
module1_sample
.pdf
Module 1 |
Unit 3 ● Fishing Jobs |
9. Answer the following questions.
1.From your listening practice in Unit 1, you know that Peter is the mud engineer. What job do you think Barry does? Why do you think so?
2.Why is the kelly in the rathole now?
3.In the oil business, what is a fihs?
4.What are the crew going to do about the junk in the hole?
5.Keith politely asks Barry to explain what the driller and the floormen are doing. What expressions does he use?
10.Listen to the conversation between Michael and Barry. While you are listening, look at the diagram below.
|
Michael: |
Hello, Barry. |
|
Barry: |
Welcome to the rig, Michael. |
|
Michael: |
Well then, Barry, where's |
|
|
the BOP stack? |
BOP Stack |
Barry: |
Not here on the rig floor. |
|
|
It's underneath us. Follow |
|
|
me and I'll show you. |
|
(they climb down some steel steps) |
|
|
Barry: |
Here it is, right in the |
|
|
middle, under the rig floor. |
|
|
The rotary table is just above |
|
|
it and us. |
|
Michael: |
So this is the BOP stack. It's |
|
|
quite a big piece of machinery. |
|
Barry: |
It has to be big and strong. |
|
|
If there's a kick or a blowout, |
|
Figure 1.7 |
the BOP stack will shut in the |
|
well and control it. |
|
|
|
|
Michael: |
And what's this? What's this that the stack is standing on? |
|
Barry: |
That's the well head, Michael. That's where the casings are |
|
|
connected here at the top of the hole. |
|
Michael: |
I see. And what's the working pressure of the stack? |
|
Barry: |
That depends, of course, on the depth of the well and the |
|
|
pressure that we expect. The working pressure of this BOP |
|
|
system is ten thousand pounds per square inch. |
Michael: |
Ten thousand p. s. t. You must be planning to drill down a very |
|
long way. |
Barry: |
We are. Or at least, that's our programme. |
Michael: |
Do you mean that you may be lucky, and hit an oil zone soon? |
Barry: |
In this business, Michael, you never know. It's full of surprises. |
25

Unit 3 ● Fishing Jobs |
Module 1 |
11. Answer the questions.
1.BBC stands for British Broadcasting Corporation. BOP stands for blowout preventer. What does p. s. t. stand for?
2.Is Barry's rig onshore or offshore? How do you know?
3.A «kick» is a sudden push upwards, against the drilling fluid. If there's a kick, what will the BOP stack do?
4.What's the working pressure of the BOP system on Barry's rig?
5.The working pressure of BOP stacks are not all the same. What does the working pressure of a BOP stack depend on?
Grammar
12.Do you remember these sentences from the tape?
«We're going to try to latch on to the cutter now.» «We're going to use special fishing tools.»
«We're going to fish for it now.»
All given sentences mean that the crew plan to do something soon. Make sentences, as in the example.
There's a cutter in the hole (toolpusher/try to latch on to it). The toolpuserh is going to try to latch on to it.
1.There's something wrong with the bit (crew/trip the string out).
2.The mud's light (Peter/add bentonite to the tanks).
3.I'm not sure what to do (I/ask the driller).
4.I don't know what the trouble is (I/find out now).
13.Put the verbs in brackets bellow into the passive form, as in the example.
If the bit is dull (must change).
If the bit is dull, it must be changed.
1.Safety instructions (must obey).
2.Safety boots (must wear) on the rig floor at all times.
3.Fire doors (must keep) closed.
4.Smoking (must not permit) on or near the rig.
5.The string (must trip out) in stands, not in singles.
14.Examine these pairs of sentences in the Past Simple and the Present Perfect Tenses.
We've pulled out. We pulled out an hour ago. We've learned about the word «annulus».
We learned about the word «annulus» in Unit 1.
26

Module 1 |
Unit 3 ● Fishing Jobs |
Those actions all happened in the past. The first sentence in each pair, however, does not give us any information about when the actions happened. Examples:
1.We’ve stopped the drilling.
