
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Introduction
- •The importance of cross-sectional anatomy
- •Orientation of sections and images
- •Notes on the atlas
- •References
- •Acknowledgements
- •Interpreting cross-sections: helpful hints for medical students
- •BRAIN
- •HEAD
- •NECK
- •THORAX
- •ABDOMEN
- •PELVIS
- •LOWER LIMB
- •UPPER LIMB
- •Index

102
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
4 |
1 |
|
|
|
39 |
10 |
8 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
||||
|
9 |
|
6 |
13 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
38 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
18 |
15 |
|
||
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
||
40 |
|
12 |
|
16 |
|
||
|
|
19 |
25 |
||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
22 |
||
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
23 |
26 |
41 |
37 |
|
|
21 |
24 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32
30
31
1 |
Platysma |
12 |
Inferior constrictor muscle |
|
within foramen |
30 |
Splenius |
|
uncovertebral synovial |
2 |
Anterior jugular vein |
|
of pharynx |
|
transversarium |
31 |
Ligamentum nuchae |
|
joint (of Lushka) |
3 |
Sternohyoid |
13 |
Sternocleidomastoid |
22 |
Phrenic nerve |
32 |
Spine of fifth cervical |
38 |
Lateral lobe of thyroid |
4 |
Omohyoid |
14 |
Common facial vein |
23 |
Scalenus anterior |
|
vertebra |
|
gland |
5 |
Sternothyroid |
15 |
Internal jugular vein |
24 |
Scalenus medius and |
33 |
Erector spinae |
39 |
Accessory anterior jugular |
6 |
Thyroid cartilage |
16 |
Common carotid artery |
|
posterior |
34 |
Root of sixth cervical nerve |
|
vein |
7 |
Cricoid cartilage |
17 |
Vagus nerve (X) |
25 |
External jugular vein |
35 |
Spinal cord within dural |
40 |
Lymph node of internal |
8 |
Rima glottidis |
18 |
Sympathetic chain |
26 |
Fat of posterior triangle |
|
sheath |
|
jugular chain |
9 |
Arytenoid cartilage |
19 |
Longus capitis |
27 |
Accessory nerve (XI) |
36 |
Body of fifth cervical |
41 |
Cervical lymph node |
10 Thyro-arytenoid |
20 |
Longus colli |
28 |
Trapezius |
|
vertebra |
|
|
|
11 Pharynx |
21 |
Vertebral artery and vein |
29 |
Levator scapulae |
37 |
Neurocentral or |
|
|
|
THORAX
Male – 1 section Axial

