
module1_sample
.pdf
Module 1 |
|
|
|
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Study the following vocabulary before reading.
boreholes |
in the petroleum industry, the words «borehole», «hole», |
|
«well» and «oil well» usually mean the same thing. |
rotary |
turning like a wheel. |
rotates |
turns around and around like a wheel. |
crushes |
breaks up into small pieces, using great power. |
cuttings |
the pieces of rock drilled by the bit. |
fluid |
anything that flows. Liquids, gases and melted substances |
|
are all fluids. Clay an earthy material, plastic when it is wet. |
|
The most common clay in drilling fluid is bentonite. Bentonite |
|
consists of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and aluminium |
|
(Al). |
is made up of |
consist of. Bentonite is made up of Ca, Mg and Al. |
hollow |
having an empty space on the inside. Drill pipe is hollow, so |
|
that mud can pass through it. |
hexagonal |
having six angles and six sides. |
floormen |
workers on a rig. Floormen are also called «roughnecks». |
|
A mud man or driller can tell a flooman what to do. |
dull |
not sharp; worn out; gone. If the bit is gone, it must be |
|
changed. |
driller |
the person in charge of the drilling. |
Reading
2. Read the text.
Oil is contained in rocks under the ground and in rocks under the sea. To find it, oilmen have to drill boreholes. The equipment for drilling these holes is the drilling rig. Most rigs work on the rotary system. A bit rotates at the end of a pipe. As the bit rotates, it cuts and crushes the rock at the bottom of the hole. The cuttings are carried to the surface by a special fluid. This fluid is called «mud». Mud is a mixture of clay, water and chemicals.
Look at the diagram of the rotary rig (Figure 1.1). Notice the string. This is made up of «joints» or «singles». Each joint or single is a hollow section of pipe, 30 ft. long. The string is made up of a number of these singles, all joined together. The bit is connected to the bottom of the string. At the top of the string there is a special pipe called the «kelly». The kelly isn’t round, but hexagonal. It fits into a hexagonal hole in the rotary table. The rotary table turns the kelly, the kelly turns the string, and the string turns the rotary table.
5
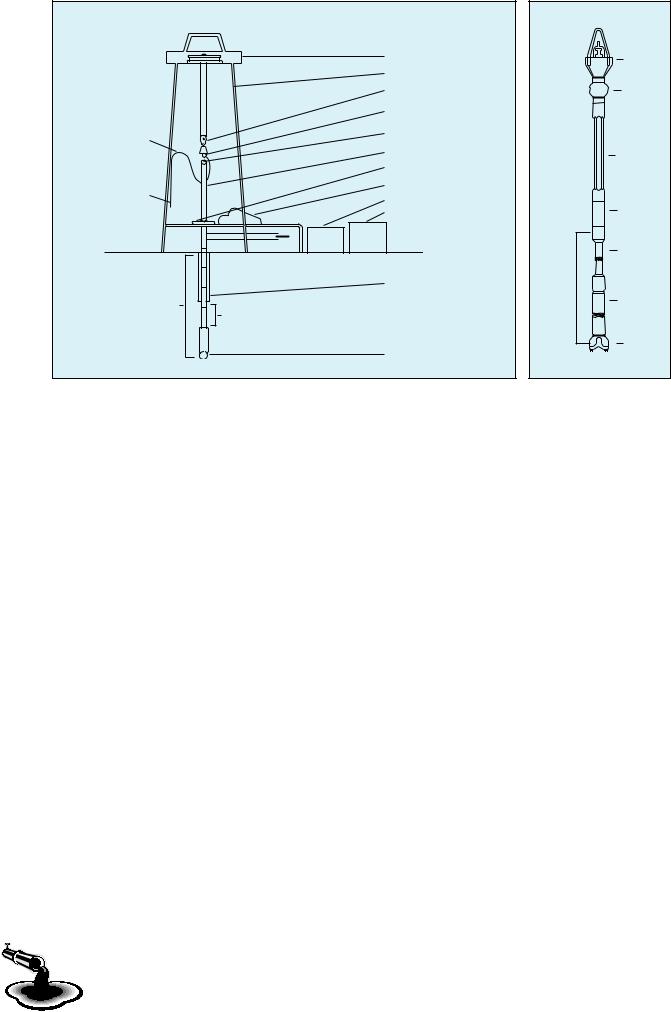
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
Module 1 |
|
Crown Block |
Swivel |
|
Derrick |
|
|
Travelling Block |
Kelly cock |
|
Hook |
|
Kelly Hose |
Swivel |
|
|
|
|
|
Kelly |
Kelly |
|
|
|
|
Rotary table |
|
|
Drawworks |
|
Standpipe |
Mud Tanks |
|
|
Kelly saver |
|
|
Shale Shaker |
|
|
sub |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drillpipe |
|
Annulus |
Drillstring |
|
|
|
|
String |
Drill collars |
|
|
|
|
Joint/Single |
|
|
|
Bit |
|
Bit |
|
|
Figure 1.1 |
Figure 1.2 |
Mud is not only used for carrying the cuttings up to the surface. It is also used for keeping the bit cool. The mud is pumped down through the bit string. It comes back up again through the annulus. The mud engineer or «mud man» is in charge of the mud. For example, he tells the floorman how to mix the mud at the mud tanks.
