
uchebnik_dlya_1_semestra
.pdf2.Read the text again. Make a short list of recommendations, using the titles of main parts of the text. Prioritize them according to their importance. For ex. Read more. Educate yourself. Study languages.etc.
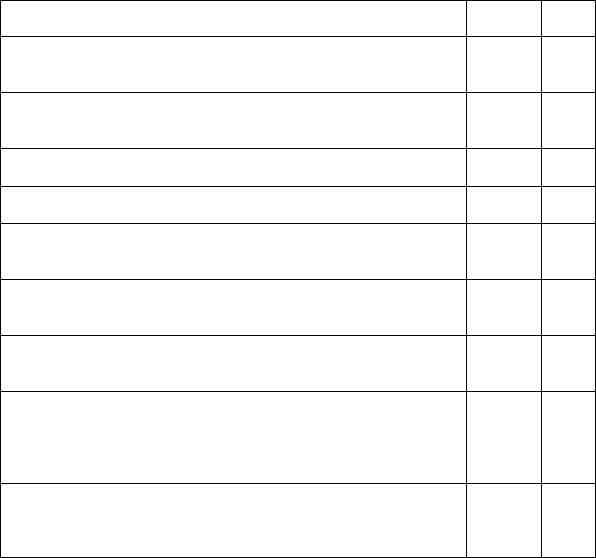
Fill in the following table. Take expressions from the text and add some of your own.
Read |
Write |
|
Watch |
|
Broaden |
Participate in |
Learn |
a |
Get |
hob- |
||||||||||
more |
|
|
films, TV, |
your |
|
|
Internet |
cul- |
new |
|
lan- |
bies |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
Videos |
|
musical |
|
ture. |
|
|
|
guage |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
horizons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Read |
Write |
|
Watch films |
A |
person |
The |
digital |
Travelling |
Study art |
|||||||||||
classical |
poetry |
regularly. |
of |
culture |
age |
is |
very |
introduces |
|
|
||||||||||
books |
or short |
|
|
|
|
knows |
|
important and |
you |
to the |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
stories |
|
|
|
|
how |
|
to |
a huge miles- |
many |
dif- |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
enjoy |
|
tone |
for |
|
so- |
ferences |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
even |
the |
ciety |
|
|
and |
simi- |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
niche mu- |
|
|
|
|
larities |
be- |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sic genres |
|
|
|
|
tween |
cul- |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tures, |
and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
opens |
up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
your mind |
|
|
||
Be |
first- |
Try |
to |
There |
|
are |
Enjoy |
|
You ought to |
The |
|
only |
Go in for |
|||||||
time |
|
write |
|
many |
films, |
songs |
|
follow all lat- |
way to dis- |
sports |
||||||||||
reader |
books |
|
and |
|
you |
with |
non- |
est |
achieve- |
cover |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
or plays |
may |
be |
un- |
cliché lyr- |
ments. |
|
|
another |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
sure |
|
as |
to |
ics, |
it |
is |
|
|
|
|
culture |
is |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
which |
|
|
also |
im- |
|
|
|
|
to go |
and |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
watch. |
|
portant |
|
|
|
|
|
see |
|
for |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
You |
are |
to |
that one is |
|
|
|
|
ourselves. |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
chose |
prop- |
able |
|
to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
erly! |
|
|
|
enjoy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
music |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
without |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lyrics |
at |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
all. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chose a |
Create |
Word-of- |
Just listen |
Set |
your |
|
ho- |
The |
|
best |
Visit |
|
||||||||
genre you |
your |
|
mouth is the |
to |
|
some |
mepage |
|
to |
way |
|
to |
places |
|||||||
are |
inter- |
own |
|
best |
way to |
famous |
|
Wikipedia |
|
study |
lan- |
where |
||||||||
ested in.. |
style |
of |
watch |
films |
musical |
|
and |
read |
an |
guage is by |
you |
can |
||||||||
|
|
writing |
of |
today's |
pieces. |
|
article |
each |
immersiom |
receive |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
culture. |
|
|
|
|
|
day |
about |
|
|
|
an educa- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
something |
|
|
|
|
tion |
in a |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
which seems |
|
|
|
fun way. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"cultured" |
to |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
you |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What main part or activity is missed? Why it is so important to educate yourself? What do you do to learn more? Make one more column about education and development. Add three items from the text and make up a list of yours.
3. Scan the text and pick up the key words that can help you to express its general idea. Give the summary.
Scan the text and pick up the key words that can help you to express its general idea. Give the summary.

