
- •Dedication
- •Editors and Contributors
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •PREPARING FOR THE SURGERY CLERKSHIP
- •SURGICAL NOTES
- •COMMON ABBREVIATIONS YOU SHOULD KNOW
- •RETRACTORS (YOU WILL GET TO KNOW THEM WELL!)
- •SUTURE MATERIALS
- •WOUND CLOSURE
- •KNOTS AND EARS
- •INSTRUMENT TIE
- •TWO-HAND TIE
- •COMMON PROCEDURES
- •NASOGASTRIC TUBE (NGT) PROCEDURES
- •CHEST TUBES
- •NASOGASTRIC TUBES (NGT)
- •FOLEY CATHETER
- •CENTRAL LINES
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •THIRD SPACING
- •COMMON IV REPLACEMENT FLUIDS (ALL VALUES ARE PER LITER)
- •CALCULATION OF MAINTENANCE FLUIDS
- •ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCES
- •ANTIBIOTICS
- •STEROIDS
- •HEPARIN
- •WARFARIN (COUMADIN®)
- •MISCELLANEOUS AGENTS
- •NARCOTICS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ATELECTASIS
- •POSTOPERATIVE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
- •PULMONARY EMBOLISM
- •ASPIRATION PNEUMONIA
- •GASTROINTESTINAL COMPLICATIONS
- •ENDOCRINE COMPLICATIONS
- •CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK
- •SEPTIC SHOCK
- •CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
- •NEUROGENIC SHOCK
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI)
- •CENTRAL LINE INFECTIONS
- •WOUND INFECTION (SURGICAL SITE INFECTION)
- •NECROTIZING FASCIITIS
- •CLOSTRIDIAL MYOSITIS
- •SUPPURATIVE HIDRADENITIS
- •PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS
- •PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTICS
- •PAROTITIS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •CHEST
- •ABDOMEN
- •MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •OVERVIEW
- •CHOLECYSTOKININ (CCK)
- •SECRETIN
- •GASTRIN
- •SOMATOSTATIN
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •GROIN HERNIAS
- •HERNIA REVIEW QUESTIONS
- •ESOPHAGEAL HIATAL HERNIAS
- •PRIMARY SURVEY
- •SECONDARY SURVEY
- •TRAUMA STUDIES
- •PENETRATING NECK INJURIES
- •MISCELLANEOUS TRAUMA FACTS
- •PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD)
- •DUODENAL ULCERS
- •GASTRIC ULCERS
- •PERFORATED PEPTIC ULCER
- •TYPES OF SURGERIES
- •STRESS GASTRITIS
- •MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME
- •ESOPHAGEAL VARICEAL BLEEDING
- •BOERHAAVE’S SYNDROME
- •ANATOMY
- •GASTRIC PHYSIOLOGY
- •GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
- •GASTRIC CANCER
- •GIST
- •MALTOMA
- •GASTRIC VOLVULUS
- •SMALL BOWEL
- •APPENDICITIS
- •CLASSIC INTRAOPERATIVE QUESTIONS
- •APPENDICEAL TUMORS
- •SPECIFIC TYPES OF FISTULAS
- •ANATOMY
- •COLORECTAL CARCINOMA
- •COLONIC AND RECTAL POLYPS
- •POLYPOSIS SYNDROMES
- •DIVERTICULAR DISEASE OF THE COLON
- •ANATOMY
- •ANAL CANCER
- •ANATOMY
- •TUMORS OF THE LIVER
- •ABSCESSES OF THE LIVER
- •HEMOBILIA
- •ANATOMY
- •PHYSIOLOGY
- •PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
- •DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
- •BILIARY SURGERY
- •OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE
- •CHOLELITHIASIS
- •ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS
- •ACUTE ACALCULOUS CHOLECYSTITIS
- •CHOLANGITIS
- •SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS
- •GALLSTONE ILEUS
- •CARCINOMA OF THE GALLBLADDER
- •CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS CONDITIONS
- •PANCREATITIS
- •PANCREATIC ABSCESS
