
- •What is the main difference between the railway and all other modes of transport?
- •A) Match the pictures and the types of engineering structures.
- •3. Read the text and fill the gaps with a word from the list.
- •Study the chart and complete the text.
- •Before you read answer the questions.
- •Now read the text quickly and check your answers.
- •3. Give Russian terms of the elements of a turnout.
- •4. Work in pairs. Explain the following statements.
- •5. Translate the following paragraph into Russian. Use a dictionary. Then compare your translation with a partner to improve. Location and construction
- •6. Read the Russian text, title and render it in English.
- •Put the verb into the correct form
- •Write a passive sentence.
- •Write questions using the passive. Then ask and answer the questions with a partner.
Write a passive sentence.
This method does not require additional measures. Additional measures are not required (due to this method).
In the earlier days of railway construction, workers often laid a temporary track to transport materials. In the earlier days of railway construction, a temporary track ___.
Track machines do all the necessary track maintenance tasks.
Rails guide wheels of rolling stock.
The sleepers support the rails.
Continuous welded rails provide a smoother running of trains.
North America and most of Europe use the standard gauge of 4 feet 8 1/2 inches.
Write questions using the passive. Then ask and answer the questions with a partner.
Ask about rails. (fix) How ___?
Ask about rails and sleepers. (lay) What ___?
Ask about wooden sleepers . (treat) What ___ with?
Ask about ballast. (use) What ___ for?
Ask about rail anchors . (fit) Where ___?
WebProject
Work in small groups. Get information to make a short presentation to your class on the aspects of a gauge.
The world standard gauge.
The standardisation of gauge in North America.
A narrow gauge. A wide gauge. Countries with different gauges.
The gauge problem.
These sites may help:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_tracks
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glossary_of_rail_terminology
Checklist
Assess your progress in this unit. Say which statements are true.
I can
I can
My listening and reading are good enough to understand most of each text in this unit.
I can use key words to discuss with my classmates.
track путь
permanent way верхнее строение пути
rail рельс
sleeper (UK)/tie (US) шпала
ballast (layer) балласт(ный слой)
fasteners = fastening скрепления
rail anchor противоугон
turnout стрелочный перевод
bridge timber мостовые брусья
crossing sleeper переводные брусья
strong прочный
stable устойчивый
provide обеспечивать
safety безопасность
smooth плавный
running ход
passing train проходящий поезд
fishplate стыковая накладка
length длина rail length рельсовое звкно
depends on зависеть от
traffic density грузонапряженность
axle load нагрузка на ось
bolt соединять, стягивать болтами
cross-section поперечное сечение
grade классифицировать
weight вес
produce производить
branch line ж.д.ветка
siding подъездной путь; запасный путь
yard сортировочная станция
guide направлять
wheel колесо
rolling stock подвижной состав
be subject to подвергаться
stress давление, нагрузка
durable долговечный
reliable надежный
support выдерживать, нести
alloy сплав
continuous welded rail бесстыковой рельс
The basic kinds of fixed bridges are beam, arch, and suspension. Movable bridges are bascule, swing span, vertical lift, floating, and transporter.
__________________________________________________________
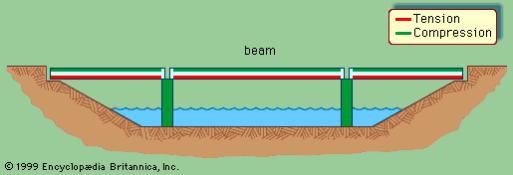
A beam bridge, with forces of tension represented by red lines and forces of compression by green lines.
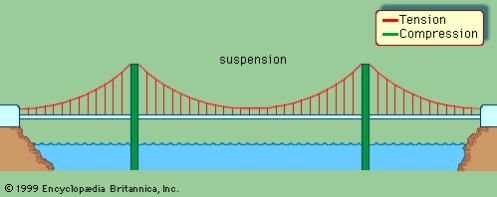
A suspension bridge, with forces of tension represented by red lines and forces of compression by green lines.
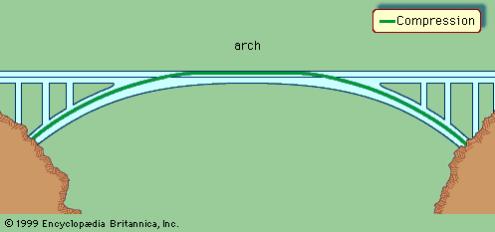
An arch bridge, with forces of compression represented by the green line.
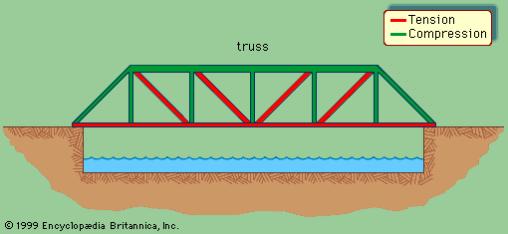
A single-span truss bridge, with forces of tension represented by red lines and forces of compression by green lines.
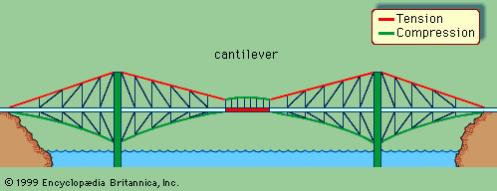
A cantilever bridge, with forces of tension represented by red lines and forces of compression by green lines.