4. Find out in the text compound adjectives and make your own sentences with them.
Grammar Practice
Modal verbs. Modal verbs are used to express ideas like ability, possibility, certainty etc.
The same ideas can be also expressed in other words such as: be able to, be obliged to, it’s possible that, it’s unnecessary to. Modal verbs can refer to ability: can/be able to, inability: can’t/unable to/not be able to. Modal verbs can refer to possibility and certainty: may/might/could. Modal verbs can be used when giving or refusing permission: can/may, can’t/mustn’t. Modal verbs also can refer to obligation or responsibility: must/have to/have got to/ought to.
1.Use the appropriate modal verb according to information from the text in the sentences below.
1)You … want to look up books in other genres which may catch your fancy. (may/ought)
2)You … take full advantage of this and learn all those things that you never understood before.
3)(should/can)
4)If you read a great article about Mozart or other composer, take the article to a store where you buy CDs and ask the counter attendant to direct you to some Mozart CDs that you might like. (can/must)
5)A person of culture … be ignorant of where countries or famous landmarks are.( should not/can not)
6)You …write poetry or short stories or even books and plays. (must/can)
7)You … take full advantage of this and learn all those things that you never understood before.
8)(should/to be to)
9)You …aim to be reasonably educated in these topics: world history,geography,basic sciences, psychology, economics. (can/should).
10)Famous singers have better songs on their albums which they left out of mainstream because they wouldn't be popular with the main market.(should/ may)
2.Make up your 10 sentences using different modal verbs describing what should/ought to/must a person learn and know to be a man of culture in modern society.
Activity
Discuss the following
What kind of person is a cultured one?
What books should be read to develop personality culturally?
What basic sciences should educated and cultured person be aware of?
What kind of music do you like? Do you like classical music?
Writing
1.Write a small essay on the following topic ―How to survive in foreign culture? Recommendation and advice‖.
Discussion
Pair work. Discuss the issues raised in the questions below.
1.What does living interesting ―cultural life‖ mean to you?
2.What are the aspects of the "cultural life" for you? In your opinion, what things should a person possess to say that he lives a life of a ―cultural ―man?

3.Would you include both material and spiritual things into the concept of "cultural life"? Explain why ―yes‖ or ―no‖.
4.Can you think of somebody to model your life on?
5.Do you think that you are a representative of Russian cultural society? Explain why ―yes‖ or ―no‖.
6.What is to be ―cultural‖, to be ―uncultured‖ from Russian point of view?
7.Is language a part of national culture? What is Russian language for you?
8.What’s your attitude towards knowledge of English language in Russian ―cultural‖ socie-
ty?
9.How many languages should a man of culture speak? Understand? Learn?
Project Work“Cultural Banner”.
Work together to create a ―cultural banner‖ expressing values, traditions, activities, and places important in their families and friends.
Vocabulary: Culture
Materials: Crayons, markers, and construction paper Create a Culture Web
Step 1. 1. Write the word culture in the center of a piece of chart paper and circle it.
2.Brainstorm associations with the word, record the words and phrases that come up on the chart paper, and connect them to culture, creating a web.
3.Discuss the web and agree on a definition along these lines: culture is the values, beliefs, and traditions shared by a group of people.
Step 2. Introduce Cultural Banners
1.Take paper and markers or crayons.
2.Write your name on the banner and any symbols (words or pictures) that show values, traditions, activities, and places that are important for their family. Use words or drawings to represent holidays, foods, sports, flags and so on.
3.After you have created the banners, pass the banners to your neighbors and keep doing so until everyone has had a chance to see every banner. Share your banners with each other.
Step 3. Discussion
How was this activity for you? What did you learn from doing it?
What are some of the cultures represented in the group?
Module 5
Unit 1. What is Xenophobia?
Lead in
Do you know any scientific definition of the ―unreasonable fear of foreigners or strangers‖? Skim the following text about xenophobia.
What is your personal attitude towards this phenomenon?
Can you give any examples you have ever heard, seen, experienced?
Reading and vocabulary
Read the text for general understanding .
Pay attention to the words in bold?
What is Xenophobia?

Xenophobia refers to the fear and/or hatred towards foreigners or people with different nationalities, culture, ethnicity, or background. Many people also use the term ―xenophobia‖ and casually inter-change it with ―racism‖ although there is quite a big difference between the two terms. Racism may almost always mean some form of anger or hatred towards people of different nationalities, while xenophobia may or may not involve hatred. Sometimes, xenophobia may just manifest itself as a feeling of fear or unease and anxiety towards ―foreign‖ or ―strange‖ people.
