
- •Quick Quiz 1
- •Quick Quiz 2
- •Quick Quiz 3
- •Quick Quiz 4
- •Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part2»
- •Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- •Images Formed by Refraction
- •Images Formed by Refraction
- •Images Formed by Refraction
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Thin Lenses
- •Lens Aberrations
- •The Camera
- •The Simple Magnifier
- •The Simple Magnifier
- •The Compound Microscope
- •The Telescope
- •The Telescope
- •Quick Quiz 1
- •Quick Quiz 2
- •Quick Quiz 3
- •Quick Quiz 4
- •Quick Quiz 5
- •Quick Quiz 6
- •Quick Quiz 7
- •Quick Quiz 8

 Quick Quiz 1
Quick Quiz 1
Light passes from a material with index of refraction 1.3 into one with index of refraction 1.2. Compared to the incident ray, the refracted ray
(a)bends toward the normal (b)undeflected
(c)bends away from the normal.

Quick Quiz 2
Lenses in a camera use refraction to form an image on a film. Ideally, you want all the colors in the light from the object being photographed to be refracted by the same amount. Of the materials shown in Figure 35.20, which would you choose for a camera lens?
(a)crown glass (b)acrylic (c)fused quartz
(d) impossible to determine
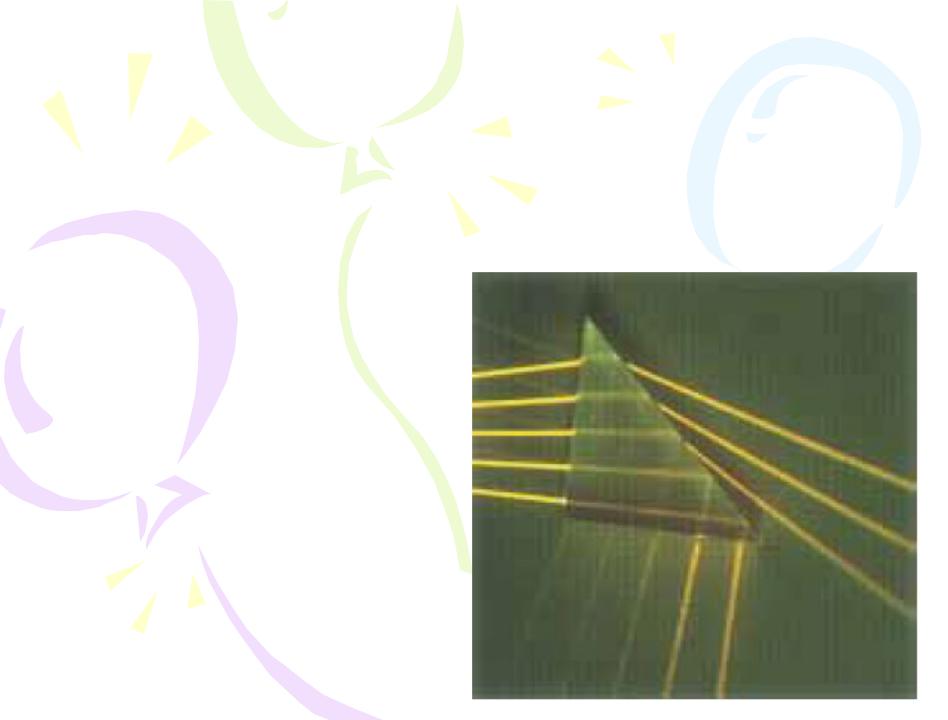

Quick Quiz 3
In Figure, five light rays enter a glass prism from the left. How many of these rays undergo total internal reflection at the slanted surface of the prism?
(a)1
(b)2
(c)3 (d)4
(e)5.
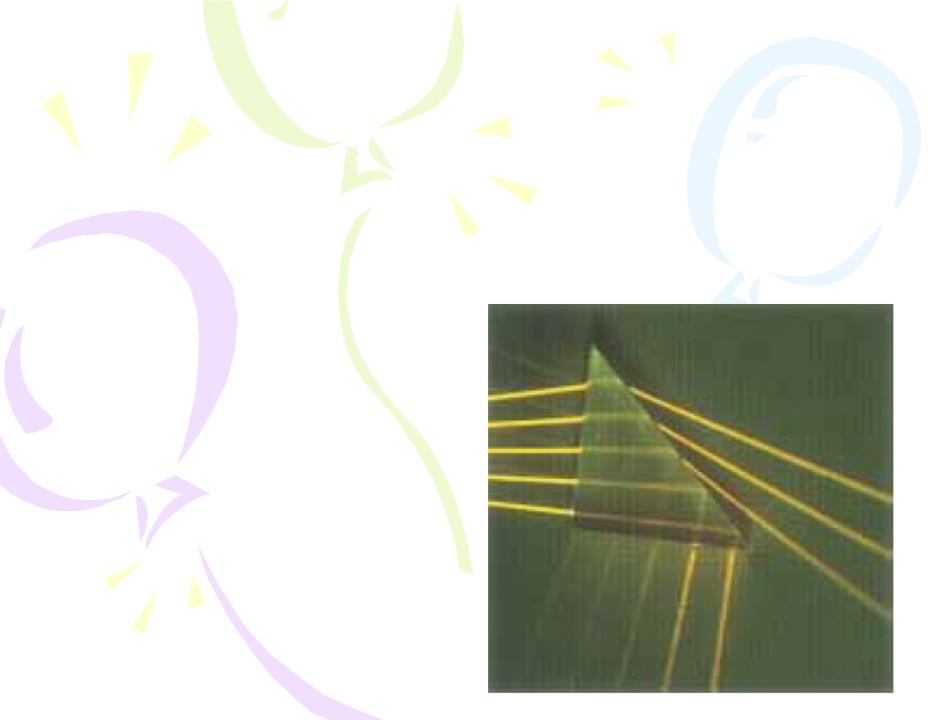