It is often necessary to pull the string out of the hole. There are different reasons for this. Perhaps, for example, the drill bit is dull. If the bit is dull, it must be changed. To do this, the driller and the floorman must trip the pipe. They must pull the string out (a), change the bit (b), and then run the string back into the hole (c). Tripping the pipe is also called «making a round trip». Round trips are expensive. Oilmen make them only if they must.
3. Answer the following questions.
1.What is the driller's job? (He is …)
2.How long is a single? How long is a joint?
3.As the bit rotates, what tow things does it do?
4.In the petroleum industry, what is mud?
5.What is the string made up of?
6.What is the name of the space between the drill pipe and the sides of the borehole? (The space is called…)
7.Who mixes the mud? Where is the mud mixed?
8.Oilmen make round trips only if they must. Why?
9.What is bentonite? What does it consist of?
10.Why is the drill pipe hollow?
6

Module 1 |
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
Language development
4.Find the English equivalents for these words and word combinations in the text:
1.буровая вышка
2.скважина
3.долото
4.крошит и режет породу
5.полые трубки
6.шестигранная форма
7.роторный стол
8.буровой раствор
9.произвести замену трубы
10.дорогостоящая процедура
5.Give the three forms of the following verbs and find the sentences with the verbs in the text.
To be, to call, to carry, to change, to come, to connect, to crush, to cut, to do, to find, to fit, to join, to have, to keep, to make, to mix, to pull, to pump, to rotate, to run, to tell, to trip, to turn, to use, to work.
6.Mark the correct sentences with the letter T and the false ones with the letter F.
1. |
Oil is contained in rocks under rivers. |
____ |
2. |
Most rigs work on the rotary system. |
____ |
3. |
The cuttings are carried to the surface by rotary. |
____ |
4. |
Mud is a mixture of clay, water and chemicals. |
____ |
5. |
At the bottom of the string there is a pipe, 30 ft. long. |
____ |
6. |
The rotary table turns the string. |
____ |
7. |
Mud is used for keeping the bit cool. |
____ |
7.Complete the paragraph below using the given words and expressions: cuttings, fluid, shale shaker, rotary, mud tanks, annulus, crushes.
The _______ bit cuts and _______ the rock at the bottom of the hole. Drilling _______ carries the _______ from the bottom of the hole, up the
_______ to the surface.
The cuttings are separated from the mud at the _______ and the clean mud then returns to the _______ .
7
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
Module 1 |
Grammar
8. Make the sentences using the Present Continuous tense.
1.Driller/examine/bit — e.g. Driller is examining the bit.
2.Floorman/mix/clay and chemicals.
3.Drilling crew/trip/pipe out of hole.
4.Mud man/check/drilling fluid.
5.Supply boat/deliver/bentonite.
6.Roughneck/move back/single.
