
Physical properties
Nitrogen is a colorless gas without any smell.
Since three bonds between atoms in the molecule of N2 are covalent, molecular nitrogen is nonpolar. This gas is poorly soluble in polar solvents, for example, in H2O. 2.35 volume of nitrogen gas is dissolved in 100 volumes of H2O at STP.
Strong intramolecular nonpolar covalent| bond in N2 is|appear| a result|cause| of a very weak intermolecular| interaction between molecules of this substance. That is why|that is why| nitrogen gas has very low boiling and melting temperatures:
b.p.= -1960С, m.p.= -2100С.
As a
result of the bond strength of N2
molecule,
the
rate constant of decomposition process N2
2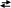 N
is
extremely low (k
=
10-120).
The degree of dissociation of N2
reaches only 0.1% even at 30000.
N
is
extremely low (k
=
10-120).
The degree of dissociation of N2
reaches only 0.1% even at 30000.
On that| reason,|cause| most of nitrogen compounds|halving,compound,junction,joint,coupling| are endothermic. In addition, entropy of their formation|formation| is negative because N2 is a gas. On that reasons molecular nitrogen is a relatively inactive| substance, and|but| compounds|halving,compound,junction,joint,coupling| of nitrogen are thermally unstable and have tendency to decompose at moderate heating |in relation to| easily. That is why|that is why| elemental nitrogen exists mainly in the free state on Earth being unavailable for plants nourishing.
Phosphorus

waxy white (yellow), red, violet and black phosphorus
Physical properties. A molecule of phosphorus consists of four atoms, P4, in the gaseous state (t < 1000oC). Its thermal dissociation takes place at higher temperature and diatomic, P2, molecules appear dissociated, in turn, into isolated atoms at t > 2500oC.
The total number of allotropes of phosphorus that has been described in literature is 11; the most investigated are white, red, and black allotropes.
 White
phosphorus
is
a
transparent, soft (waxy) solid, (density is 1.8 g/cm3),
m.p. = 44 oC,
b.p. = 280.5 oC.
It has a molecular crystal lattice, with P4
molecules occupying
crystallographic positions. P4
has a regular tetrahedron structure (
P-P-P 60o):
White
phosphorus
is
a
transparent, soft (waxy) solid, (density is 1.8 g/cm3),
m.p. = 44 oC,
b.p. = 280.5 oC.
It has a molecular crystal lattice, with P4
molecules occupying
crystallographic positions. P4
has a regular tetrahedron structure (
P-P-P 60o):
It is worth noting that the composition of a phosphorus molecule was detected by measurements of elevation of its solutions boiling temperature in non-polar solvent.
White phosphorus molecules have weak intermolecular forces of attraction. That is why, this allotrope is volatile, fusible, is cut with a knife and soluble in nonpolar solvents (CS2, ether). Water dissolves white phosphorus a little; it is usually stored under water layer.
The valence angle P-P-P is small and P4 molecule is in the state of tension, so it is extremely unstable and chemically very active. It interacts vigorously with O2, Hal2, S and metals. It easily burns (spontaneous inflammability is possible) even after touch with hot water test tube. Oxidation of P accompanies heating and air glow (phosphorescence). The mechanism of this process is not fully understood. Perhaps the reason of glow is slow oxidation of P with formation of volatile lower oxides PO, PO2, P2O3; electronic transitions in them cause phosphorescence.
B

White P is very poisonous, its lethal dose is 0.1 g.
Red phosphorus is a dark-red fine non-volatile substance, its sublimation temperature is 400oC. Its density is 2.0 - 2.4 g/cm3.
Red allotrope is obtained:
Рwhite
![]() Рred
Но
=
-16.7 kJ / mol
Рred
Но
=
-16.7 kJ / mol
(This process needs continuous heating in a sealed vessel).
Red phosphorus is not soluble in CS2, less toxic than white allotrope. It is oxidised with more difficulties than white P, does not glow in the dark and only when selfigniting at t> 250oC.
