
Lecture bioorganic 3
.docLecture 3. Poly- and hetero-functional compounds, participating in life processes.
Majority of organic substances, taking part in metabolism processes, are compounds with 2 or more functional groups. Such compounds are classified as follows:
 1)
poly-functional, which contain the same functional groups for
example, etyleneglikol CH2OH-CH2OH,
hydrohynon HO- -OH, oxalate acid HOOC-COOH;
1)
poly-functional, which contain the same functional groups for
example, etyleneglikol CH2OH-CH2OH,
hydrohynon HO- -OH, oxalate acid HOOC-COOH;
 2)
hetero-functional, which contain different functional groups for
example, colamine CH2OH-CH2NH2,
π-aminobensoic acid H2N-
-COOH, pirogrape acid CH3-C(O)-COOH;
2)
hetero-functional, which contain different functional groups for
example, colamine CH2OH-CH2NH2,
π-aminobensoic acid H2N-
-COOH, pirogrape acid CH3-C(O)-COOH;
3) hetero-poly-functional for example, different monosaccharides, apple acid HOOC-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH.
3.1. Acid-base features. General rule is executed: the presence of OH, SH, COOH groups in molecule leads to increase of its acid features. besides, presence of additional electron acceptor group near acid centre leads to increase of acid features. thus, etyleneglikol CH2OH-CH2OH has stronger acid features as compared to etanole CH3-CH2OH.
3.2. Nucleophilic and electrophilic features. General rule is executed: presence of electron acceptor substitute (-I-effect) makes going of nucleophilic reaction easier and electrophilic reaction more difficult. Thus, in the presence of carboxylic group halogen atom for example, in α-halogen-carboxylic acids is substituted not only by hydroxylic group but also by amino group:
R -CH-COOH
+ 3NH3
R-CH-COONH4
+ NH4C1
-CH-COOH
+ 3NH3
R-CH-COONH4
+ NH4C1
Cl NH2
This reaction goes according to SN mechanism, giving salts of α-acids.
3.3. Reaction of cyclation refer to specific reactions of hetero-functional compounds and could go both inner molecule and inter molecule according to the distance between functional groups.
Inner molecule cyclation. There is a general law: reactions are characteristic to hetero-functional compounds with γ- and δ-position of functional groups. Nucleophilic and electrophilic centres are inside one molecule and appear closer in space due to molecule existence in coagulated or claw conformation. As a result of inner molecule reaction of cyclation there could appear cyclic half-acetal from aldehyde alcohols on AN mechanism, cyclic ethers – laktones from hydroxylic acids on SN mechanism, cyclic amides – laktames from amino acids on SN mechanism:

I nter
molecule cyclation. There is a general rule: reactions characterize
α-substituted acids, they go on the mechanism of inter molecule
elimination and are accompanied by formation of stable six member
cycles – cyclic diethers – laktydes from α- hydroxylic acids:
nter
molecule cyclation. There is a general rule: reactions characterize
α-substituted acids, they go on the mechanism of inter molecule
elimination and are accompanied by formation of stable six member
cycles – cyclic diethers – laktydes from α- hydroxylic acids:
3.4. Reactions of complex formation. There is a general rule: poly- and hetero-functional compounds with α-position of functional group are bidenant or poly-denant ligands at reaction with ions of transition metals with formation inner complex compound – helates:

3.5. Classes of hetero-functional compounds.
Many atom alcohols.
According to number of hydroxylic groups alcohols are divided into single atom, double atom and other alcohols. Double atom alcohols (2 – OH-groups) have the name diole or glicol. Three atom alcohols are called trioles or glycerines, alcohols with more number of hydroxylic groups are called polyoles.
Many atom alcohols have more acidity as compared to single atom alcohols, what is the consequence of –I-effect of one hydroxylic group in relation to another. Examples of many atom alcohols of highest degree of atom are pentites and hecsites, five and six member alcohols with open chain. Accumulation of hydroxylic groups in a molecule leads to sweet taste. Representatives of these alcohols are xylyt and sorbyt are sugar substitutes for people with diabetes.
Two atom phenols are pirocatehin, resorcin, hydrohynon, they are included in many natural compounds. The first is used in many biologically active substances, used as medicines. The second is used to cure skin illnesses. The third is used in photo activities.
Dicarboxylic and non-saturated carboxylic acids.
Carboxylic acids containing one carboxylic group are called one-base, 2 0 two-base and so on.
Oxalate acid HOOC-COOH is the simplest two-base acid.
Amino alcohols contain both amino- and hydroxylic groups. One carbon atom does not hold them strongly, so there is splitting of ammonia with formation of carbonile compound or water with amine. Holine is a structural element of complex lipides and is important as vitamin resembling substance and regulates fat exchange in organism.
Cateholamines are representatives of bio-gene amines formed in the organism as result of metabolism processes. They play the role of neuro-mediators.
Hydroxylic and amino acids.
Hydroxylic acids have both hydroxylic and carboxylic groups, amino acids – carboxylic and amino group.
According to position of hydroxylic or amino-group in relation to carboxylic we divide α-, β-, γ- and so on hydroxylic or amino acids. The examples of such acids are glicolic acid, milk acid.
Oxo acids.
Oxo acids are compounds, containing both carboxylic and aldehyde (or ketone) groups. Examples of such acids are glioxylic acid, pirogrape acid, aceto acetic acid.
3.6. Hetero-functional derivatives of bensole as medicines.
Last decades are characterized by appearance of many new medicines, the nucleus of this rank is formed by bensole and its derivatives.
Bensole itself could be the cause of sharp and chronic poisoning. It produces allergic reaction on skin and its steams in high concentration have toxic features. bensole many functional derivatives in most cases are also toxic. Among mono functional derivatives bensoic acid is used in medicine as expectoration means in the form of natrium salt.
P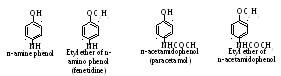 aracetamol
is N-acetil derivative of π-amino phenol. Fenacetin is received at
acetilizing of etyl ether of π-amino phenol, which is called
fenetidine:
aracetamol
is N-acetil derivative of π-amino phenol. Fenacetin is received at
acetilizing of etyl ether of π-amino phenol, which is called
fenetidine:
E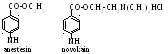 thers
of aromatic amino acids have general feature. It is an ability to
produce local anaesthesis, that is, the loss of sensibility. Medicine
uses anestesin (etyl ether) and novokain (β-dietylaminoetyl ether):
thers
of aromatic amino acids have general feature. It is an ability to
produce local anaesthesis, that is, the loss of sensibility. Medicine
uses anestesin (etyl ether) and novokain (β-dietylaminoetyl ether):