We stopped drilling when we lost the cutter.
2.I’ve completed the job.
I completed the job last shift.
Reform the sentences below without using the words in italics.
1.The drilling stopped when the cutter was lost.
2.As soon as they got the junk out of the hole, they ran in again.
3.We tried the junk basket at 5 o’clock and we tried the spear forty five minutes later but that fish is still down there.
4.While she was on the rig, Keith learned some interesting things about fishing operations.
5.The kelly's in the rathole because we hoisted the pipe out a couple of hours ago.
15.Make questions in the Past Simple Tense, as in the example.
Ask when the drilling stopped. (When/drilling/stop) (when the cutter was lost)
When did the drilling stop? — It stopped when the cutter was lost.
1.Ask when Barry arrived. (When/Barry/arrive) (an hour ago)
2.Ask when the bit broke down. (When/bit/break down) (very soon after it was run in)
3.Ask when the supply boat left.(When/supply boat/leave) (early yesterday afternoon)
4.Ask when time he came on shift. (What time/he/come on shift) (at 9.30 am)
5.Ask when he shut down the pumps. (When/he/shut down the pumps) (when the toolpusher told him to do so)
Revision box
16.Fill in the gaps with given words and word combinations.
Barrel, bit cutters, bore, borehole, casing, diameter, fish, fishing job, fishing tools, forced, grip, hard faced teeth, hoisting it, hoist, hole, hole items, junk, junk basket, latching on to, pipe, spear, spring loaded, teeth, well.
1.Sometimes, ________ of the drilling equipment get lost in the ________ .
2.When an item of equipment is lost in the hole it is called a ________ .
27

Unit 3 ● Fishing Jobs |
Module 1 |
3. A lost item is also called ________ . 4. Drilling cannot continue until the fish or the junk is recovered from the ________ . 5. To recover the lost item, a ________ is necessary. 6. Special ________ are used for
________ the fish and ________ up to the surface. 7. There are many types of ________ . 8. For example, there is a type of fishing tool called a
________ , there is another type called a ________ . 9. The spear is used for recovering the ________ . 10. The spear enters the ________ of the lost ________ . 11. The ________ of the spear, therefore, must be smaller than the ________ of the pipe in the hole. 12. When the spear enters the pipe, its ________ push out and ________ the inner sides of the pipe tightly. 13. That is usually possible to ________ the fish out of the
________ . 14. The ________ is used for ________ the smaller pieces of junk. 15. It is used for recovering the ________ , for example. 16. The bottom part of the basket is a shoe with ________ . 17. The shoe has a ________
in its centre. 18. The fish is ________ through the hole and enters the
________ of the basket. 19. ________ fingers prevent the fish from dropping out of the barrel and falling back into the ________ .
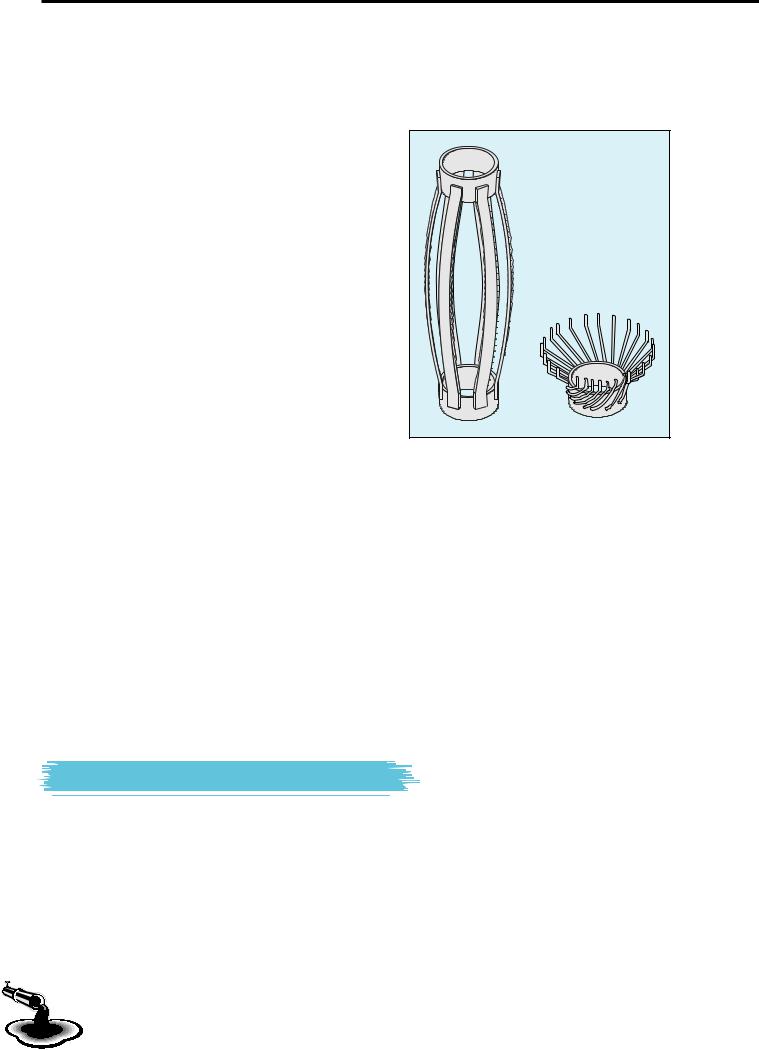
16. Describe the device or the process.
1.Junck basket.
2.Spear.
3.Getting prepared for fishing job.
17. Translate the sentences into English.