8 |
3/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
6 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
11 |
16 |
15 |
|
21 |
|
19/20 |
|
26 |
|
23/24 |
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|
|
|
■ Notes |
|
|
|
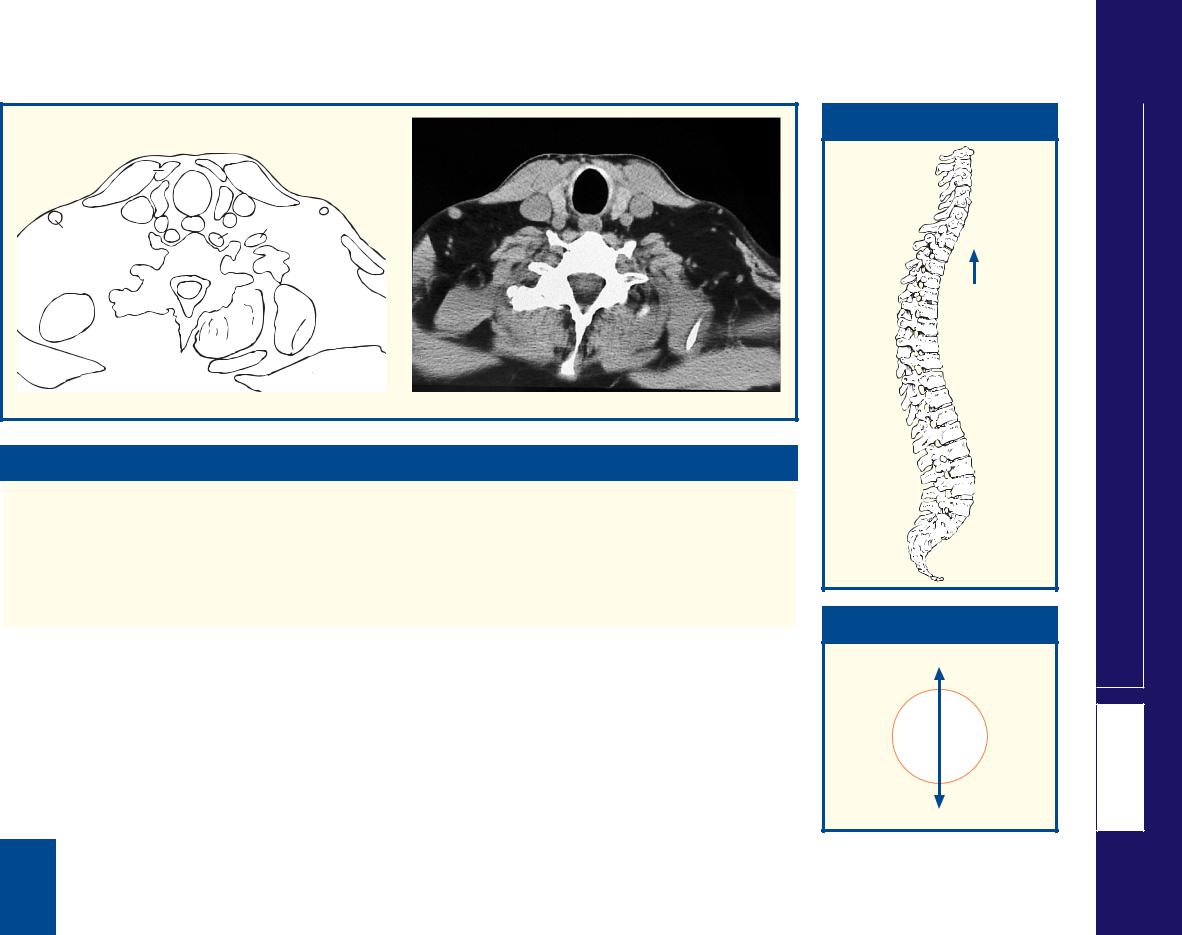
This section passes through the body of the fifth cervical |
rima glottidis (8) are adducted. |
vertebra (36), immediately above the level of the shoulder |
The posterior triangle of the neck has, at its boundaries, |
joint. Here the fibres of the trapezius (28) arch over the |
the posterior border of sternocleidomastoid (13) anteriorly, |
posterior extremity of the posterior triangle. Just below this |
the anterior border of trapezius (28) posteriorly and the |
level, at C6, lies the junction between the pharynx (11) and |
middle third of the clavicle below. Its floor comprises, from |
oesophagus, and the larynx (6, 7, 9) and the trachea. In |
above downwards, splenius capitis (30), levator scapulae |
both the section and the CT image, the pharynx (11) has a |
(29) and scalenus medius and posterior (24). |
narrow anteroposterior diameter; it distends considerably |
Not unusually, as in this case, the external jugular vein |
during deglutition. On the CT image, the vocal cords of the |
(39) is double. |
|
|
■ Section level
 C5
C5
View
■ Orientation
Anterior
Right 
 Left
Left
Posterior
Male – 1 section Axial
THORAX
103

104
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
||
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
11 |
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
7 |
|
|
|
28 |
|
14 |
13 |
15 |
|
|
|
29 |
|
9 |
|
30 |
||||
|
27 |
25 |
|
17 |
16 |
35 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|||
|
|
24 26 |
|
|
|
31 |
||
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
30 |
|
22 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
38 |
33 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
1 |
Platysma |
13 |
Recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
vertebra prominens |
32 |
Capsule of shoulder joint |
2 |
Anterior jugular vein |
14 |
Oesophagus |
22 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
33 |
Supraspinatus |
3 |
Sternohyoid |
15 |
Lymph node |
23 |
Inferior articular facet of seventh |
34 |
Spine of scapula |
4 |
Sternothyroid |
16 |
Ventral ramus of sixth cervical |
|
cervical vertebra |
35 |
Coracoid process of scapula |
5 |
Sternocleidomastoid |
|
nerve |
24 |
Body of seventh cervical vertebra |
36 |
Trapezius |
6 |
Omohyoid |
17 |
Scalenus anterior |
25 |
Longus colli |
37 |
Rhomboideus minor |
7 |
Internal jugular vein |
18 |
Scalenus medius |
26 |
Vertebral artery and vein |
38 |
Levator scapulae |
8 |
Vagus nerve (X) |
19 |
Ventral ramus of seventh cervical |
27 |
Ascending cervical artery and vein |
39 |
Erector spinae |
9 |
Common carotid artery |
|
nerve |
28 |
Inferior thyroid artery |
|
|
10 Isthmus of thyroid gland |
20 |
Dorsal root ganglion of eighth |
29 |
Phrenic nerve |
40 |
External jugular vein |
|
11 Lateral lobe of thyroid gland |
|
cervical nerve |
30 |
Deltoid |
|
|
|
12 Trachea |
21 |
Spine of seventh cervical vertebra – |
31 |
Head of humerus |
|
|
|
THORAX
Male – 2 section Axial
3/4
12 |
|
5 |
|
11 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
9 |
|
|
14 |
|
17 |
|
40 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
39 |
38 |
|
|
34 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
■ Notes
This section traverses the body of the seventh cervical |
the trachea (12) and the oesophagus (14). The phrenic |
vertebra, which bears the longest spine of the cervical |
nerve (29) hugs the anterior aspect of scalenus anterior |
series, the vertebra prominens (21). This is shorter, |
(17) deep to the prevertebral fascia; three structures – the |
however, than the spine of T1, as can be ascertained easily |
common carotid artery (9), the internal jugular vein (7) and |
by feeling the back of your own neck. |
the vagus nerve (8) – lie together within the fascial carotid |
Three important relationships are demonstrated well. The |
sheath. The deep cervical chain of lymph nodes (15) lies |
recurrent laryngeal nerve (13) lies in the groove between |
lateral to the carotid sheath. |
|
|
■ Section level
 C7
C7
View
■ Orientation
Anterior
Right 
 Left
Left
Posterior
Male – 2 section Axial
THORAX
105