The fear involved in xenophobia may come from different aspects. Some people experience ill-feelings toward other cultures and nationalities because of a fear in losing one’s identity. Some also are extremely suspicious of other people’s activities and personalities that they resort to either “withdrawal” from the unpleasant situation or ―aggression‖ towards the foreign people involved. Others have this extremist type of feeling that his/her culture or background is superior over the others with accompanying prejudice to other groups of people as inferior.
To further distance the word ―xenophobia‖ from ―racism‖, many experts point out that the fear involved in xenophobia is irrational. This means that people who have this condition do not actually have control over their emotions and prejudices on people and situations. Unlike in racism, where much of the thoughts and actions involved are pre-determined, purposeful, and done at a person’s own free will. Another point is that xenophobia does not only involve feelings of fears towards foreigners or people with different nationalities. Fear may also be experienced with people who seem to be ―foreign‖ or who are labeled as strangers. And since these feelings are uncontrollable, xenophobic have a
chance to get better through behavioral and psychotherapies.
2. Match the words with their definitions.
1.Xenophobia |
a)the belief that men are superior to women; |
|
|
|
|
2.Racism |
b)typical of a particular cultural group |
|
|
|
|
3.Prejudice |
c) the group of a people or a race from which one is descended |
|
|
|
|
4.Race |
d)unfair treatment of people, especially woman because of |
|
|
|
their sex |
5. |
Ethnic |
e) any of the group into which humans can be divided according |
|
|
to their physical characteristics |
6. |
Ancestry |
f)a good opinion of one’s own character |
|
|
|
7.Self-esteem |
g) the deliberate killing of a nation or race of people |
|
|
|
|
8. |
Male chauvinism |
h)dislike or distrust of a person |
|
|
|
9.Sexism |
i) the belief that some races are superior to others |
|
|
|
|
10. Genocide |
j) deep-rooted antipathy towards foreigners |
|
|
|
|
2.The word Xenophobia comes from the Greek words ξένος (xenos), meaning "stranger," "foreigner" and φβος (phobos), meaning “fear”. There are a lot of words possessing the stem meaning “fear”. Find the meaning of the following words, using on-line dictionary:
-acrophobia is a fear of…..
-aerophobia is a fear of….
-agoraphobia is a fear of…
-Anglophobia is a fear of…
-claustrophobia is a fear of…
-homophobia is a fear of…
-hydrophobia is a fear of…
-negrophobia is a fear of…
-photophobia is fear of…
Read and discuss
1. Read and translate the text about forms of Xenophobia. Try to give your own definition to the word. Have ever experienced xenophobia yourself? Anywhere for anyone? Do agree that Xenophobia can also be directed simply to anyone outside a culture, not necessarily one particular race or people? How do you think Xenophobia may be expressed? Skim the text about two main forms of Xenophobia and say what is the main difference of these two forms?
Two forms of Xenophobia
The first is a population group present within a society that is not considered part of that society. Often they are recent immigrants, but xenophobia may be directed against a group which has been present for centuries, or became part of this society through conquest and territorial expansion. This form of xenophobia can elicit or facilitate hostile and violent reactions, such as mass expulsion of immigrants, pogroms or in other cases, genocide. The second form of xenophobia is primarily cultural, and the objects of the phobia are cultural elements which are considered alien.
Chauvinism, in its original and primary meaning, is an exaggerated, bellicose patriotism and a belief in national superiority and glory. A contemporary use of the term in English is in the phrase male chauvinism. Because "chauvinism" is most often heard in this context, it is often mistakenly believed to refer exclusively to "male chauvinism" such as anti-feminism and sexism.
Chauvinism as nationalism
Chauvinism is an almost natural product of the national concept in so far as it springs directly from the old idea of the "national mission." ... A nation's mission might be interpreted precisely as bringing its light to other, less fortunate peoples that, for whatever reason, have miraculously been left by history without a national mission. As long as this concept did not develop into the ideology of chauvinism and remained in the rather vague realm of national or even nationalistic pride, it frequently resulted in a high sense of responsibility for the welfare of backward people.
1.3Chose the most appropriate word for the sentences below:
A.Xenophobia comes from the Greek word meaning..
a)strength and health; b) stranger and fear; c) faith and belief.
