
Individual Home Work 3
Questions for this IHW are by my presentations for Module 3: Lectures 7 – 12.
Problems
1 The tungsten filament of a certain 100-W light bulb radiates 2 W of light. (The other 98 W is carried away by convection and conduction.) The filament has a surface area of 0.250 mm2 and an emissivity of 0.950. Find the filament’s temperature. (The melting point of tungsten is 3683 K.)
2 A 75-kg cross-country skier moves across the snow. The coefficient of friction between the skis and the snow is 0.2. Assume that all the snow beneath his skis is at 0°C and that all the internal energy generated by friction is added to the snow, which sticks to his skis until it melts. How far would he have to ski to melt 1 kg of snow?
3
The threshold wavelength for the photoelectric effect in tungsten is 270 nm. Calculate the work function of tungsten, and calculate the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron can have when radiation of 120 nm falls on tungsten.
4
The wavelength of the incoming X rays in a Compton scattering experiment is 7.1*10-2 nm and the wavelength of the outgoing X rays is 7.3*10-2 nm. At what angle was the scattered radiation measured?
5
For what range of values of n will the radiation from singly ionized helium lie in the visible range; that is, with wavelengths in the range 400 nm to 700 nm?

6
The Paschen series is a series of spectral lines for hydrogen whose wavelengths correspond to
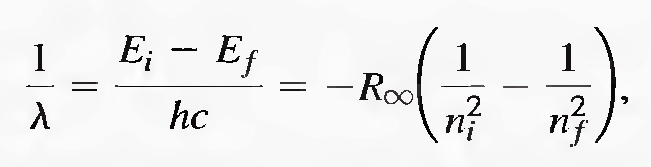
when nf = 3
(a) What are the quantum numbers of the states involved in the three transitions of the Paschen series with the longest wavelengths?
(b) Calculate the wavelengths for the transitions of part (a).
Are these wavelengths in the visible or infrared regions?

7
A light source at A = 600 nm emits radiation at a rate of 0.01 W. How many photons per second are emitted by that source?
8
The energy density of electromagnetic radiation in some region of space is 3.2*10-8 J/m3. Assume that the radiation has a wavelength 610 nm. What is the photon density?
9
Consider a case of Compton scattering in which a photon collides with a free electron and scatters backward while it gives up half its energy to the electron
(a) What are the frequency and energy of the incident photon?
(b) What is the electron's velocity after the collision?

10
The uncertainty in momentum of an electron with a kinetic energy of approximately 6 keV is 12 percent. What is the minimum uncertainty in its position?
Individual Home Work 3 Questions
Questions for this IHW are by my presentations for Module 3: Lectures 7 – 12.
Problems
1
What is the value of the Fermi energy of calcium, which has two valence electrons per atom? The gram-atomic weight of calcium is 40.1 g/ mol, and its mass density is 2.30 g/ cm3.
2
What is the speed of an electron with the Fermi energy in magnesium, given that ne = 8.60*1028 electrons/m3?
3
Calculate the Fermi energy for the neutrons confined to the nucleus 96Mo, which roughly forms a sphere of radius 5.5*10-15 m. (There are 54 neutrons in the 96Mo nucleus).
4
Assume that the Fermi energy depends only on ћ, the electron density ne, and the speed of light c. Use dimensional analysis to find that dependence (just find the powers in the formula Fe= ћ c ne).
5
A simple pendulum consists of a ball of mass M hanging from a uniform string of mass m and length L, with m << M. If the period of oscillations for the pendulum is T, determine the speed of a transverse wave in the string when the pendulum hangs at rest.
6
How many neutrons and how many protons do the following nuclides have: 9Be, 13C, 22Na , 31P , 57Fe , 72Ge, 107Ag , 131Cs, 208Pb, 241Am?
7
An particle with (nonrelativistic) speed V is approaching the center of a nucleus of radius R and charge + Ze. Calculate the distance of closest approach. Assume that the nucleus is much heavier than the a particle. For what value of V wi1l the distance of closest approach equal R?
8
A 6 MeV proton collides head-on (i.e. this is a central collision – 180° scattering) with a gold atom.
(a) How close did the proton come to the center of the nucleus?
(b) To the surface of the gold nucleus? (Assume that the proton is pointlike.)
9
According to the shell model, closed shells of protons occur for Z = 2, Z = 8, Z = 20. Z = 40. Z = 70 and similarly for neutrons. Use the shell model to determine whether the following nuclides have a closed shell (magic number) for either neutrons or protons: 15N, 39K, 40Ca, 56Fe, 140Ce. Does your answer correlate to whether the respective nucleus is tightly bound?
10
Assume that the two protons inside a He nucleus are approximately 4 fm apart.
(a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them.
(b) Use the binding energy of 4He to estimate the nuclear force.
(c) Find the ratio of the two forces.
