
2 lec Eng
.pdf
Introduction to the Fundamentals of Automatic Control Theory
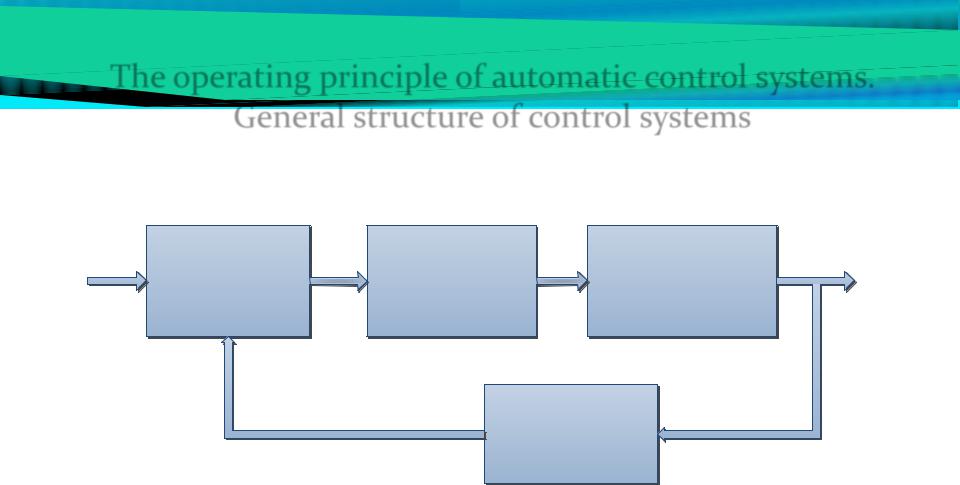
The operating principle of automatic control systems. General structure of control systems
 f
f
g |
Actuators |
Object |
y |
Controller |
(Pr |
|
|
|
|
|
ŷ
Sensors
g – inputs (desired output response) |
y – outputs (actual output response) |
f – disturbance |
ŷ – measured outputs |
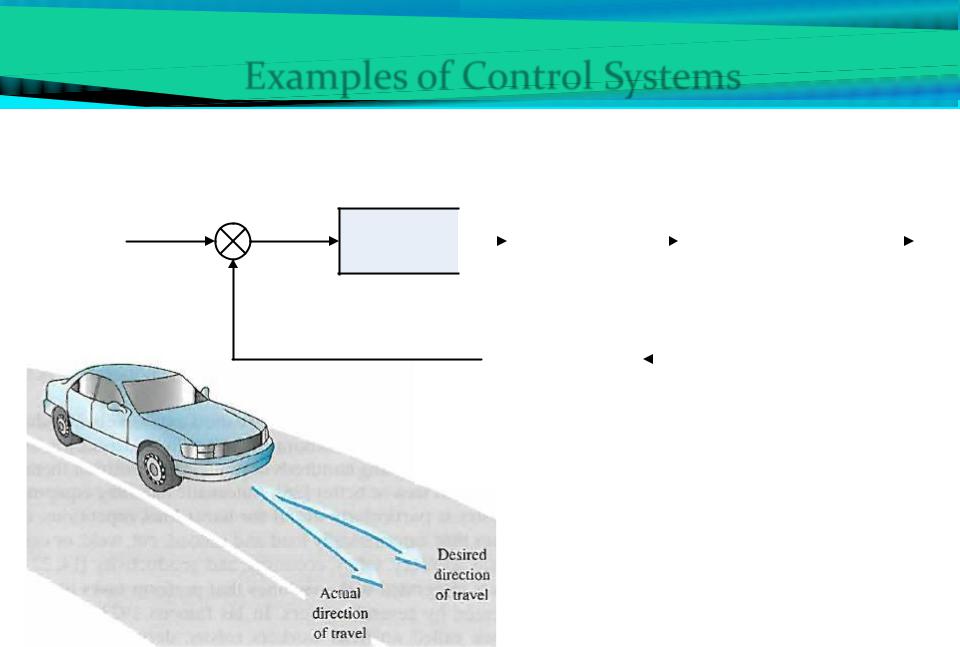
Examples of Control Systems
Example 1. Automobile Steering Control System
Controller
Desired
course of + - Error signal Driver travel
|
|
|
Actuator |
|
|
|
|
Object |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Actual |
|
|
|
Steering |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Automobile |
|
course of |
|
|
|
|
mechanism |
|
|
|
|
|
travel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
(visual) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The driver uses the difference between the actual and the desired direction of travel to generate a controlled adjustment of steering wheel

Examples of Control Systems
Example 2. Automobile interior cabin temperature control system
|
Desired |
|
|
|
Controller |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Error signal |
On-board |
|
||||
temperature |
+ - |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
set by the |
|
|
computer |
|
|||
|
driver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Measured temperature
Actuator |
Object |
|
|
Thermostat and |
Automobile |
Automobile |
|
air-conditioning |
cabin |
cabin |
|
temperature |
|||
|
|
||
Sensor |
|
|
|
Temperature |
|
|
|
sensor |
|
|
Many automobiles have thermostatically controlled airconditioning systems for the comfort of the passengers. This is the block diagram of an air-conditioning system where the driver sets the desired interior temperature on a dashboard panel.

Examples of Control Systems
Example 3. An aircraft flight path control system using GPS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Controller |
|
|
|
Actuators |
|
|
|
|
Object |
|
|
Desired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ailerons, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Error signal |
Computer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
flight path |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
elevators, rudder, |
|
|
|
|
Aircraft |
|
|||||
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
from air |
|
|
|
Auto-pilot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
engine power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
traffic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
controllers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measured flight pass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Global Positioning |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System (GPS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Actual flight pass
GPS allows each aircraft to know its position in the airspace landing corridor very precisely. This is the block diagram depicting how an air traffic controller might use GPS for aircraft collision avoidance.