1.Иногда части бурильного оборудования теряются в скважине, и в таком случае необходимо произвести ловильные работы.
2.Часть оборудования, потерянная в скважине, называется «потеря» или «аварийное оборудование».
3.Для захвата потери и подъема ее на поверхность используются специальные ловильные инструменты: колокол и труболовка.
4.Перед тем, как начинать ловильные работы, необходимо достать колонну бурильных труб из скважины.
5.Для этого ведущую бурильную трубу ставят в нору, где ее разбирают на свечи.
28

Module 1 |
|
Unit 4a ● Cementing Jobs |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Study the following vocabulary before reading.
elevators |
latches that secure the drill pipe. Attached to the traveling |
|
block which raises and lowers the pipe from the hole. |
centralizers |
spring steel guides that are attached to casing to keep it |
|
centered in the hole. |
scratcher |
a device fastened to casing which removes the mud cake |
|
from the hole to condition it for cementing. It is made of |
|
stiff wire. |
wall cake |
the solid material deposited along the wall of the hole resulting |
|
from filtration of the fluid part of the mud into the formation. |
slurry |
suspension of cement in water, oil, or mixture of both. |
waiting on |
|
cement |
the time needed after the casing has been cemented to |
|
suspend operations and allow time for the cement to set or |
|
harden in the well bore. |
Reading
2. Read the text.
At predetermined times, the drill pipe is removed and the casing crew moves in to do its work. The first string of casing they run is called surface casing. Running casing into the hole is very similar to running drill pipe, except that the casing diameter is much larger and requires special elevators, tongs and slips to fit it. Also centralizers and scratchers are often installed on the outside of the casing before it is lowered into the hole. Centralizers keep the casing centered in the hole. Scratchers remove the wall cake formed by the drilling mud and allow the cement bond better to the formation.
After the casing string is run, the next task is to cement the casing in place. For this reason, bulk cement and handling equipment is moved out to the rig, making it possible to mix large quantities of cement at the site. The cementing crew mixes the dry cement with water, using a recirculating mixer, to make slurry (very thin, watery cement).
Special pumps pick up the cement slurry and send it up to a valve called a cementing head (also called a plug container) mounted on the topmost joint of casing that is hanging in the mast or derrick a little above the rig floor. Just before the cement slurry arrives, a rubber plug (called the bottom plug) is released from the cementing head and precedes the slurry down the inside of
29
Unit 4a ● Cementing Jobs Module 1
the casing until it stops or «seats» in the float collar, but continued pressure from the cement pumps opens a passageway through the bottom plug (by rupturing the diaphragm). So, the slurry passes through the bottom plug downwards and starts up the annulus gradually filling it up.
