
4. Construction of block matrices
4.1 Finding the shortest path connecting to the network
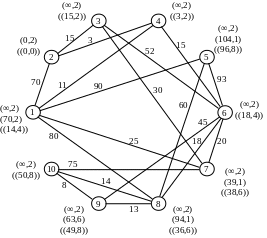
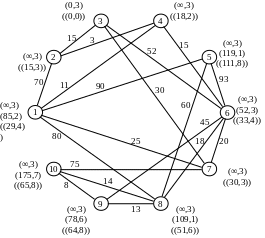
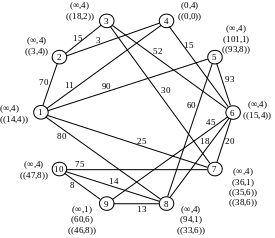
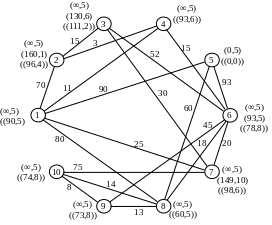
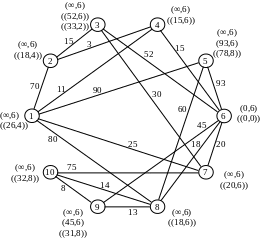
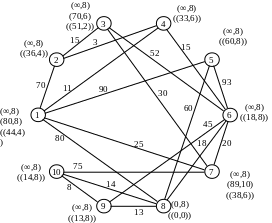
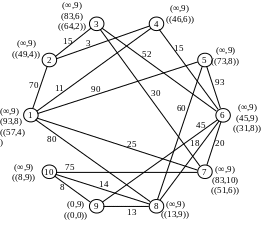
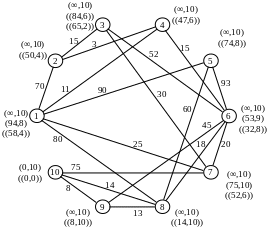
Recalculate the temporary notes for the vertices adjacent to vertex 1:

Flag P4 = (11.1) becomes constant. We carry out conversion of notes for the vertices that are adjacent to the vertex 4:
Р2=(14,4)
Р6=(26,4)
Flag P3 = (14.4) becomes constant. After the conversion notes for the vertices adjacent to vertex 2, it becomes the constant mark Р7=(25,1):
Р3=(29,2)
Р7=(25,1)
Counting the notes for the vertices adjacent to the vertex 7 get the constant mark Р6=(26,4):
Р10=(100,7)
Draw recalculation of notes for the vertices that are adjacent to vertex 6:
Р8=(44,6)
Р9=(71,6)
Next the minimum weight is vertex 3, but because All have regular direct contact, then select the next vertex with minimum weight - is vertex 8:
Р9=(57,8)
Р10=(71,6)
After that, all notes become permanent, as there are no direct links.
Similarly, we find the shortest path connecting the network to all other vertices.

4.2 Determination of the given transient path sets
Among the restrictions that are imposed in the organization of the connecting channels of transmission in communication networks can be considered limitations on the number of transit points or hops in them.
Under the transit points refers to switching nodes that occur in the way of passing messages from a particular user's point i to point j, which is a redistribution of message flows. Transit sites are, respectively, communication lines, which connect the transit points.
Restrictions on transit in the transmission of messages due to the requirements for quality of service on the network (for example, at the time of passing the message on the network, time, message processing in the switching nodes).
One of the most convenient and easily implemented by computer methods to identify ways that correspond to (T transit option does not exceed a certain preset value T 0), is to build a so-called "long-line of the tree" of paths from a given vertex s to other vertices of the graph.