- •PANCREATIC NECROSIS
- •PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST
- •PANCREATIC CARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ANATOMY OF THE BREAST AND AXILLA
- •BREAST CANCER
- •DCIS
- •LCIS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •MALE BREAST CANCER
- •BENIGN BREAST DISEASE
- •CYSTOSARCOMA PHYLLODES
- •FIBROADENOMA
- •FIBROCYSTIC DISEASE
- •MASTITIS
- •BREAST ABSCESS
- •MALE GYNECOMASTIA
- •ADRENAL GLAND
- •ADDISON’S DISEASE
- •INSULINOMA
- •GLUCAGONOMA
- •SOMATOSTATINOMA
- •ZOLLINGER-ELLISON SYNDROME (ZES)
- •MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA
- •THYROID DISEASE
- •ANATOMY
- •PHYSIOLOGY
- •HYPERPARATHYROIDISM (HPTH)
- •PARATHYROID CARCINOMA
- •SOFT TISSUE SARCOMAS
- •LYMPHOMA
- •SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
- •BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
- •MISCELLANEOUS SKIN LESIONS
- •STAGING
- •INTENSIVE CARE UNIT (ICU) BASICS
- •INTENSIVE CARE UNIT FORMULAS AND TERMS YOU SHOULD KNOW
- •SICU DRUGS
- •INTENSIVE CARE PHYSIOLOGY
- •HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING
- •MECHANICAL VENTILATION
- •PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE
- •LOWER EXTREMITY AMPUTATIONS
- •ACUTE ARTERIAL OCCLUSION
- •ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSMS
- •MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA
- •MEDIAN ARCUATE LIGAMENT SYNDROME
- •CAROTID VASCULAR DISEASE
- •CLASSIC CEA INTRAOP QUESTIONS
- •SUBCLAVIAN STEAL SYNDROME
- •RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS
- •SPLENIC ARTERY ANEURYSM
- •POPLITEAL ARTERY ANEURYSM
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •PEDIATRIC IV FLUIDS AND NUTRITION
- •PEDIATRIC BLOOD VOLUMES
- •FETAL CIRCULATION
- •ECMO
- •NECK
- •ASPIRATED FOREIGN BODY (FB)
- •CHEST
- •PULMONARY SEQUESTRATION
- •ABDOMEN
- •INGUINAL HERNIA
- •UMBILICAL HERNIA
- •GERD
- •CONGENITAL PYLORIC STENOSIS
- •DUODENAL ATRESIA
- •MECONIUM ILEUS
- •MECONIUM PERITONITIS
- •MECONIUM PLUG SYNDROME
- •ANORECTAL MALFORMATIONS
- •HIRSCHSPRUNG’S DISEASE
- •MALROTATION AND MIDGUT VOLVULUS
- •OMPHALOCELE
- •GASTROSCHISIS
- •POWER REVIEW OF OMPHALOCELE AND GASTROSCHISIS
- •APPENDICITIS
- •INTUSSUSCEPTION
- •MECKEL’S DIVERTICULUM
- •NECROTIZING ENTEROCOLITIS
- •BILIARY TRACT
- •TUMORS
- •PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
- •OTHER PEDIATRIC SURGERY QUESTIONS
- •POWER REVIEW
- •WOUND HEALING
- •SKIN GRAFTS
- •FLAPS
- •SENSORY SUPPLY TO THE HAND
- •CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
- •ANATOMY
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUSES
- •ORAL CAVITY AND PHARYNX
- •FACIAL FRACTURES
- •ENT WARD QUESTIONS
- •RAPID-FIRE REVIEW OF MOST COMMON CAUSES OF ENT INFECTIONS
- •THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME (TOS)
- •CHEST WALL TUMORS
- •DISEASES OF THE PLEURA
- •DISEASES OF THE LUNGS
- •DISEASES OF THE MEDIASTINUM
- •DISEASES OF THE ESOPHAGUS
- •ACQUIRED HEART DISEASE
- •CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
- •CARDIAC TUMORS
- •DISEASES OF THE GREAT VESSELS
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •BASIC IMMUNOLOGY
- •CELLS
- •IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
- •OVERVIEW OF IMMUNOSUPPRESSION MECHANISMS
- •MATCHING OF DONOR AND RECIPIENT
- •REJECTION
- •ORGAN PRESERVATION
