
KAPLAN_USMLE_STEP_1_LECTURE_NOTES_2018_BIOCHEMISTRY_and_GENETICS
.pdf

U S M L E®
STEP 1
Lecture Notes 2018
Biochemistry and Medical Genetics

USMLE® is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME), neither of which sponsors or endorses this product.
This publication is designed to provide accurate information in regard to the subject matter covered as of its publication date, with the understanding that knowledge and best practice constantly evolve. The publisher is not engaged in rendering medical, legal, accounting, or other professional service.
If medical or legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought. This publication is not intended for use in clinical practice or the delivery of medical care. To the fullest extent of the law, neither the Publisher nor the Editors assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property arising out of or related to any use of the material contained in this book.
© 2018 by Kaplan, Inc.
Published by Kaplan Medical, a division of Kaplan, Inc. 750 Third Avenue
New York, NY 10017
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Course ISBN-13: 978-1-5062-2827-3
All rights reserved. The text of this publication, or any part thereof, may not be reproduced in any manner whatsoever without written permission from the publisher. This item comes as a set and should not be broken out and sold separately.
Retail ISBN-13: 978-1-5062-3954-5
Kaplan Publishing print books are available at special quantity discounts to use for sales promotions, employee premiums, or educational purposes. For more information or to purchase books, please call the Simon & Schuster special sales department at 866-506-1949.

Editor
Sam Turco, PhD
Professor, Department of Biochemistry
University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Lexington, KY
Contributors
Roger Lane, PhD
Professor, Department of Biochemistry
University of South Alabama College of Medicine
Mobile, AL
Ryan M. Harden, MD, MS
Physician, Family Medicine
Gateway Family Health Clinic, Ltd
Sandstone, MN
Assistant Professor, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health
University of Minnesota Medical School, Duluth Campus
Duluth, MN

We want to hear what you think. What do you like or not like about the Notes? Please email us at medfeedback@kaplan.com.

Table of Contents
Part I: Biochemistry
Chapter 1: Nucleic Acid Structure and Organization 3
Chapter 2: DNA Replication and Repair 17
Chapter 3: Transcription and RNA Processing 33
Chapter 4: The Genetic Code, Mutations, and Translation 49
Chapter 5: Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression 75
Chapter 6: Genetic Strategies in Therapeutics 87
Chapter 7: Techniques of Genetic Analysis 103
Chapter 8: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 119
Chapter 9: Hormones 135
Chapter 10: Vitamins 149
Chapter 11: Energy Metabolism 163
Chapter 12: Glycolysis and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase 175
Chapter 13: Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation 193
Chapter 14: Glycogen, Gluconeogenesis, and the Hexose
Monophosphate Shunt 205
Chapter 15: Lipid Synthesis and Storage 223
Chapter 16: Lipid Mobilization and Catabolism 243
Chapter 17: Amino Acid Metabolism 265
Chapter 18: Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism 289
v
Part II: Medical Genetics
Chapter 1: Single-Gene Disorders 303
Chapter 2: Population Genetics 333
Chapter 3: Cytogenetics 347
Chapter 4: Genetics of Common Diseases 371
Chapter 5: Recombination Frequency 379
Chapter 6: Genetic Diagnosis 391
Index 407
Additional resources available at
www.kaptest.com/usmlebookresources
vi

PART I
Biochemistry

Nucleic Acid Structure
and Organization
Learning Objectives
Explain information related to nucleotide structure and nomenclature
Use knowledge of organization of DNA versus RNA
Understand general features of a chromosome
CENTRAL DOGMA OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
An organism must be able to store and preserve its genetic information, pass that information along to future generations, and express that information as it carries out all the processes of life. The major steps involved in handling genetic information are illustrated by the central dogma of molecular biology.
Replication
Transcription Translation
DNA 
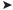
 RNA
RNA 
 Protein
Protein
Reverse transcription
Figure I-1-1. Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Genetic information is stored in the base sequence of DNA molecules. Ultimately, during the process of gene expression, this information is used to synthesize all the proteins made by an organism.
Classically, a gene is a unit of the DNA that encodes a particular protein or RNA molecule. Although this definition is now complicated by our increased appreciation of the ways in which genes may be expressed, it is still useful as a working definition.
Gene Expression and DNA Replication |
High-Yield |
|
Gene expression and DNA replication are compared below. Transcription, the first stage in gene expression, involves transfer of information found in a dou- ble-stranded DNA molecule to the base sequence of a single-stranded RNA molecule. If the RNA molecule is a messenger RNA, then the process known as translation converts the information in the RNA base sequence to the amino acid sequence of a protein.
1
3
