
final_prep
.pdfB) only saving
C) only saving and the government budget surplus
D) only the government budget surplus and international borrowing |
|
140) Suppose Molly has an income of $35,000 annually and has inherited a savings account of |
140) _____ |
$20,000. Wyatt has a job that pays $35,000 annually, but has debts totaling $6,000. Which of the |
|
following is true? |
|
A)We can expect Wyatt and Molly to save the same proportion of their incomes this year.
B)We can expect Wyatt and Molly to have equal amounts of consumption this year.
C)We can expect Molly to save more than Wyatt this year.
D)We can expect Wyatt to save more than Molly this year.
141) Savings definitely increases if |
141) _____ |
A)future disposable income falls.
B)current disposable income falls.
C)current and future disposable income rise.
D)current and future disposable income fall.
142) |
Sarah and Diane are both billing clerks for the local trucking company earning $17,000 per year. |
142) |
_____ |
|
|
Sarah is attending college, plans to graduate in one year and earn $35,000 as an economist. |
|
|
|
|
Diane is not in college or undergoing any specialized training and will have the same job next |
|
|
|
|
year. According to economic theory, which of the two individuals would tend to have a higher |
|
|
|
|
current savings rate? |
|
|
|
|
A) Economic theory sheds no light on this question |
|
|
|
|
B) Both will have the same saving rate |
|
|
|
|
C) Diane |
|
|
|
|
D) Sarah |
|
|
|
143) |
The supply of loanable funds curve has loanable funds on one axis and |
143) |
_____ |
|
|
A) wealth on the other axis. |
B) the real interest rate on the other axis. |
|
|
|
C) disposable income on the other axis. |
D) consumption on the other axis. |
|
|
144) |
In the market for loanable funds, an increase in wealth shifts the ________ loanable funds curve |
144) |
_____ |
|
|
________. |
|
|
|
|
A) demand for; leftward |
B) supply of; rightward |
|
|
|
C) demand for; rightward |
D) supply of; leftward |
|
|
145) |
Which of the following will shift the supply of loanable funds curve leftward? |
145) |
_____ |
|
|
A) a decrease in the real interest rate |
B) a decrease in disposable income |
|
|
|
C) a decrease in expected future income |
D) a decrease in real wealth |
|
|
146) |
In the market for loanable funds, as the interest rate rises the ________ and the ________. |
146) |
_____ |
|
A)quantity of loanable funds supplied increases; quantity of loanable funds demanded decreases
B)quantity of loanable funds supplied decreases; quantity of loanable funds demanded increases
C)supply of loanable funds decreases; demand for loanable funds increases
D)supply of loanable funds increases; demand for loanable funds decreases
147) An increase in disposable income shifts the supply of loanable funds curve |
147) _____ |
A) rightward and increases the real interest rate. |
|
B) rightward and decreases the real interest rate. |
|
C)leftward and decreases the real interest rate.
D)leftward and increases the real interest rate.
148) A fall in the real interest rate |
148) _____ |
A)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
B)results in a movement along the demand for loanable funds curve.
C)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward.
D)has no effect on the demand for loanable funds curve
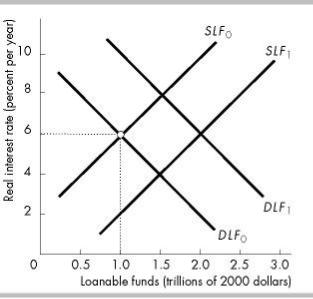
149) In the above figure, the initial supply of loanable funds curve is SLF0 and the initial demand for |
149) _____ |
loanable funds curve is DLF0. An increase in the expected profit rate would |
|
A)shift the supply of loanable funds curve rightward to a curve such as SLF1, and shift the demand for loanable funds curve rightward to a curve such as DLF1.
B)only shift the supply of loanable funds curve rightward to a curve such as SLF1.
C)have no effect on either the demand for loanable funds curve or the supply of loanable funds curve.
D)only shift the demand for loanable funds curve rightward to a curve such as DLF1.