9. Put the verbs in the brackets into the correct tense.
1. Oil ________ (to contain) in rocks under the ground and in rocks under the sea. 2. The string ________ (to make) up of a number of singles, all joined together. 3. The rotary table ________ (to turn) the kelly. The kelly
________ (to turn) the string, and the string ________ (to turn) the rotary bit. 4. Mud ________ (to use) for keeping the bit cool. 5. The mud engineer ________ (to be) in charge of the mud.
Listening
Listen to the conversation I.
Bob: |
Hey, George! Over there! |
George: |
Yeah? |
Bob: |
We'll have to trip the pipe. |
George: |
What? |
Bob: |
I said we’ll have to trip the pipe. |
George: |
What's wrong, Bob? |
Bob: |
I'm not sure. We'll have to bring it up and find out. |
George: |
Any ideas? |
Bob: |
I think the bit is gone. |
George: |
The bit? |
Bob: |
Aye, the bit. |
George: |
It was changed last shift, Bob. |
Bob: |
I know, but I think it's gone. Let's bring up the string and find out. |
|
(the crew trip the pipe out of the hole) |
Bob: |
Well, look at that. |
George: |
You were right. It is worn out. We'll have to change it. |
Bob: |
Thanks for telling me. |
8

Module 1 |
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
11. Answer the questions.
1.Who is in charge, Bob or George? Who's the driller? Who's the roughneck? What gives you the answers to these questions?
2.Bob uses another word for «yes». What word does he use?
3.‘Any ideas?’ Is a short way of saying ‘Have you got any ideas?’ Now make complete sentences for these short expressions: Any cigarettes? Any answers? Any tools for the job?
4.What does Bob want to find out? (He wants to find out if…)
5.Offshore, in the North Sea, drilling crews usually work 12 hour shifts. Onshore, they usually work 8 hour shifts. Do you work 12 hour or 8 hour shifts?
Listen to the conversation II.
Bob: |
Hey, George. Over there. |
George: |
What's up, Bob? |
Bob: |
Get me the mud man. |
George: |
Who? |
Bob: |
The mud man, George. The mud man. |
George: |
Anything wrong? |
Bob: |
Later. Now go and get Peter. Get a move on. |
George: |
Right, I'm going. |
|
(Peter comes to talk to Bob) |
Bob: |
Oh good, there you are, Peter. |
Peter: |
What can I do for you, Bob? |
Bob: |
The hole's getting tight. |
Peter: |
Tight? |
Bob: |
Yup. How's the mud? |
Peter: |
The mud's OK. |
Bob: |
What's bottom up? |
Peter: |
About an hour. |
Bob: |
All right then. We’ll give it an hour and see. |
Peter: |
Right. |
|
(an hour passes) |
Peter: |
How’s the hole now, Bob? |
Bob: |
Better. I don't think we have to worry. |
Peter: |
Good. |
Bob: |
How's the mud? |
Peter: |
No problem. |
Bob: |
Then let's make hole. |
9

Unit 1 ● The Rig |
Module 1 |
13. Read this explanation.
Bob is worried because the hole is becoming «tight». When the hole is tight, it's difficult to turn the string and to move the pipe up and down in the hole. There can be different reasons for this. Perhaps rock or sand is falling back into the hole. Perhaps the mud isn’t supporting the open sides of the hole. Perhaps the mud isn’t moving the cuttings away from the bit. To find out, Bob wants Peter to check the mud from the bottom of the hole.
How can Peter check the mud from the bottom of the hole? He must wait for the mud to travel from the bottom, up through the annulus to the surface. In a deep hole this can take a long time. The time that it takes is called «bottoms up». Bottoms up is the time that it takes for the mud to travel from the bottom of the hole to the surface. Some oilmen also use the expression «lag time».
14. Do the exercises below.
a.Choose the right meaning of the expression ‘What's up?’
1.What is that up there?
2.What can I do for you?
3.What's the matter?
b.Choose the right meaning of the expression ‘Get a move on’.
1.Move that for me.
2.Put something on.
3.Hurry up!
c.Why doesn't Bob explain to George what the trouble is?
d.Bob can say ‘Get me the mud man’ to George, but George cannot say ‘Get me the mud man’ to Bob. Why not?
e.What's another expression for «bottom up»?
15.Join the sentences below using so that + can.
