
- •The words to be studied in 1.1:
- •An Ecosystem
- •What Do You Know about Ecology
- •The words to be studied in 1.2:
- •Fast Facts about Biomes
- •The Taiga Biome
- •The words to be studied in 1.3:
- •Ecological Problems – Definition
- •Ecosystem-Based Management
- •The words to be studied in 1.4:
- •Pollution Facts
- •Main Sources of Pollution and General Health of Our Planet
- •The words to be studied in 1.5:
- •Climate Change: Who is to Blame?
- •What You Can Do about Global Warming
- •The words to be studied in 1.6:
- •Global Dimming and Global Warming: How They Are Connected
- •The words to be studied in 1.7:
- •What are the major water pollutants?
- •The words to be studied in 1.8:
- •Green living
- •Living Green – What Does It Mean
- •Durable
- •The Green Tips
- •Facts and Fiction
- •The words to be studied in 1.9:
- •Ecological Monitoring
- •Ecological Monitoring
The words to be studied in 1.7:
industrial/household waste промышленные/бытовые отходы
smog густой туман с дымом и копотью; смог
authorized landfill site разрешенное место для захоронения отходов
paddy field рисовое поле
soil fertilization удобрение почвы
intensive husbandry интенсивное земледелие
water table водная поверхность; уровень грунтовых вод
pesticide пестицид; средство для борьбы с вредителями
intensive farming интенсивное животноводство
septic tank септик
animal dung органическое удобрение; навоз, помёт
to deplete истощать
sewage system канализационная система
untreated waste необработанные сточные воды
suspended sediment взвешенный осадок
lead свинец
suspended particulate matter взвешенные частицы
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) фреон
Exercise 1. Study the definitions (Figures 14, 15) given by Visual Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Look at the pictures and make up sentences about the pollution sources.
When answering you can use:
I think … can contribute to air/water pollution.
The main air/water pollutants are … .
I see that … can contribute to air/water pollution.
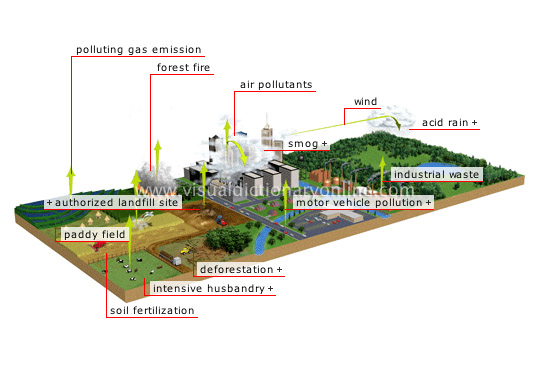
Air pollution: the presence in the atmosphere of large quantities of particles or gases produced by human activity; these are harmful to both animal and plant life.
Figure 14
Water pollution: the cycle of the Earth’s waters is continuous, carrying and spreading pollutants introduced by human activity all around the planet.
Figure 15
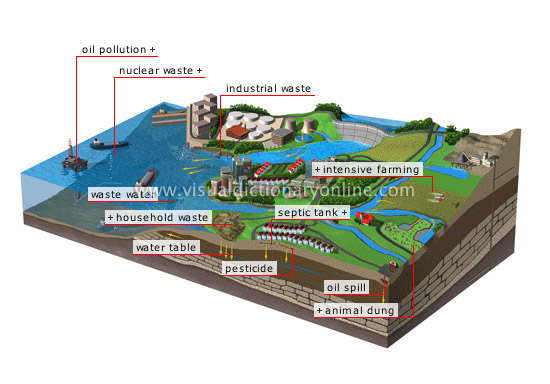
Exercise 2. Can you guess the meaning of the words: industrial/household/nuclear waste, smog, authorized landfill site, paddy field, soil fertilization, intensive husbandry, water table, pesticide, intensive farming, septic tank, animal dung?
If you are not sure about the meaning, look the words up in the dictionary.