150) As the ________ rises, the supply of loanable funds ________ other things remaining the same. |
150) _____ |
|
A) nominal interest rate; increases |
B) real interest rate; decreases |
|
C) real interest rate; increases |
D) inflation rate; increases |
|
In 2005, Armenia had a real GDP of approximately $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million. In 2006, real GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million.
151) |
In 2005, Armenia had a real GDP of $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million. In 2006, real |
151) |
_____ |
|||
|
GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million. What was Armenia's economic growth |
|
|
|||
|
rate from 2005 to 2006? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 3.8 percent |
B) 0.38 percent |
C) 8.3 percent |
D) 9.0 percent |
|
|
152) |
Which of the following is used to calculate the standard of living? |
|
152) |
_____ |
||
A)the one-third rule
B)real GDP/aggregate hours
C)((real GDP in the current year - real GDP in previous year)/real GDP in previous year) x
100
D) real GDP/population
153) The Rule of 70 is used to |
153) _____ |
A)calculate the standard of living
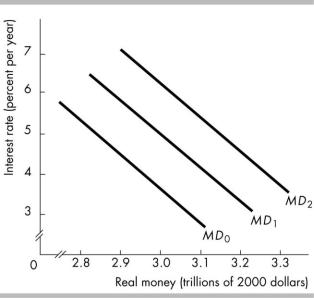
B)calculate the economy’s growth rate
C)estimate how long it will take the level of any variable to double
D)estimate how much of an economy’s growth rate is due to increases in capital per hour of labor
154) |
If real GDP per person is growing at 4 percent per year, approximately how many years will it |
154) |
_____ |
|||
|
take to double? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 17.5 |
B) 8 |
C) 4 |
D) 25 |
|
|
155) |
Real GDP per person in the country of Flip is $10,000, and the growth rate is 10 percent a year. |
155) |
_____ |
|||
|
Real GDP per person in the country of Flap is $20,000 and the growth rate is 5 percent a year. |
|
|
|||
|
When will real GDP per person be greater in Flip than in Flap? |
|
|
|
||
|
A) never |
B) in 2 years |
C) in 15 years |
D) in 10 years |
|
|
156) |
The best measure of long-term economic growth potential is changes in |
|
156) |
_____ |
||
|
A) nominal GDP. |
|
B) nominal GDP per person. |
|
|
|
|
C) real GDP. |
|
D) real GDP per person. |
|
|
|
157) |
Real GDP grows when |
|
|
|
157) |
_____ |
I.the quantities of the factors of production grow
II. persistent advances in technology make factors of production increasingly productive
III.human capital grows
A) Only I. |
B) Only II. |
C) I, II, and III. |
D) Both I and III. |
158) Labor productivity rises |
|
|
158) _____ |
A)in the absence of technological progress.
B)if the amount of capital per worker increases.
C)if the amount of capital per worker decreases.
D)if firms invest in hiring more workers rather than buying more capital.
159) |
What increased labor productivity during the Industrial Revolution? |
159) |
_____ |
|
A) increases in the amount of capital per worker |
|
|
|
B) a slowdown in technological advances |
|
|
|
C) increases in average hours per worker |
|
|
|
D) decreases in average hours per worker |
|
|
160) |
An increase in education and training |
160) |
_____ |
A)increases the employment-to-population ratio.
B)increases aggregate hours.
C)decreases real GDP growth.
D)increases labor productivity.
161) If real GDP is $800 million and aggregate labor hours are 20 million, labor productivity is |
161) _____ |
|||
________. |
|
|
|
|
A) $160 per hour |
B) $40 per hour |
C) $40 million |
D) $16,000 million |
|
162) |
The more education that workers have, the ________ is their human capital and ________ is their |
162) |
_____ |
|
|
productivity. |
|
|
|
|
A) smaller; smaller |
B) larger; smaller |
|
|
|
C) smaller; larger |
D) larger; higher |
|
|
163) |
Economic growth can begin when people ________, but in order to continue, there must be an |
163) |
_____ |
|
|
incentive system which encourages people to pursue activities ________. |
|
|
|
A)are educated; in which they have a comparative advantage
B)increase working hours; that use more capital
C)specialize and trade; such as investment in human capital
D)have comparative advantage; having absolute advantage
164) According to the law of diminishing returns, an additional unit of |
164) _____ |
A)labor produces less output than the previous unit.