- •KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
- •LIVER TRANSPLANT
- •PANCREAS TRANSPLANT
- •HEART TRANSPLANT
- •INTESTINAL TRANSPLANTATION
- •LUNG TRANSPLANT
- •TRANSPLANT COMPLICATIONS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TERMS
- •TRAUMA GENERAL PRINCIPLES
- •FRACTURES
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA
- •DISLOCATIONS
- •THE KNEE
- •ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
- •ROTATOR CUFF
- •MISCELLANEOUS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC INFECTIONS
- •ORTHOPAEDIC TUMORS
- •ARTHRITIS
- •PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS
- •HEAD TRAUMA
- •SPINAL CORD TRAUMA
- •TUMORS
- •VASCULAR NEUROSURGERY
- •SPINE
- •PEDIATRIC NEUROSURGERY
- •SCROTAL ANATOMY
- •UROLOGIC DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- •RENAL CELL CARCINOMA (RCC)
- •BLADDER CANCER
- •PROSTATE CANCER
- •BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA
- •TESTICULAR CANCER
- •TESTICULAR TORSION
- •EPIDIDYMITIS
- •PRIAPISM
- •ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
- •CALCULUS DISEASE
- •INCONTINENCE
- •URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI)
- •MISCELLANEOUS UROLOGY QUESTIONS
- •Rapid Fire Power Review
- •TOP 100 CLINICAL SURGICAL MICROVIGNETTES
- •Figure Credits
- •Index

Chapter 70 / Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 615
What are the disadvantages? |
May result in increased mortality from |
|
|
|
local recurrence |
FACIAL FRACTURES |
|
|
|
|
|
MANDIBLE FRACTURES |
|
|
|
|
|
What are the symptoms? |
Gross disfigurement, pain, malocclusion, |
|
|
|
drooling |
What are the signs? |
Trismus, fragment mobility and |
|
|
|
lacerations of gingiva, hematoma in floor |
|
|
of mouth |
What are the possible |
Malunion, nonunion, osteomyelitis, TMJ |
|
complications? |
ankylosis |
|
What is the treatment? |
Open or closed reduction |
|
|
|
MMF MaxilloMandibular Fixation |
|
|
(wire jaw shut) |
MIDFACE FRACTURES |
|
|
|
|
|
How are they evaluated? |
Careful physical examination and CT scan |
|
Classification |
|
|
|
|
|
Le Fort I? |
Transverse maxillary fracture above the |
|
|
|
dental apices, which also traverses the |
|
|
pterygoid plate; palate is mobile, but |
|
|
nasal complex is stable |
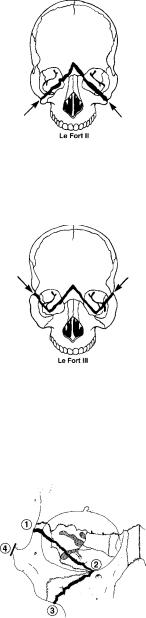
616 Section III / Subspecialty Surgery
Le Fort II?
Le Fort III?
What is a “tripod” fracture?
Fracture through the frontal process of the maxilla, through the orbital floor and pterygoid plate; midface is mobile
Complete craniofacial separation; differs from II in that it extends through the nasofrontal suture and frontozygomatic sutures
Fracture of the zygomatic complex; involves four fractures:
1.Frontozygomatic suture
2.Inferior orbital rim
3.Zygomaticomaxillary suture
4.Zygomaticotemporal suture

Chapter 70 / Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 617
What is a “blowout” fracture? Orbital fracture with “blowout” of supporting bony structural support of orbital floor; patient has enophthalmos (sunken-in eyeball)
What is “entrapment”? Orbital fracture with “entrapment” of periorbital tissues within the fracture opening, including entrapment of extraocular muscles; loss of extraocular muscle mobility (e.g., lateral tracking) and diplopia (double vision)
What is a “step off”?