Exercise 3. In pairs/groups try to find out what chemical pollutants are the main ones in both types of pollution. Information from Exercise 1 can help you.
When discussing you can use these expressions:
It seems to me that … can be the main pollutant in air/water pollution.
I/we may be wrong, but … can be the main pollutant in air/water pollution.
I/we believe that … .
I’m sure that … .
Exercise 4. Read the articles What are the major water pollutants? and Here are the major air pollutants and their sources. Check if your previous ideas about the main air and water pollutants were right.
What are the major water pollutants?
There are several groups of water pollutants. The first are disease-causing agents. These are bacteria, viruses and parasitic worms that enter sewage systems and untreated waste.
A second group of water pollutants is oxygen-demanding wastes; wastes that can be decomposed by oxygen-requiring bacteria. When large populations of decomposing bacteria are converting these wastes it can deplete oxygen levels in the water. This causes other organisms in the water, such as fish, to die.
A third category of water pollutants is water-soluble inorganic pollutants, such as acids, salts and toxic metals. Large quantities of these compounds will make water unfit to drink and will cause the death of aquatic life.
Another class of water pollutants are nutrients; they are water-soluble nitrates and phosphates that cause excessive growth of algae and other water plants, which deplete the water's oxygen supply. This kills fish and, when found in drinking water, can kill young children.
Water can also be polluted by a number of organic compounds such as oil, plastics and pesticides.
A very dangerous category is suspended sediment, because it causes depletion in the water's light absorption and the particles spread dangerous compounds such as pesticides through the water.
Also, water-soluble radioactive compounds can cause cancer, birth defects and genetic damage and are very dangerous water pollutants.
Here are the major air pollutants and their sources
By Ms Krishna Bharali, the Energy and Recourses Institute, 2009
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of fuels including petrol, diesel, and wood. It is also produced from the combustion of natural and synthetic products such as cigarettes.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the principle greenhouse gas emitted as a result of human activities such as the burning of coal, oil, and natural gases.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are gases that are released mainly from air-conditioning systems and refrigeration. When released into the air, CFCs rise to the stratosphere, where they come in contact with few other gases, which leads to a reduction of the ozone layer that protects the earth from the harmful ultraviolet sun radiation.
Lead is present in petrol, diesel, lead batteries, paints, hair dye products, etc. It can cause nervous system damage and digestive problems and, in some cases, cause cancer.
Ozone occurs naturally in the upper layers of the atmosphere. This important gas shields the earth from the harmful ultraviolet sun radiation. However, at the ground level, it is a pollutant with highly toxic effects. Vehicles and industries are the major source of ground-level ozone emissions.
Nitrogen oxide (Nox) causes smog and acid rain. It is produced from burning fuels including petrol, diesel, and coal.
Suspended particulate matter (SPM) consists of solids in the air in the form of smoke, dust, and vapour that can remain suspended for extended periods. These particles, when breathed in, can stay in our lungs and cause lung damage and problems.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is a gas produced from burning coal, mainly in thermal power plants. Some industrial processes, such as production of paper, produce sulphur dioxide. It is a major contributor to smog and acid rain.
Exercise 5. Read the articles again. Write two annotations (summaries) up to 100 words for a scientific journal. To write an annotation (summary) you should mention: 1) the author, 2) the name of the article, 3) where and when it is published and 4) main ideas of the article.
Also, there are useful word combinations for annotation writing:
The author of the article/text is … .
The article/text/book was published … .
The text/article under review gives us a sort of information about … .
The subject of the text is … .
At the beginning (of the text) the author describes… (explains …/touches upon …/analyses …/ characterizes …/underlines …/gives account of …).
The article begins with the description of …/a review of …/the analysis of … .
The article opens with … .
Then/After that/Next/Further on the author gives a detailed analysis (description)… /goes on to say that … .
To finish with, the author describes … .
The author sums it all up by saying … .
Unit 1.8 Are You Green Enough?