B)labor produces more output than the previous unit.
C)capital produces more output than an additional unit of labor.
D)labor decreases output.
165) |
The law of diminishing returns states that if a given number of hours of labor use more capital |
165) |
_____ |
|
|
(with the same technology), the additional output that results from the additional capital |
|
|
|
|
________ as the amount of capital increases. |
|
|
|
|
A) gets larger |
B) stays the same |
|
|
|
C) gets smaller |
D) first gets smaller, then larger |
|
|
166) |
Labor productivity is measured by |
|
166) |
_____ |
|
A) capital per hour of labor. |
B) real GDP. |
|
|
|
C) real GDP per unit of capital. |
D) real GDP per hour of labor. |
|
|
167) |
According to MIT economist Robert Solow, in the absence of a change in technology, a 1 percent |
167) |
_____ |
|
|
increase in capital per hour of labor |
|
|
|
A)brings about a three percent increase in real GDP per hour of labor.
B)brings about a percentage increase in real GDP per hour of labor equal to the real interest rate.
C)has no significant effect on real GDP per hour of labor.
D)brings about a 1/3 (0.33 percent) percent increase in real GDP per hour of labor.
168) |
The one-third rule states that, holding technology constant, for every 1 percent increase in |
168) |
_____ |
|||
|
A) real wages, hours of work decrease by 0.33 percent. |
|
|
|
||
|
B) real wages, hours of work increase by 0.33 percent. |
|
|
|
||
|
C) hours worked, real GDP will increase by 0.33 percent. |
|
|
|
||
|
D) capital per hour of labor, real GDP per hour of labor will increase by 0.33 percent. |
|
|
|||
169) |
Assume that capital per hour of labor grows 4 percent and real GDP per hour of labor grows 3 |
169) |
_____ |
|||
|
percent. According to the one-third rule, what part of the 3 percent growth of real GDP per hour |
|
|
|||
|
of labor is attributable to the growth of capital? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 1 percentage point |
|
B) 2.67 percentage points |
|
|
|
|
C) 1.67 percentage point |
|
D) 1.33 percentage point |
|
|
|
170) |
In 2006, capital per hour of labor was $250 and real GDP per hour of labor was $50. In 2007, real |
170) |
_____ |
|||
|
GDP per hour of labor was $55. If there was no change in technology between 2006 and 2007, |
|
|
|||
|
then capital per hour of labor in 2007 was ________. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) $280 |
B) $325 |
C) $252 |
D) $275 |
|
|
171) The functions of money are |
171) _____ |
A)pricing, contracts, and means of payment.
B)medium of exchange, unit of account, and means of payment.
C)medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value.
D)medium of exchange and the ability to buy goods and services.
172) |
Which of the following is a primary function of money? |
172) |
_____ |
|
|
A) to serve as an encouragement to work |
B) to serve as a unit of account |
|
|
|
C) to raise funds for the government |
D) to reduce the burden of excessive |
|
|
|
|
imports |
|
|
173) |
Barter is |
|
173) |
_____ |
A)the exchange of goods and services directly for other goods and services.
B)another type of money.
C)printing too much money.
D)the exchange of goods and services for any type of money.
174) Liquidity is the |
174) _____ |
A)ease with which an asset can be converted into money.
B)same as the velocity of money.
C)inverse of the velocity of money.
D)speed with which the price of an asset changes as its intrinsic value changes.
175) |
If you use $500 of currency to purchase a saving deposit, |
175) |
_____ |
|
|
A) M1 decreases, but M2 is unchanged |
B) M1 and M2 both increase |
|
|
|
C) M1 decreases and M2 increases |
D) M1 is unchanged, but M2 increases |
|
|
176) |
Credit cards are NOT money because they |
|
176) |
_____ |
A)do not serve as a unit of account.
