to tell about it
to customer by means of advertising.
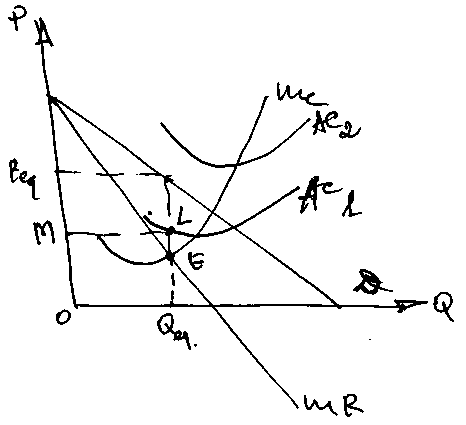
SR equilibrium(!!! like in pure monopoly).
MR = MC
P > MR and MC no allocative efficiency(! it takes place only under p. competition)
If AC1 AC(av.costs) = OM P >AC and TR > TC ec. profit
TR = OPKQ; TC = OMLQ; TП = PKLM.
If AC2 ec. losses.
Conclusion: In the SR firm can earn ec. profit, suffer losses or earn normal profit(AC = P)
Lr equilibrium
In the LR mon. competitive firm earns normal profit, because competition is pretty high and it eliminates LR ec. profit, loss and all the firms earn only economic profit.
Ec. profit in the SR in the LR new firms will enter the industry and the existing firms will expand the dem. curve for a single firm becomes flatter as competition grows, until it toches the AC –curve(at the point of LR equilibrium).
!!! This is not a min point of AC-curve, because the dem. curve doesn’t become horizontal.
P>LRACmin no productive efficiency.
Minuses”-”.
No allocative efficiency(P>MC)
No productive efficiency(P>LRACmin)
Underproduction and overpricing
Deadweight welfare loss and Waste of resources on advertising
Pluses”+”.
High degree of competition
Differentiation of the product helps to satisfy various human wants
Firms have incentives to innovate
There is practically no necessity in gov. regulation(as competition is close to perfect and all the negative outcomes are not great)
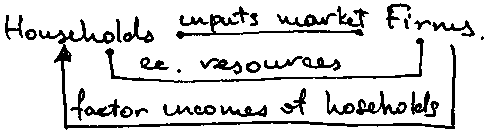
The theory of distribution of income(production and the dem. for ec. resources).
