
Lecture 3. Morphological structure of the english word. Productive types of word-formation
1. Morphemes. Types of morphemes. Free and bound morphemes. Allomorphs.
2. Morphemic analysis.
3. Affixation. Classification of affixes.
4. Word-composition. Classification of compound words.
5. Conversion. Types of conversion.
6. Shortening.
7. Clipping.
Basic notions of the lecture.
Morpheme is the minimum meaningful language unit, constituent part of words, not independent, not divided into smaller meaningful units.
Types of morphemes:
Root morpheme – lexical nucleus of the word. It has a very general and abstract lexical meaning, common to a set of semantically related words, constituting one word cluster. Besides lexical meaning, root morphemes possess other types of meaning, proper to morphemes, except the part-of-speech meaning, which is not found in roots.
Affixational morphemes, which are divided into inflexional affixes (inflexions) and derivational affixes (prefixes and suffixes). They are lexically dependent on the root they modify.
Inflexions carry only grammatical meaning and are relevant only for the formation of word forms.
Derivational affixes are relevant for building various types of words.
Lexicology is concerned only with derivational affixes.
Morphemes may be:
Free – coincide with word forms of independently functioning words.
Free morphemes can be found only among roots.
E.g.: boy, undesirable, screensaver
Bound – do not coincide with independently functioning words. These are prefixes and suffixes.
E.g.: -un, -able, -er, -dis, re-
Positional variant of morpheme occurring in the soecific environment and characterized by complementary distribution is called allomorph.
E.g.: allomorphs of prefix in-: il- (illegal, illogical)
im- (impossible, impolite)
ir- (irregular, irrational)
Between the inflexions allomorphs also occur (variants of pronunciation of plural ending –s, ending –ed).
According to number of morphemes words are classified into monomorphic and polymorphic.
Monomorphic (root) word consists of only one root morpheme (cat, book, knife).
Polymorphic words are divided into:
Derived words, which are composed of one root morpheme and one or several derivational morphemes (disagree, illness, impossibility, unlikely).
Compound words contain at least 2 root morphemes and number of derivational morphemes is insignificant. There can be root and derivational morphemes (lampshade, light-mindedness).
Morphemic analysis.
The morphological analysis aims at splitting the word into its constituent morphemes – the basic units at this level of analysis – and at determining their number and types.
The segmentation of words is carried out according to the method of Immediate and Ultimate Constituents (ICs and UCs).
It is based on binary principle. Each stage of the procedure involves 2 components the word immediately breaks into.
At each stage these 2 components are named Immediate Constituents (ICs). Each IC at the next stage of analysis is broken into smaller meaningful elements. The analysis is completed when we get constituents incapable of future division – morphemes. These are named UCs.
E .g.:
friendliness
.g.:
friendliness
f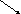
 riendly ness
riendly ness

friend ly