B)are ID cards that make borrowing easier.
C)are not issued by the government.
D)have a value in exchange but little intrinsic value.
177) Using a credit card can best be likened to |
177) _____ |
A)taking out a loan.
B)using any other form of money because you immediately get to take the goods home.
C)writing a check on your demand deposit account.
D)a barter exchange.
178) |
Which of the following is NOT a function of money? |
178) |
_____ |
|
A) unit of account |
B) store of value |
|
|
C) medium of exchange |
D) barter |
|
179) |
Money ________. |
179) |
_____ |
A)loses its value as it becomes older
B)is any commodity that is generally acceptable as a means of payment
C)is always composed of coins and paper
D)requires a double coincidence of wants
180) A new financial innovation results in people switching their funds from checking deposits to |
180) _____ |
savings accounts. The quantity of M1 ________ and the quantity of M2 ________. |
|
A) decreases; does not change |
B) decreases; decreases |
|
|
C) decreases; increases |
|
D) increases; decreases |
|
181) The reserve ratio is a bank's reserves as a fraction of its |
181) _____ |
||
A) total assets. |
B) total loans. |
C) total deposits. |
D) currency. |
182)Excess reserves are
A)actual reserves minus desired reserves.
C)liquidity funds minus actual reserves.
182) _____
B) required reserves minus actual reserves. D) desired reserves minus actual reserves.
183) A bank creates money by |
183) _____ |
A)purchasing currency from the Federal Reserve
B)buying bonds from the Federal Reserve
C)lending its excess reserves
D)printing more checks
184) |
You deposit $4,000 in currency in your checking account. The bank holds 20 percent of all |
184) |
_____ |
|
|
deposits as desired reserves. As a direct result of your deposit, your bank will create |
|
|
|
|
A) $3,200 of new money. |
B) $1,600 of new money. |
|
|
|
C) $800 of new money. |
D) $200 of new money. |
|
|
185) |
You withdraw $2,000 from your account. Your bank has a desired reserve ratio of 20 percent. |
185) |
_____ |
|
|
This transaction, by itself, will directly reduce |
|
|
|
|
A) the quantity of money by $1,600. |
B) deposits by $2,000. |
|
|
|
C) deposits by $1,600. |
D) the quantity of money by $2,000. |
|
|
186) |
When part of the quantity of money is held in currency, then |
186) |
_____ |
|
A)the money multiplier will increase in value.
B)the Fed will find it beneficial to increase the discount rate.
C)there is a higher level of excess reserves.
D)a currency drain occurs.
187) The money multiplier is the ratio of the change in the |
187) _____ |
A)currency drain to the change in the quantity of money.
B)monetary base to the change in the quantity of money
C)desired reserve ratio to the change in the monetary base
D)quantity of money to the change in the monetary base
188) The money multiplier is |
188) _____ |
A)the amount by which a change in the monetary base is multiplied to determine the change in the quantity of money.
B)the amount by which a change in the quantity of money is multiplied to determine the change in the monetary base.
C)equal to bank reserves divided by the change in the monetary base.
D)equal to bank reserves divided by the change the quantity of money.