A top plug is similar to the bottom plug but it is solid. It is released with the last
portion of the cement slurry and some displacement fluid (usually drilling mud or water) moves it downwards. Meanwhile,
most of the slurry flows out of the casing and into the annular space. By the time the top plug seats or «bumps» the bottom plug in the float collar the cement is only in the casing below the float collar and the annulus.
After the cement is run, a waiting time is
needed to allow the slurry to harden. This period of time is referred to as waiting on cement (WOC). After the cement hardens,
tests may be run to ensure a good cement job.
3. Answer the following questions.
1.What kinds of jobs are needed after the well is complete?
2.Who does the cementing job?
3.What equipment and materials are used to perform cementing?
4.What is a «cementing head» and what is its purpose?
5.Why must the bottom plug have a diaphragm?
6.Why must the top plug be solid?
7.What might signal the cementing pump operator to shut down the pumps?
8.Can displacement fluid be mud?
9.What is WOC?
10.What is the other task for the rig crew after the WOC and tests?
Language development
4.Find in the text English equivalents for these words and word combinations:
1.погрузочно разгрузочное оборудование
2.рециркулирующая цементомешалка
3.самая верхняя труба
4.отверстие
30

Module 1 |
Unit 4a ● Cementing Jobs |
5.цементировочная головка
6.продавочная жидкость
7.закрыть
8.предшествовать
9.упорное кольцо
5.Mark the correct sentences with the letter T and the false ones with the letter F.
1.The rig crew is not competent enough to assist in cementing jobs.
2.There is special transport equipment to handle cement in bulk.
3.To mix dry cement with water a blender is used.
4.Slurry is a fluid for cementing the well.
5.A plug container is a part of a cementing head.
6.A plug container has two types of plugs.
7.Pumping continues till the cement slurry fills the annular space.
8.The top plug is absolutely similar to the bottom plug.
9.Drilling is resumed as soon as WOC is over.
10.Waiting on cement is allotted to allow the slurry to harden.
6.Complete the paragraph below using given words and expressions. Cement crew, pressure tested, to set, WOC, bit, nipples up.
________ casing, the casing and ________ run and cement a string of casing. After the ________ and tests indicate that the job is good, the rig crew attaches or ________ the blowout preventer (BOP) stack to the top of the casing. The BOP stack is ________ , and drilling is resumed with a smaller
________ that fits inside the surface casing.
Revision box
7.Fill in the gaps with given words and word combinations.
Operating company, except, production, the bottom of the hole, producing formation, seal off.
If the ________ decides to set production casing, casing will be brought to the well and for one final time, the casing and cement crew trip in and cement the casing string. Typically, the ________ casing is set and cemented through the pay zone, that is, hole is drilled to a depth beyond ________ , and the casing is set to a point near ________ . As a result, the casing and cement
31

Unit 4a ● Cementing Jobs |
Module 1 |
actually ________ the producing zone, but only temporarily. After the production string is cemented, the drilling contractor has almost finished his job
________ for a few final touches.
8. Explain the word or the process.
1.Slurry.
2.Cementing.
9. Translate the sentences into English
1.После спуска обсадной колонны следующей задачей становится цементирование спущенной колонны.
2.Оборудование хранения рассыпного цемента и по работе с ним доставляют к скважине, получая возможность приготовления большого количества цементного раствора на месте работ.
3.В определенное время бурильные трубы убирают, и к скважине прибывает бригада для спуска обсадной колонны.
4.Спуск обсадной колонны во многом напоминает спуск бурильной трубы намного больше, и поэтому требуются специальные элеваторы, ключи и клиновые захваты.
5.Центраторы устанавливают на обсадной трубе, и, поскольку они имеют дугообразные пружины, они удерживают обсадную трубу в центре скважины после ее спуска.