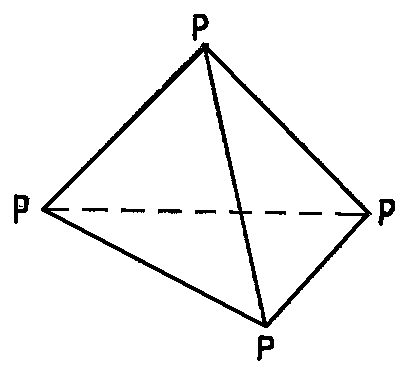
Solvents dissolving Pred are not known. The reason is its polymeric structure consisting of octahedrons connected to endless chains. Polymeric structure causes chemical inertness of Pred.
The main consumer of red phosphorus is matchmaking industry [a match’s head is a mixture of KClO3, K2Cr2O7, glass, glue; a block contains a mixture of Pred, Sb2S3, glue].
Red P is not a completely homogeneous product, its properties are somewhat dependent on the conditions of preparation. It consists of very small crystals of violet phosphorus in a mixture with solution of white in violet P.
Violet. Violet phosphorus is a thermodynamically stable form of phosphorus that can be produced by day-long heating of red phosphorus above 500oC or when phosphorus was recrystallized from molten lead.
Black. This is the most stable modification, which is formed from white allotrope when heated under pressure:
Рwhite
![]() Рblack
Но
= - 41.8
kJ/mol
Рblack
Но
= - 41.8
kJ/mol
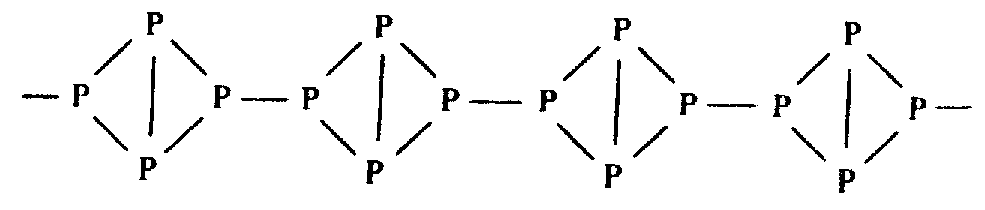
In appearance and properties it resembles graphite: wet to the touch, easily divided into flakes. Like Pred each black phosphorus atom has bonds with three neighbours. Crystal lattice consists of “ribbed” layers of atoms. The distance between neighbouring layers of P atoms makes up 0.387 nm. If white and red P are dielectrics, black P has a semiconductive energy gap 0.33 eV. It is also extremely low soluble in any solvent, chemically very inactive, non-toxic, with self-ignition temperature 490oC. Density - 2.7 g/cm3.
Other allotropes. There are the so-called purple, ruby, light red modificationsformed as a result of polymerization of white phosphorus, proceeding in different solvents or under high pressure at the presence of various catalysts. These modifications differ in physical properties and have different resistance to chemical attack of oxidants.
Arsenic, Antimony, and Bismuth Allotropes
As has several allotropic forms. Gray metallic allotropic form of arsenic possesses maximal stability. Yellow nonmetallic allotrope of arsenic that consists of As4 molecules (r = 2,0 g/сm3) can be obtained at rapid cooling. It is isomorphous to white phosphorus and well soluble in CS2. Stable black arsenic can be obtained after sublimation of arsenic in the stream of hydrogen (r = 4,7 g/сm3).
Sb. Yellow nonmetallic Sb is less stable than yellow arsenic.
Bi. Nonmetallic allotropes are absent.
Grey arsenic, stibium, bismuth that are stable at STP have metallic luster and conduct electricity. Their structure is layered like that of black phosphorus.
In the series As—Sb—Bi the difference between internuclear distances inside and between layers decreases (0,063—0,050—0,037 nm), whereas typical metals have identical distances.
 All
elements are brittle and easily form powders.
All
elements are brittle and easily form powders.