189) |
________ in the desired reserve ratio will ________ the money multiplier. |
189) |
_____ |
|
|
A) A decrease; will have no effect on |
B) An increase; have no effect on |
|
|
|
C) A decrease; decrease |
D) An increase; decrease |
|
|
190) |
The change in the quantity of money divided by the change in the monetary base is called the |
190) |
_____ |
|
|
________ multiplier. |
|
|
|
|
A) deposit |
B) money |
|
|
|
C) monetary base |
D) monetary policy |
|
|
191) |
The nominal demand for money is |
|
191) |
_____ |
|
A) inversely related to GDP. |
B) inversely related to the price level. |
|
|
|
C) proportional to the price level. |
D) measured in constant dollars. |
|
|
192) |
When price levels rise, the quantity of nominal money demanded will ________ and the |
192) |
_____ |
|
|
quantity of real money demanded will ________. |
|
|
|
|
A) increase; increase |
B) decrease; increase |
|
|
|
C) increase; stay the same |
D) increase; decrease |
|
|
193) |
Which of the following is correct? The demand for money |
193) |
_____ |
|
|
A) increases as real GDP increases. |
B) depends on the quantity of money. |
|
|
|
C) increases when the interest rate |
D) decreases as the price level increases. |
|
|
|
increases. |
|
|
|
194) |
On a given day the quantity of money is ________ and the supply of money curve is ________. |
194) |
_____ |
|
|
A) fixed; horizontal |
B) fixed; vertical |
|
|
|
C) variable; vertical |
D) variable; horizontal |
|
|
195) |
In the above figure, suppose the economy is initially on the demand for money curve MD1. |
195) |
_____ |
|
What is the effect of a fall in the interest rate? |
|
|
|
A) The demand for money curve would shift rightward to MD2. |
|
|
|
B) There would be a movement upward along the demand for money curve MD1. |
|
|
|
C) The demand for money curve would shift leftward to MD0. |
|
|
|
D) There would be a movement downward along the demand for money curve MD1. |
|
|
196) |
In the above figure, suppose the economy is initially on the demand for money curve MD1. |
196) |
_____ |
|
What is the effect of a rise in the interest rate? |
|
|
|
A) The demand for money curve would shift rightward to MD2. |
|
|
B) There would be a movement upward along the demand for money curve MD1.
C)
The demand curve would shift leftward to MD0. for money
D) There would be a movement downward along the demand for money curve MD1.
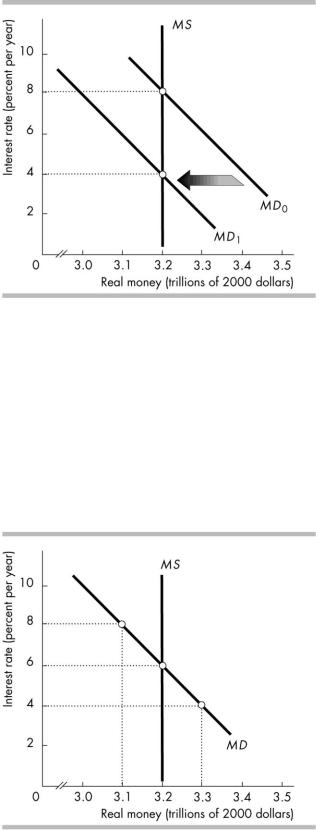
197)The figure above illustrates the effect of
A)a decrease in the monetary base.
C)a decrease in real GDP.
197) _____
B) an increase in the monetary base. D) an increase in real GDP.
198) Suppose that the interest rate is greater than the equilibrium interest rate. Which of the following 198) _____
occurs?
I.There is an excess quantity of money.
II.The quantity of money automatically increases.
III.The interest rate falls.
A) I |
B) I and II |
C) I, II and III |
D) I and III |
199) |
In the figure above, if the interest rate is 4 percent, there is a $0.1 trillion excess |
199) |
_____ |
|
A) quantity of money and the interest rate will rise. |
|
|
|
B) demand for money and the interest rate will fall. |
|
|
|
C) quantity of money and the interest rate will fall. |
|
|
|
D) demand for money and the interest rate will rise. |
|
|
200) |
In the figure above, if the interest rate is 6 percent, |
200) |
_____ |
A)there is a $0.1 trillion excess demand for money and the interest rate will rise.
B)there is a $0.1 trillion excess quantity of money and the interest rate will rise.
C)there is a $0.1 trillion excess quantity of money and the interest rate will fall.
D)the money market is in equilibrium and the interest rate will remain constant.
201) |
In the short run, which of the following actions lower the interest rate? |
201) |
_____ |
|
|
A) a decrease in bond prices |
B) an increase in the demand for money |
|
|
|
C) a decrease in the demand for money |
D) a decrease in the quantity of money |
|
|
202) |
The velocity of circulation is |
|
202) |
_____ |
A)the changes in the purchasing power of money over a given time period.