6.Контейнерная цементировочная головка устанавливается на самой верхней трубе обсадной колонны.
7.Оцентрованная обсадная колонна позже обеспечивает более эффективное цементирование.
8.Нижняя пробка останавливается или «садится» в муфте с обратным клапаном.
9.Скребки улучшают качество цементирования за счет удаления со стенки корки, образованной буровым раствором, что проделывается движением колонны вверх и вниз, либо ее вращением.
10.После закачки цемента наступает время ожидания затвердения цемента.
32

Module 1 |
|
Unit 4b ● Cementing Properties |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Study the following vocabulary before reading.
sack |
a weight measure. One sack contains 94 pounds of cement, |
|
100 pounds of bentonite, 100 pounds of barite. |
density |
weight of a volume of a material. |
slurry density |
the density of slurry expressed in either pounds per gallon or |
|
pounds per cubic foot. Suitable additives are used to modify |
|
slurry density. |
weight |
refers to the density of a drilling fluid or slurry. |
fluid loss |
the volume of fluid lost to a permeable material due to the |
|
process of filtration. |
slurry yield |
volume of slurry when one sack of cement (94 pounds) is |
|
mixed with desired amount of water containing any other |
|
additives such as accelerators, fluid loss control agents, etc. |
unpumpable |
unable to be pumped. |
Reading
2. Read the text.
According to physical properties and chemical composition, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has identified nine types of cement. They are:
●API Class A and B (Portland cement)
●API Class C (High early strength cement)
●API Class D, E and F (Retarded cement)
●API Class G and H (Basic cement)
●API Class ? (Special order only)
API Classes G and H cements are commonly used across a large geographical area. Classes A, B and C are used in specific geographic locations where down hole conditions require special cement properties. Classes D, E and F are pearly used and only in special situations. You may hear the terms Standard, Premium and Premium Plus when referring to oil field cements.
The properties of cements used in the oil field depend on the factors like geographic location, downhole conditions (depth, temperature, etc.), type of cement job, and type of mixing water.
The properties of cement slurry are influenced by factors such as water ratio of cement slurries (gal/sk), slurry density (lb/gal), and slurry yield (ft3/sk). One must remember that if there is too much water in the slurry free water appears on top of the slurry and retards setting. If there is too little water the slurry is thick and difficult to pump and accelerates setting.
33

Unit 4b ● Cementing Properties |
Module 1 |
Slurry density (or cement slurry weight) must be always carefully monitored, too. While on the job, one must be alert to slurry property changes that can be the result of improper slurry density. The slurry properties most affected by changes in density are thickening time, flow characteristics (pumpability), drilling fluid displacement efficiency, free water, settling, compressive strength, fluid loss.
What about slurry yield, too much cement rather than too little is always advisable.
The thickening time is the time required for a cement to become unpumpable. Such well conditions like bottomhole circulating temperature (BHT), well depth and well pressure influence the thickening time. One must always remember that temperature, rather than depth has the greatest effect on cement thickening times. It can also be affected by conditions such as water invasion, loss of water to the formation, shutdown during cement slurry placement and contamination.
Compressive strength is the amount of strength required to support a string of casing. It provides the basis for most WOC regulations. It is a generally accepted rule that a compressive strength of 500 psi is the minimally acceptable standard for most cement operations.
3. Answer the following questions.
1.What types of cement are there according to API?
2.Cement of what class do you think is used in our region?
3.What factors do the cement properties depend on?
4.Is too much water more preferable in the slurry than too little water? Why?
5.What is fluid loss?
6.Why is it so important to observe the slurry density?
7.What well conditions influence the thickening time of cement?
8.Which has more effect on cement thickening time, the temperature of the well or the depth?
9.What might the consequences of slurry contamination be?
10.Why should the cementing crew never stop moving the cement until it is in place?
11.What is a compressive strength?
Language Development
4.Find the English equivalents for these words and word combinations in the text:
1.химический состав
2.физические свойства
34