Example: Drill pipe is hollow. The reason for this is to make it possible for the mud to pass through it.
Drill pipe is hollow, so that mud can pass through it.
1.Mud is heavy. The reason for this is to make it possible for the to support the open sides of the borehole.
2.Peter is going to the mud tanks. The reason for this is to make it possible for Peter to check the drilling fluid.
3.The driller is making a round trip. The reason for this is to make it possible for the driller to examine the bit.
4.Rotary bits are made of very hard steel. The reason for this is to make it possible for the rotary bits to drill through many feet of rock without getting dull too quickly.
5.The kelly is hexagonal. The reason for this is to make it possible for the rotary table to turn the kelly without slipping.
10

Module 1 |
Unit 1 ● The Rig |
Revision box
16.Fill in the gaps with given words and word combinations: annulus, bit, bit string, boreholes, chemicals, clay, crushes, cuts, cuttings, down, drilling rig, floorman, fluid, hole, in rocks, mud, mud man, mud tanks, oilmen, rotary, surface, water.
1. Oil is contained ________ under the ground and ________ under the sea. 2. To find it ________ have to drill ________ . 3. The equipment for drilling these holes is the ________ . 4. Most rigs work on the ________
system. 5. A ________ rotates, it ________ and ________ the rock at the bottom of the ________ . 6. The ________ are carried to the surface by a special ________ . 7. The fluid is called «mud». Mud is a mixture of
________ , ________ and ________ . 8. ________ is not only used for carrying the cuttings up to the ________ . 9. It is also used for keeping the
________ cool. 10. The mud is pumped ________ through the ________ . 11. It comes back up again, through the ________ . 12. The mud engineer or ________ is in charge of the mud. 13. For example, he tells the
________ how to mix the mud at the ________ .
17. Describe the device or the process.
1. Round trip. 2. Circulation of mud.
18. Translate the sentences into English.
1.Нефть содержится в породе под водой и под землей.
2.Буровая вышка — это оборудование, предназначенное для бурения скважин.
3.Вращаясь, долото крошит и режет породу на дне скважины.
4.Шлам доставляется на поверхность буровым раствором, который является смесью глины, воды и химикатов.
5.Колонна бурильных труб составляется из полых трубок, длина которых тридцать футов.
6.В верхней части колонны бурильных труб находится ведущая буровая труба шестигранной формы.
7.Роторный стол вращает ведущую бурильную трубу, которая, в свою очередь, вращает колонну бурильных труб, а она вращает долото.
8.Буровой раствор используется не только для доставки шлама на поверхность, но и для охлаждения долота.
9.Раствор прокачивается на дно скважины через колонну бурильных труб.
10.В обязанности растворщика входит следить за состоянием бурового раствора.
11.Если долото затупилось, нефтяники должны произвести замену трубы, но эта процедура дорогостоящая, поэтому производится в крайних случаях.
11

Unit 2 ● Jobs on the Rig |
Module 1 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Study the following vocabulary before reading.