Quick Quiz 4
Suppose that the prism in Figure can be rotated in the plane of the paper. In order for all five rays to experience total internal reflection from the slanted surface, should the prism be rotated
(a) clockwise or
(b) counterclockwise?

Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part2»
Lecture №2
 Image Formation. Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors. Images Formed by Refraction. Thin Lenses. Lens Aberrations. The Camera. The Eye. The Simple Magnifier. The Compound Microscope.
Image Formation. Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors. Images Formed by Refraction. Thin Lenses. Lens Aberrations. The Camera. The Eye. The Simple Magnifier. The Compound Microscope.
The Telescope.

Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
Images are located either at a point from which rays of light actually diverge or at a point from which they appear to diverge.
A real image is formed when light rays pass through and diverge from the image point; a virtual image is formed when the light rays do not pass through the image point but only appear to diverge from that
point.
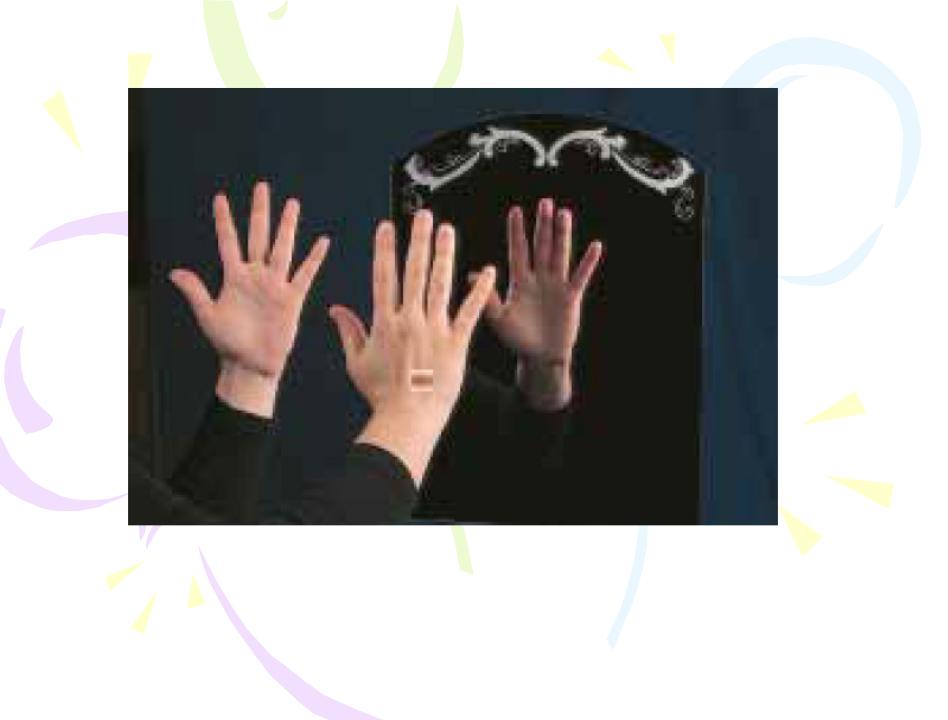
The image of an object seen in a flat mirror is always virtual.

Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
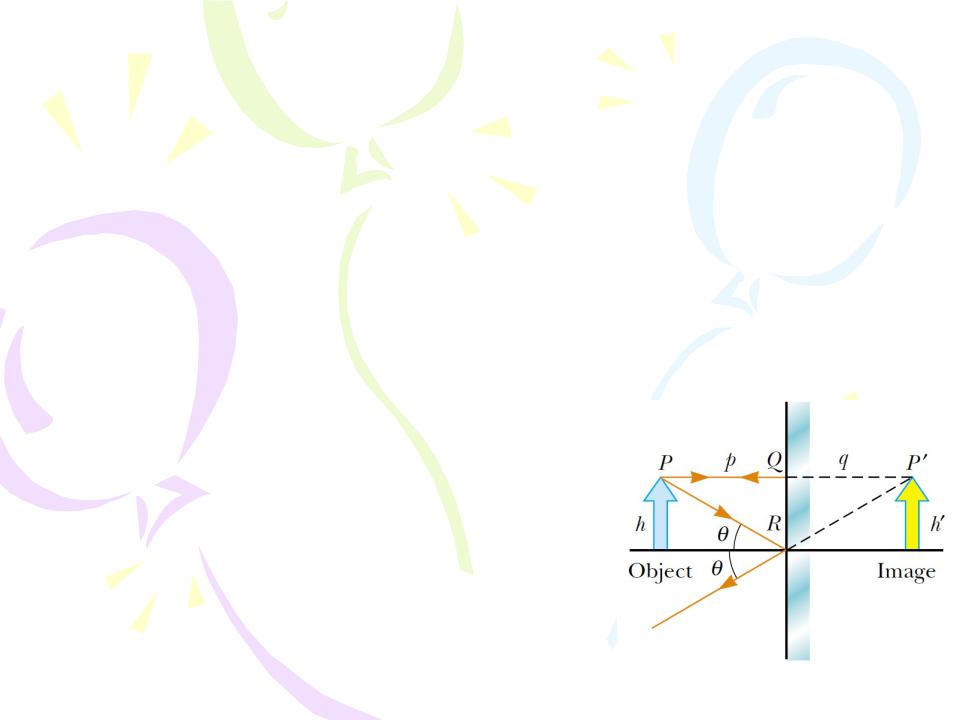
The image formed by an object placed in front of a flat mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
Lateral magnification M:
(2.1)

Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
We conclude that the image that is formed by a flat mirror has the following properties: 
•The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front.
•The image is unmagnified, virtual, and upright. (By upright we mean that, if the object arrow points upward as in Figure, so does the image arrow.)
•The image has front–back reversal.
Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
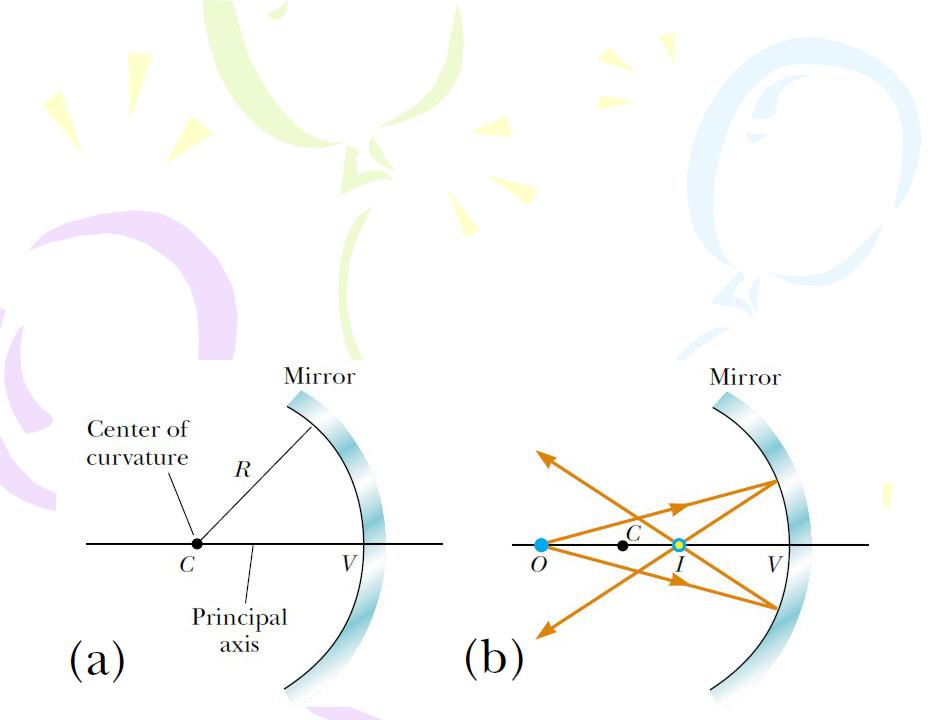
Concave Mirrors
A spherical mirror, as its name implies, has the shape of a section of a sphere.
Such a mirror, in which light is reflected from the inner, concave surface, is called a concave mirror.
Point V is the center of the spherical section, and a line through C and V is called the principal axis of the mirror.