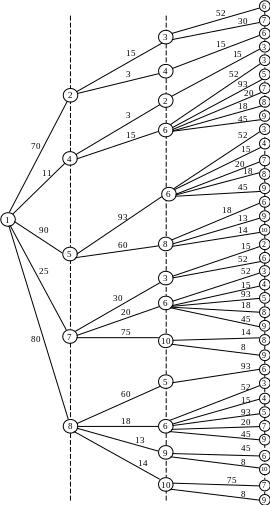
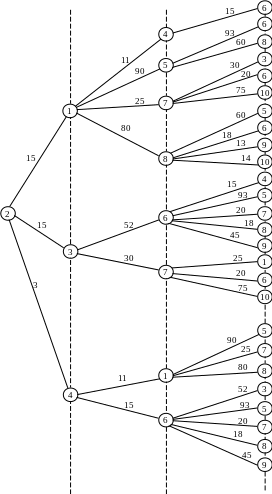
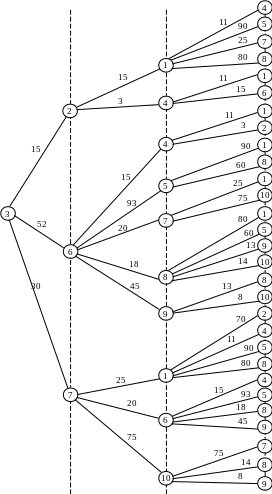
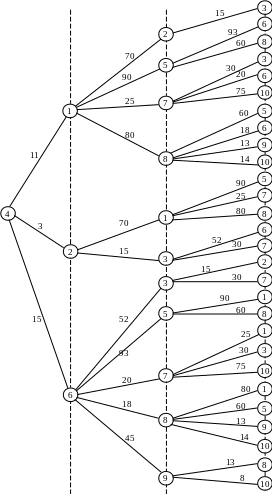
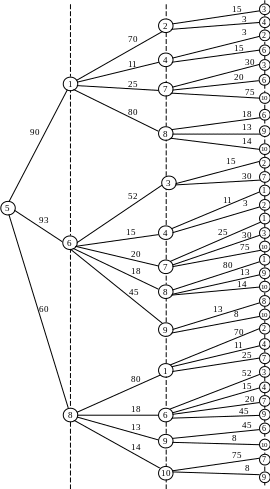
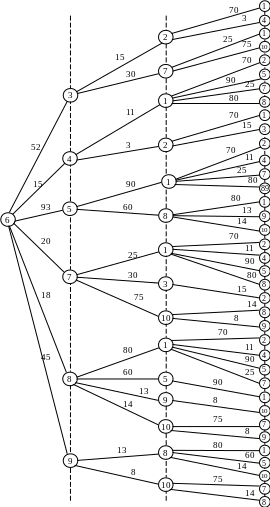
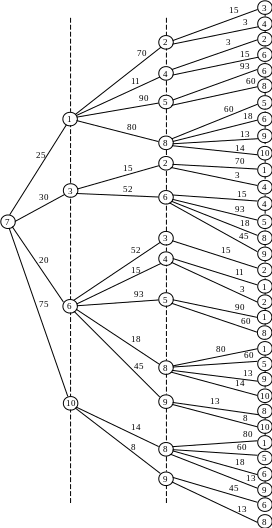
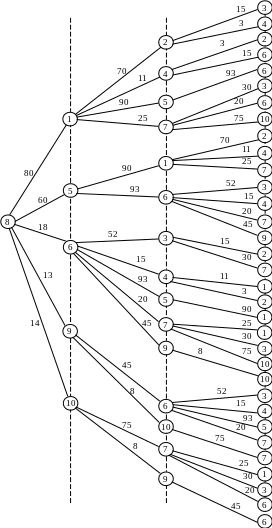

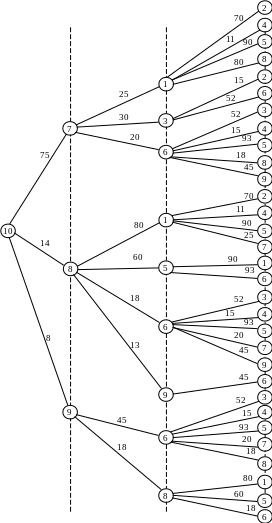
Table 4.1 − The routing table
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
70 |
− |
11 |
90 |
− |
25 |
80 |
− |
− |
1 |
4/14 |
7/55 |
2/73 |
8/140 |
4/26 |
− |
5/150 |
8/93 |
8/94 |
||
2 |
7,3/70 |
4,2/29 |
7,6/60 |
4,6/119 |
2,4/88 |
4,6/46 |
4,6/44 |
4,6/71 |
8,9/101 |
||
2 |
0 |
70 |
|
15 |
3 |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
1 |
4/14 |
− |
1/81 |
1/160 |
4/18 |
3/45 |
1/150 |
− |
− |
||
2 |
3,7/70 |
4,6/70 |
3,6/82 |
4,1/104 |
1,4/96 |
4,6/38 |
4,6/36 |
4,6/63 |
1,8/164 |
||
3 |
0 |
− |
15 |
|
− |
− |
52 |
30 |
− |
− |
− |
1 |
7/55 |
− |
2/18 |
6,145 |
7/50 |
6/72 |
6/70 |
6/97 |
7/105 |
||
2 |
2,4/29 |
6,4/70 |
7,6/65 |
6,8/130 |
2,4/33 |
2,1/110 |
7,6/68 |
6,8/83 |
6,8/84 |
||
4 |
0 |
11 |
3 |
− |
|
− |
15 |
− |
− |
− |
− |
1 |
2/73 |
1/81 |
2/18 |
1/101 |
− |
6/35 |
6/33 |
6/60 |
− |
||
2 |
6,7/60 |
6,3/82 |
1,7/56 |
6,8/93 |
2,3/70 |
2,3/48 |
6,9/73 |
6,8/46 |
6,8/47 |
||
5 |
0 |