B)the average number of times a dollar of money is used in a year to buy goods and services in GDP.
C)constant.
D)the rate of change of the GDP deflator.
203) |
Which of the following equations represents the equation of exchange? |
203) |
_____ |
||
|
A) MV = PY |
B) M = VP/Y |
C) MY = PV |
D) PM = VY |
|
204) |
Which of the following is the equation of exchange? |
|
204) |
_____ |
|
|
A) MV = PY |
B) V = MY/P |
C) MY = PV |
D) M = VP/Y |
|
205) |
According to the quantity theory of money, |
|
205) |
_____ |
|
A)V and P are not affected by the quantity of money.
B)V and M are constant.
C)V and Y are not affected by the quantity of money.
D)V and M are not affected by changes in the price level.
206) |
The quantity theory of money asserts that an increase in the quantity of money |
206) |
_____ |
|
A) by n percent will lead to an increase in the price level by n + 1 percent. |
|
|
|
B) will lead to an equal percentage increase in real GDP. |
|
|
|
C) will decrease the price level by an offsetting amount. |
|
|
|
D) will lead to an equal percentage increase in the price level. |
|
|
207) |
According to the quantity theory of money, money growth and inflation are |
207) |
_____ |
A)positively correlated.
B)positively if the inflation rate is positive and negatively correlated if the inflation rate is negative.
C)independent, that is, not correlated.
D)negatively correlated.
208) According to the quantity theory of money, a 25 percent change in M, the quantity of money, |
208) _____ |
|
leads to a 25 percent change in |
|
|
A) R, the interest rate. |
B) Y, real GDP. |
|
C) V, the velocity of circulation. |
D) P, the price level. |
|
209) |
Suppose the money growth rate is 3 percent, velocity is constant, and real GDP is growing at 2 |
209) |
_____ |
|||
|
percent. What is the inflation rate? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) 1 percent |
B) 6 percent |
C) 5 percent |
D) 3 percent |
|
|
210) |
According to the quantity theory, in the long run, an increase in the growth rate of ________ |
210) |
_____ |
|||
|
leads to an increase in the ________ . |
|
|
|
|
|
A)real GDP; growth rate of velocity
B)the quantity of money; growth rate of real GDP
C)the quantity of money; inflation rate
D)real GDP; inflation rate
211) |
The quantity of money in an economy is $9 million, and the velocity of circulation is 3. Nominal |
211) |
_____ |
|||
|
GDP in this economy is ________. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A) $9 million |
B) $27 million |
C) $3 million |
D) $6 million |
|
|
212) |
In the macroeconomic long run, |
|
|
212) |
_____ |
|
A)GDP always is below potential GDP.
B)output always is above potential GDP.
C)there is full employment and real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
D)there is full employment with no unemployment.
213) In the macroeconomic short run, |
213) _____ |
A)actual real GDP always equals potential GDP.
B)the unemployment rate is zero.
C)the economy is always moving away from full employment.
D)actual real GDP may be less than or more than potential GDP.
214) The supply of real GDP is a function of |
214) _____ |
A)only the state of technology.
B)the quantities of labor, capital and the state of technology.
C)the total expenditures of consumers, investors and government.
D)the sum of wages, salaries, corporate profits, rents and interest.
215) |
Which of the following variables does NOT directly influence the supply of real GDP? |
215) |
_____ |
|
|
A) the quantity of capital |
B) the quantity of labor |
|
|
|
C) the state of technology |
D) the quantity demanded |
|
|
216) |
When talking about aggregate supply, it is necessary to |
216) |
_____ |
|
A)focus on the short run.
B)focus on the long run.
C)distinguish between long-run full employment and short-run full-employment.
D)distinguish between long-run aggregate supply and short-run aggregate supply.
217) If the economy is at the natural unemployment rate, |
217) _____ |
A)real GDP > potential GDP.
B)real GDP = potential GDP.
C)real GDP < potential GDP.
D)All of the above can occur when the economy is at the natural unemployment rate.
218) At potential GDP |
218) _____ |
A) unemployment is at its natural rate. |
|