Requirements to Automatic Control Systems
•Stability
•Accuracy
•Performance/Quality
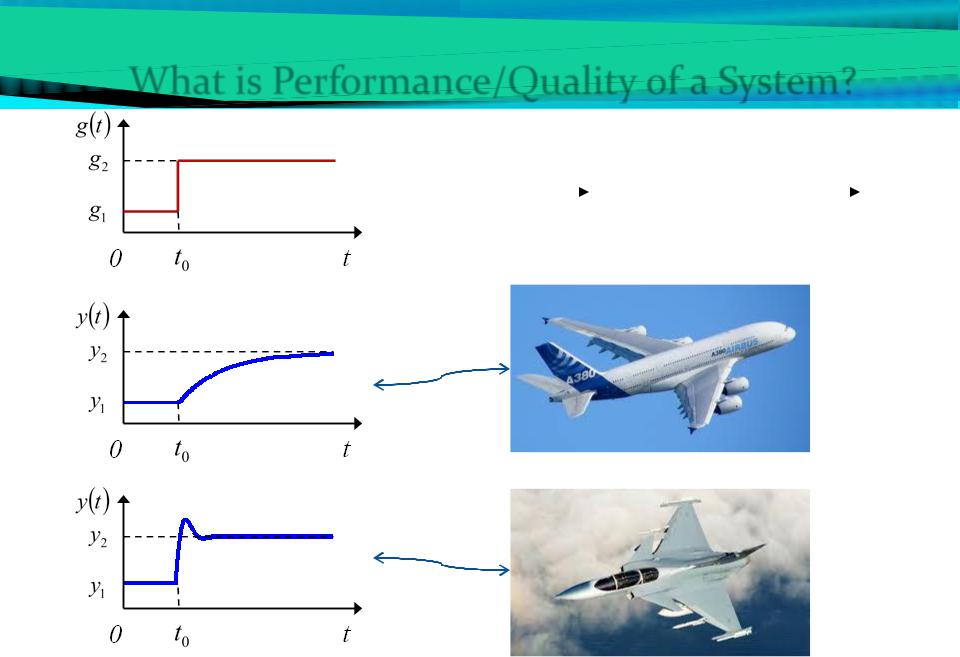
What is Performance/Quality of a System?
|
g(t) |
|
|
y(t) |
||
|
System |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input signal |
|
Output signal |
|||
|
|
|
||||
(desired altitude) |
|
(actual altitude) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Classification of automatic control systems
On the basis of Mathematical description
Linear or |
|
Stationary or |
|
Lumped or |
|
Deterministic |
|
|
distributed |
|
|||
Non-linear |
|
Non-stationary |
|
|
or stochastic |
|
|
|
parameters |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On the basis of Operating principle
Open-loop |
|
Closed-loop |
|
Combined |
|
Self-tuning |
|
|
|
(self-adapting) |
|||
systems |
|
systems |
|
control systems |
|
|
|
|
|
systems |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Classification of automatic control systems
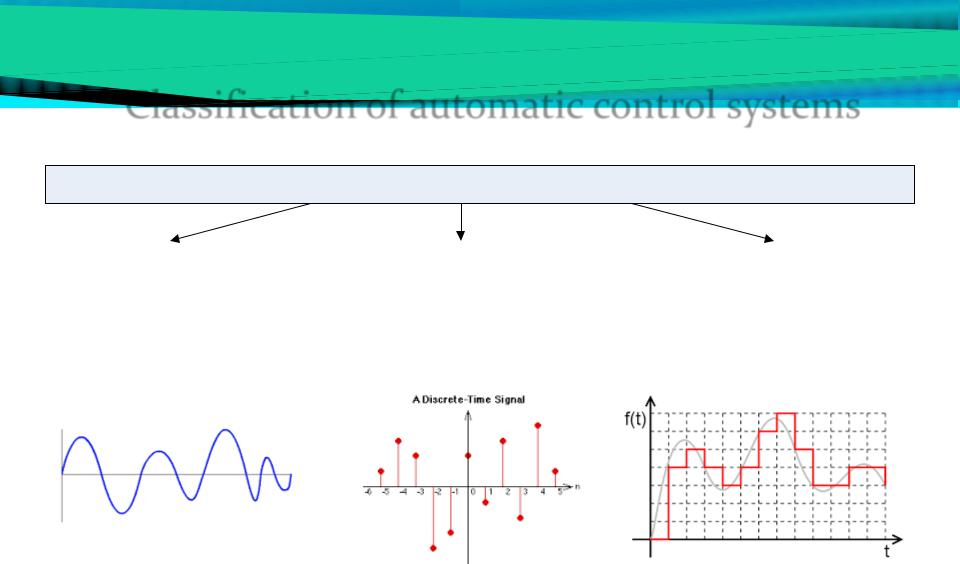
On the basis of signal types
Continuous |
|
Discrete |
|
Digital |
(Analog) |
|
(Discrete-Continuous) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Classification of automatic control systems
On the basis of problems to solve
|
|
Programmed control |
|
Tracking systems |
Stabilization problem |
|
|
(servomechanisms) |
|
|
g(t) - predetermined |
|
||
g(t) = const |
|
|
g(t) - indeterminate |
|
|
function |
|
||
|
|
|
function |
|
|
|
|
|
e.g. temperature |
e.g. radar station |
|
control in an |
||
|
||
incubator |
|