90 |
− |
− |
− |
|
93 |
− |
60 |
− |
− |
1 |
8/140 |
1/160 |
6/145 |
1/101 |
8/78 |
6/113 |
6/111 |
8/73 |
8/74 |
||
2 |
6,4/119 |
1,4/104 |
8,6/130 |
8,6/93 |
1,4/116 |
8,6/98 |
6,9/151 |
8,10/82 |
8,9/81 |
||
6 |
0 |
− |
− |
52 |
15 |
93 |
|
20 |
18 |
45 |
− |
1 |
4/26 |
4/18 |
7/50 |
− |
8/78 |
3/82 |
9/58 |
8/31 |
8/32 |
||
2 |
4,2/88 |
7,3/65 |
4,2/33 |
7,1/56 |
7,1/116 |
4,1/51 |
9,10/67 |
8,10/40 |
8,9/39 |
||
7 |
0 |
25 |
− |
30 |
− |
− |
20 |
|
− |
− |
75 |
1 |
− |
3/45 |
6/72 |
6/35 |
6/113 |
6/82 |
6/38 |
6/65 |
− |
||
2 |
6,4/46 |
6,4/38 |
1,2/110 |
3,2/48 |
6,8/98 |
1,4/51 |
6,9/78 |
6,8/51 |
6,8/52 |
||
8 |
0 |
80 |
− |
− |
− |
60 |
18 |
− |
|
13 |
14 |
1 |
5/150 |
1/150 |
6/70 |
6/33 |
6/111 |
9/58 |
6/38 |
10/22 |
9/21 |
||
2 |
6,4/44 |
6,4/36 |
6,7/68 |
9,6/73 |
9,6/151 |
10,9/67 |
9,6/78 |
5,6/198 |
6,9/71 |
||
9 |
0 |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
45 |
− |
13 |
|
8 |
1 |
8/93 |
− |
6/97 |
6/60 |
8/73 |
8/31 |
6/65 |
10/22 |
8/27 |
||
2 |
6,4/71 |
6,4/63 |
8,6/83 |
8,6/46 |
10,8/82 |
10,8/40 |
8,6/51 |
6,5/198 |
6,8/77 |
||
10 |
0 |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
75 |
14 |
8 |
|
1 |
8/94 |
− |
7/105 |
− |
8/74 |
8/32 |
− |
9/26 |
8/27 |
||
2 |
9,8/106 |
7,3/120 |
8,6/84 |
8,6/47 |
9,8/86 |
9,8/44 |
8,6/52 |
9,6/71 |
− |
||