Fracture of the orbit with palpable “step off” of bony orbital rim (inferior or lateral)
Are mandibular fractures No; because the mandible forms an usually a single fracture? anatomic ring, 95% of mandible
fractures have more than one fracture site
What is the best x-ray study for mandibular fractures?
What must be ruled out and treated with a broken nose (nasal fracture)?
ENT WARD QUESTIONS
Panorex
Septal hematoma; must drain to remove chance of pressure-induced septal necrosis
How can otitis externa be |
Otitis externa is characterized by severe |
distinguished from otitis |
pain upon manipulation of the auricle |
media on examination? |
|
What causes otitis media? |
Most cases are caused by pneumococci |
|
and H. influenzae |
What causes otitis externa? |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
What must be considered in |
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
unilateral serous otitis? |
|
What is the most common |
Bell’s palsy, which has an unidentified |
cause of facial paralysis? |
etiology |
618 Section III / Subspecialty Surgery
What is the single most important prognostic factor in Bell’s palsy?
What is the most common cause of parotid swelling?
What is Heerfordt’s syndrome?
Which systemic disease causes salivary gland stones?
What is the most common salivary gland site of stone formation?
Whether the affected muscles are completely paralyzed (if not, prognosis is95% complete recovery)
Mumps
Sarcoidosis with parotid enlargement, facial nerve paralysis, and uveitis
Gout
Submandibular gland
What is Mikulicz’s |
Any cause of bilateral enlargement of the |
|
syndrome? |
parotid, lacrimal, and submandibular glands |
|
What are the three major |
1. |
Airway protection |
functions of the larynx? |
2. |
Airway/respiration |
|
3. |
Phonation |
What is a cricothyroidotomy? |
Emergent surgical airway by incising the |
|
|
cricothyroid membrane |
|
Name the four major |
1. |
Prolonged mechanical ventilation |
indications for a |
|
(usually 2 weeks) |
tracheostomy. |
2. |
Upper airway obstruction |
|
3. |
Poor life-threatening pulmonary toilet |
|
4. |
Severe obstructive sleep apnea |
What is a ranula? |
Sublingual retention cyst arising from |
|
|
sublingual salivary glands |
|
What is Frey’s syndrome? |
Flushing, pain, and diaphoresis in the |
|
|
auriculotemporal nerve distribution |
|
|
initiated by chewing |
|
What causes Frey’s |
Cutting the auriculotemporal nerve |
|
syndrome? |
causes abnormal regeneration of the |
|
|
sympathetic/parasympathetic nerves, |
|
|
which, once destined for the parotid |
|
|
gland, find new targets in skin sweat |
|
|
glands; thus, people sweat when eating |
|
Chapter 70 / Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 619
What is the classic triad of Ménière’s disease?
What is the most common posterior fossa tumor and where is it located?
Hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo (HTV)
Acoustic neuroma, usually occurring at the cerebellopontine angle
What is the most common |
Maxillary sinus |
site of sinus cancer? |
|
What tumor arises from |
Esthesioneuroblastoma |
olfactory epithelium? |
|
What cell type is most |
Squamous cell |
common in head and neck |
|
cancer? |
|
What are the most important predisposing factors to head and neck cancer?
Excessive alcohol use and tobacco abuse of any form
What is the most frequent site of salivary gland tumor?
What is the most common salivary gland neoplasm:
Benign?
Malignant?
What is the classic feature of croup?
What are the classic features of epiglottitis?
What comprises the workup of neck mass?
Parotid gland
Pleomorphic adenoma
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Barking, seal-like cough
“Hot-potato” voice, sitting up, drooling, toxic appearance, high fever, leaning forward
Do not biopsy; obtain tissue via FNA and complete head and neck examination