B.Xenophobia can be exhibited in the form of culture where culture is….
a)a part of national life; b) real and routine quality; c) unreal, stereotyped, exotic quality.
C.Chauvinism is an almost natural product of the concept of the idea of
a)―national mission‖; b) national idea; c) national identity.
D.Male chauvinism is a term used to describe …
a)the belief that women are superior to men; b) the belief that men are superior to women; c) the belief that white men are superior to all men on Earth.
E.Female chauvinism is a term used to describe …

a) attitude that women are superior to men; b) attitude that white women are superior to all men; c) attitude that men are superior to women.
b)are superior to all men; c) attitude that men are superior to women.
2.Using the dictionary and the Internet find the definition for discrimination. Are there any general or specific forms? What are the specific forms of discrimination? What is your personal attitude towards different forms of it? Have ever been a victim of discrimination? Are there any ways to fight against it?
3.Prove your feelings writing six sentences expressing your attitude towards: Xenophobia, Racisms, Discrimination, Genocide, Chauvinism, Prejudice
1)_________________________________________________________
2)_________________________________________________________
3)_________________________________________________________
4)._________________________________________________________
5)_________________________________________________________
6)_________________________________________________________
4. . Define whether the following sentences are true or false. Mark each statement as T(True) or F (or False). If false, make corrections.
T F
1)Xenophobia refers to the fear and/or hatred towards foreigners or people with different nationalities, culture, ethnicity, or background.
2)Xenophobia always involve hatred.
3)Racism always means some form of anger or hatred towards people of different nationalities
4)Xenophobia may manifest itself as a feeling of fear or unease and anxiety towards ―foreign‖ or ―strange‖ people.
5)The fear involved in xenophobia may come from only one aspect.
6)Some people experience ill-feelings toward other cultures and nationalities because of a fear in losing their personal dignity.
7)Most of the people also are extremely suspicious of other people’s activities and personalities that they resort to either ―withdrawal‖ from the unpleasant situation or ―aggression‖ towards the foreign people involved.
8)Few people have an extremist type of feeling that his/her culture or background which is superior over the others with accompanying prejudice to other groups of people as inferior.
9)Xenophobia is irrational
10)Xenophobia can also be exhibited in the form of an "uncritical exaltation of another culture" in which a culture is ascribed "an unreal, stereotyped and exotic quality".
11)A xenophobic person has to genuinely think or believe at some
level that the target is in fact a foreigner.
12)Racism is based on xenophobia.
13)Xenophobia can be directed simply to anyone outside a culture, not necessarily one particular race or people.
14)Xenophobia can be expressed in two forms: social and cultural.
15)Chauvinism is a strong belief in God.
16)Chauvinism is an exaggerated belief in national superiority and glory.
17)Chauvinism is an almost natural product of the national concept of the old idea of the "national mission‖.
18)Male chauvinism is a term used to describe the belief that one nation is superior to another.
19)Male chauvinism refers to the maintenance of fixed beliefs and attitudes of male superiority, associated with overt or covert depreciation of women.
20)Racism in Russia appears mainly in the form of negative attitudes and actions by some Russians towards people who are not considered ethnically Russian.
Pair work. Ask your partner about his attitude towards foreigners (English speakers, for example).Does he or she fear any of them? Explain why yes or no. Does he or she know about the definition of the word, meaning “ irrational fear of foreigners”? What is hia personal idea of this phenomenon? Share your ideas with the class.
Grammar Practice
State verbs. There are certain groups of verbs that are usually only used in the Present Simple. This is because their meanings are related to states or conditions which are facts and not activities. This is a feature of the use of the Present Simple. The groups of verbs are:
Verbs of thinking and opinions Believe,think,understand,suppose,expect,agree,doubt,know,remember,forget,mean, imagine, realize, deserve, prefer
I believe you.
Do you understand?
I know his face, but forget his name.
Verbs of emotions and feeling
Like, love, hate, care, hope, wish, want, admit
I like coffee.
Do you want to go out?
I don’t care.
Verbs of having and being.
Belong, own, have, possess, contain, cost, seem, appear, need, depend on, weigh, come from, resemble
The book belongs to Jane. How much does it cost? He has a lot of money.
Verbs of the senses
Look, hear, taste, smell, feel
The food smells good.
When the subject is a person, we often use can. Can you see that house?
Can you smell something burning? I can hear someone crying.
Some of these verbs can be used in Present Continuous, but with a change of meaning. In the Continuous the verb expresses an activity, not a state.
