
- •Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part2»
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Some Properties of Nuclei
- •Nuclear Binding Energy
- •Nuclear Binding Energy
- •Nuclear Models
- •Nuclear Models
- •Nuclear Models
- •Nuclear Models
- •Radioactivity
- •Radioactivity
- •Radioactivity
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •The Decay Processes
- •Natural Radioactivity
- •Nuclear Reactions
- •Nuclear Reactions
- •Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and
- •Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and

Nuclear Models
The Liquid-Drop Model
In the liquid-drop model, the nucleons interact strongly with one another and undergo frequent collisions as they jiggle around within the nucleus. This jiggling motion is analogous to the thermally agitated motion of molecules in a drop of liquid. 
Four major effects influence the binding energy of the nucleus in the liquid-drop model:
•The volume effect.
•The surface effect.
•The Coulomb repulsion effect.
•The symmetry effect.
the semiempirical binding-energy formula

Nuclear Models
The Liquid-Drop Model
The binding-energy curve plotted by using the semiempirical binding- energy formula (redbrown). For comparison to the theoretical curve, experimental values for four sample nuclei are shown.
Nuclear Models
The Shell Model
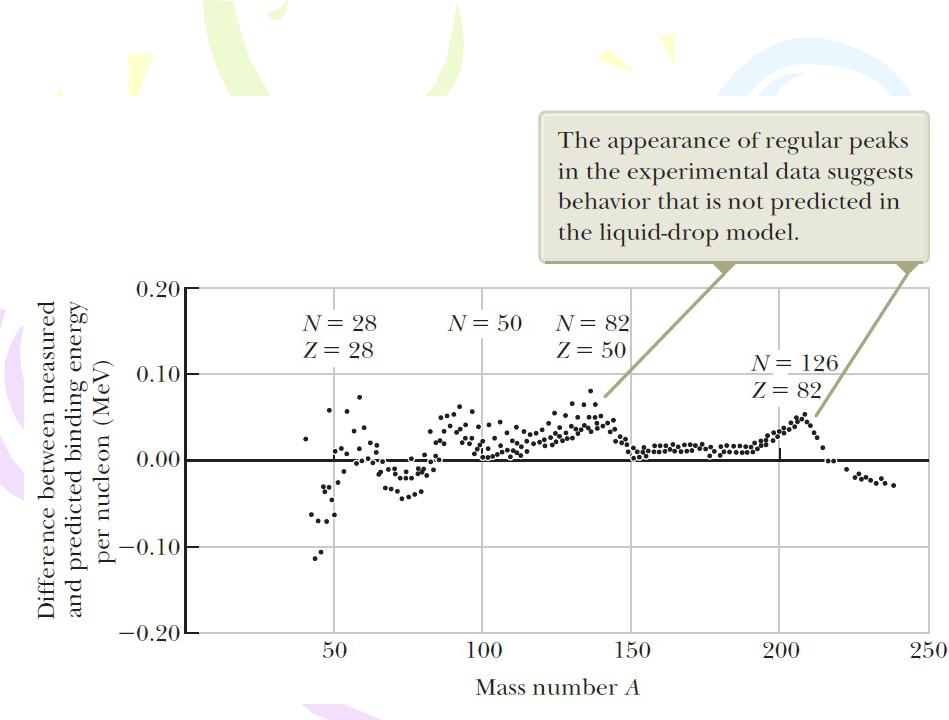
The difference between measured binding energies and those calculated from the liquid-drop model is a function of A.
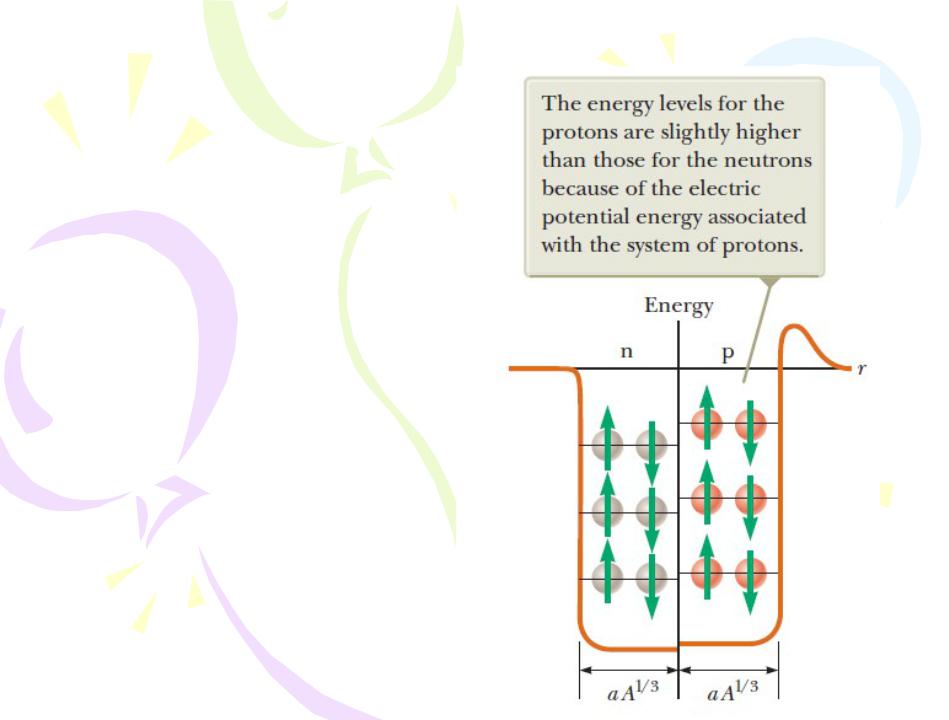
Nuclear Models
The Shell Model
A square potential well containing 12 nucleons. The red spheres represent protons, and the gray spheres represent neutrons.