boll weevil |
a rig worker or an oilfield worker without experience. |
|
Inexperienced workers are also described as «green». |
mousehole |
a shallow cased hole close to the rotary table. When making |
|
up a string, each single is stood here so that it can be |
|
connected quickly and easily to the kelly. |
hazard |
risk of harm; serious danger. |
misunderstood |
failed to understand. |
urgent |
needing immediate attention. |
scraping rust |
using a sharp tool to remove rust accumulations. Rust (ferric |
|
oxide Fe2O3) is an orange brown coating formed on iron |
|
when it is chemically attacked by water or moist air. |
hosing down |
using a water hose at pressure to clean up the rig or protect |
|
it from fire. |
dope |
special grease for pipe threads; i.e., some oily substance used |
|
to lubricate (to make smooth or slippery) the threads of |
|
tools, casing, etc. |
slush |
this is another word for «mud». |
minimum |
the least quantity. The opposite of «minimum» is «maximum». |
kelly bushing |
the part of the drive assembly which transmits motion to the |
|
kelly and permits the kelly to move vertically while rotating or |
|
still. All vertical measurements on the rig are taken from the |
|
RKB (rotary kelly bushing). |
verbal |
spoken. |
tubing |
small gauge pipe, usually of outside diameter (OD) 23/8 in. to |
|
27/8 in., also called «macaroni». Narrower gauge tubing is |
|
called «spaghetti». |
Reading
2. Read the text.
Drilling is one of those jobs where a man has to work his way up. Even if a man has a university or polytechnic education, most oil companies will want him to get rig experience by working on the floor with the rotary crew for a certain period. A boll weevil, even if he is well educated, can be a highly dangerous person around the rotary table. He may be a danger to himself (by breaking a
12
Module 1 Unit 2 ● Jobs on the Rig
leg in the mousehole, for example), and may be a hazard to the other members of the crew. What might happen, for instance, if he opened the wrong valve or misunderstood an urgent instruction?
On some rigs, the first step up the ladder is the job of roustabout. A roustabout does semi skilled labour such as scraping rust, hosing down, painting, carrying cans of dope, unloading materials and supplies, etc.
Having worked for a time as a roustabout, a man might be ready for the job of roughneck. Among a roughneck’s duties are such things as operating the cathead, handling the slips and tongs, standing pipe
back in the derrick, assisting in mixing the slush, and so on. Like a roustabout, a roughneck may have to be
told what to do. In general, though, roughnecks know their job well enough to
get on with it for the
minimum number of spoken instructions. It's noisy around the kelly bushing, and events frequently take place too fast for verbal orders to be given. Much of the time, roughnecks are expected to know automatically what must be done.
Next, between the positions of roughneck and driller, is the job of derrickman. The derrickman works from about 60 ft. to 90 ft. above the rig floor, near the top of the derrick, where he attaches or detaches the elevators when pipe or casing is run into or pulled out of the hole. The height at which he works depends on the length of the sections of pipe, casing or tubing that have to be handled. These may be in doubles, thribbles, or fourbles. The derrickman also cleans, oils, greases, inspects and repairs the pulley blocks and cables which are used to raise and lower sections of pipe and casing. When he isn’t busy on his platform up in the derrick, the derrickman usually has special responsibility for the slush pumps and tanks.
Rigs operate around the clock. The period from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. is the daylight tour, 4 p.m. to 12 midnight is the afternoon tour, and 12 midnight to 8 a.m. is referred to as «graveyard tour». Offshore crews usually work twelve hour tours.
3. Answer the following questions.
1.Which is closer to the RKB, the rathole or the mousehole? Why?
2.A derrickman must have excellent balance. Why? The platform that he uses is called «monkeyboard». For what reason?
3.Why might it be hazardous to the crew to have a green worker on the rig floor?
4.Define a thribble.
13

Unit 2 ● Jobs on the Rig |
Module 1 |
5.How are the tongs suspended at working height?
6.Would you like to work as a roustabout? Give the reasons for your answer.
7.What is the derrickman responsible for? Who is he responsible to? Who is the toolpush responsible to? What is the drilling superintendent responsible for?
8.If you knew that you had misunderstood the instruction, what could you do? If you didn't know that you had misunderstood an instruction, what might you do?
9.Why must dope be viscous?
10.«…the first step up the ladder…» What ladder?
Language development
4.Find the English equivalents for these words and word combinations in the text:
1.большинство нефтяных компаний
2.бригада
3.бурение
4.верховой работает на высоте
5.в круглосуточном режиме
6.любой новичок
7.носить бочки со смазкой
8.проложить себе дорогу
9.работа, не требующая высокой квалификации
10.разгружать различные материалы
11.соединение или отсоединение подъемников
12.соскребать ржавчину
13.сфера деятельности
14.техническое образование
15.разнорабочий
5.Say whether the following sentences are true or false. Correct the false ones.
1.Macaroni is tubing of OD less than about 23/8 in.
2.A fourble is a section of casing, pipe or tubing consisting of four singles screwed together.
3.The central hole in the kelly bushing is square.
4.If pipe threads aren’t properly doped the connections will stick.
5.If a crew is working an 8 hour tour and for some reason they have to work 101/2 hours, they will late be paid 21/2 hours’ overtime.
14