I think you are right.(opinion)
We are thinking of going to the cinema. (mental activity) He has a lot of money. (possession)
He is having a bath. (activity)
I see what you mean. (understand)
Are you seeing Nigel tomorrow? (activity) The soup tastes awful. (state)
I am tasting the soup. (activity)
1.Complete the following pairs of sentences using the verb in italics. Use the Present Simple for one and the Present Continuous for the other.
Come
1.Alec and Mary are Scottish. The … from Glasgow.
2.The will be here very soon. They…by car.
Have
1.Liza can’t answer the phone. She … a bath.
2.She … two pair of jeans.
Think
1.I … that all politicians tell lies.
2.I … about my girlfriend. She is in New York now. Not enjoy
1.We … this party at all. The music is too loud.
2.We … going to the parties.
Watch
1.Be quiet! I … my favorite program.
2.I always … on Thursday evening.
See
1.John is not at home. He … a doctor about his sore throat.
2.I … the problem, but I can’t help you.
Smell

1.Mmmmmm! Dinner … good. What is it?
2.Why … you…those roses? They are plastic.
Use
1.The room …usually …for big meetings. But today … for a party.
2.Make up your own 10 sentences with the state verb, paying special attention to the use of Present Simple as well as Present Continuous.
Group Work
1. Make up a picture of statistical person of Russia. Try to formulate “What is to be a“Russian citizen”? Prepare a spidergram. Introduce it to the group and justify all your points. The phrases in the box will help you to give your personal opinion:
In my view, I think, I consider, I am absolutely sure that,to my mind, I strongly believe that…, I feel that, in my opinion etc.
2 . Using expressions below write a small essay on the following topic “Meeting a stranger I try my best to be tolerant and polite…..”:
(to be acquainted with, to be friendly with, to get on with, to be interested in, to be proud of, to be polite to, to talk to, to talk with someone about something, to admire for something, to be involved in, to be responsible for, to be open and polite).
3.Interview the members of your family about their attitude towards discrimination, xenophobia and nationalism. Make a report and introduce it to the class.
Pair work
Ask your partner about his attitude towards foreigners (English speakers, for example).Does he or she fear any of them? Explain why yes or no. Does he or she know about the definition of the word, meaning “ irrational fear of foreigners”? Share your ideas with the class.
ГРАММАТИЧЕСКИЙ КОММЕНТАРИЙ
Module I
Раздел 1. Система английских времѐн
Времена английского глагола. Действительный залог
|
|
Употребление |
|
|
Образование |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indefinite |
|
|
|
|
Present |
глагол в личной |
показывает действие как факт (обычное, повторяемое) |
Past |
форме |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Future |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Continuous |
|
|
|
|
Present |
to be + ing |
показывает действие как процесс |
|
|
Past |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Future |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Perfect |
|
|
|
|
Present |
to have + |
показывает действие, законченное до определѐнного момента |
Past |
причастие II |
||||
в настоящем, прошедшем и будущем |
|
|
Future |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Perfect Continuous |
|
|
|
Present |
to have been + ing |
|
показывает действие, начатое некоторое время назад и все ещѐ |
Past |
|
||||
продолжающееся или только что закончившееся |
Future |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Таблица времѐн. Действительный залог |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Время |
Формы |
|
Обстоятельство времени |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I, we |
|
|
|
|
|
Present |
you, they |
ask |
usually, sometimes, every day, often, seldom |
||
|
|
he, she, it |
asks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ed или |
asked |
yesterday |
|
|
Indefinite |
Past |
II ф. |
|
|
||
wrote |
last year 3 years ago |
|
||||
|
|
неправ.глаг. |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I, we |
will |
tomorrow |
|
|
|
Future |
ask |
|
|
||
|
все остальные |
next year in 3 years |
|
|||
|
|
ask |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
am |
|
|
|
|
|
Present |
is |
asking |
now, at present |
|
|
|
|
are |
|
|
|
|
Continuous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past |
was |
asking |
yesterday from 5 till 6 |
|
||
|
|
|||||
|
were |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Future |
will be |
asking |
tomorrow from 5 till 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Present |
have |
asked |
just, ever, never, yet, already, today, this year |
||
|
|
has |
|
for, since |
|
|
Perfect |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past |
had |
asked |
by 3 o'clock yesterday |
|
||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Future |
will have |
asked |
by 3 o'clock tomorrow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Perfect |
Present |
have been |
asking |
for, since |
|
|
Continuous |
|
has |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