Radioactivity
The process of spontaneous emission of radiation is called radioactivity. 
where λ, called the decay constant, is the probability of decay per nucleus per second.

Radioactivity
where the constant N0 represents the number of undecayed radioactive nuclei at t=0.
The decay rate R, which is the number of decays per second, can be obtained by equation:
where R0= λN0 is the decay rate at t=0. The decay rate R of a sample is often referred to as its activity.

Radioactivity
The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time interval during which half of a given number of radioactive nuclei decay.
A frequently used unit of activity is the curie (Ci), defined as
This value was originally selected because it is the approximate activity of 1 g of radium. The SI unit of activity is the becquerel (Bq):

The Decay Processes
Alpha Decay
where X is called the parent nucleus and Y the daughter nucleus. 
When the nucleus of one element changes into the nucleus of another as happens in alpha decay, the process is called spontaneous decay.
the disintegration energy of the system
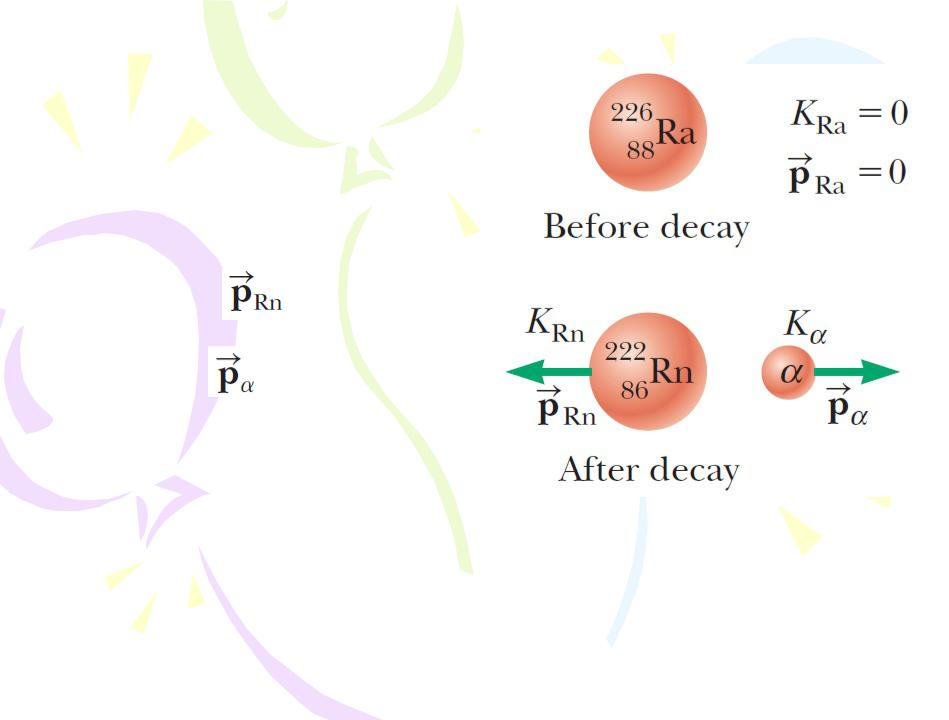
The Decay Processes
Alpha Decay
The alpha decay of radium-226. The radium nucleus is initially at rest. After the decay, the radon nucleus has kinetic energy KRn and
momentum and the alpha particle has kinetic energy Ka and
momentum .

The Decay Processes
Alpha Decay