106
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
28 |
4 |
|
|
7 |
33 |
||
|
|
6 |
|
|
|||
29 |
22 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
27 |
26 |
|
21 |
|
8 |
|
34 |
31 |
|
20 |
|
37 |
36 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
25 |
|
|
8 |
9 |
|
38 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
||||
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
23 |
19 |
13 |
|
10 |
|
33 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
40 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
11 |
||
|
|
14 |
|
45 |
41 |
||
|
|
|
12 |
|
|||
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
44 |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
43 |
33 |
|
|
15 |
51 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
50 |
48 |
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
1 |
Sternocleidomastoid sternal head |
15 |
Spine of first thoracic vertebra |
27 |
Phrenic nerve |
42 |
Infraspinatus |
2 |
Anterior jugular vein |
16 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
28 |
Vagus nerve (X) |
43 |
Scapula |
3 |
Sternohyoid |
17 |
Part of body of second thoracic |
29 |
Subclavius |
44 |
Subscapularis |
4 |
Sternothyroid |
|
vertebra |
30 |
Right subclavian vein |
45 |
Serratus anterior |
5 |
Clavicle |
18 |
Part of intervertebral disc between |
31 |
Tendon of right biceps long head |
46 |
Serratus posterior superior |
6 |
Internal jugular vein – junction |
|
first and second thoracic vertebrae |
32 |
Pectoralis major |
47 |
Superficial (transverse) cervical |
|
with left subclavian vein |
19 |
Part of body of first thoracic |
33 |
Deltoid |
|
artery and vein |
7 |
Left subclavian vein |
|
vertebra |
34 |
Subdeltoid bursa |
48 |
Rhomboideus minor |
8 |
Subclavian artery |
20 |
Oesophagus |
35 |
Head of humerus |
49 |
Trapezius |
9 |
First rib |
21 |
Common carotid artery |
36 |
Tendon of left biceps long head |
50 |
Rhomboideus major |
10 Intercostal muscles |
22 |
Trachea |
37 |
Coracoid process of scapula |
51 |
Erector spinae |
|
11 Second rib |
23 |
Right lung apex |
38 |
Nerve to serratus anterior |
|
|
|
12 Intercostal neurovascular bundle |
24 |
Scalenus medius |
39 |
Tendon of subscapularis |
52 |
Supraspinatus |
|
13 Apex of left lung |
25 |
Root of first thoracic nerve |
40 |
Glenoid fossa of scapula |
53 |
Pectoralis minor |
|
14 Head of second rib |
26 |
Scalenus anterior |
41 |
Suprascapular artery and vein |
|
|
|
THORAX
Male – 3 section Axial

|
|
|
5 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
6/7 |
|
|
|
|
|
6/7 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
8 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
20 |
8 |
|
44 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
13 |
|
23 |
20 |
|||
23 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
|
43 |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
||||||
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
Right 
 Left
Left
T1–2
Posterior
View
■ Notes
This section, through the intervertebral disc |
Here, posterior to the medial end of the clavicle |
overlying rib and lies protected within the subcostal |
|
between the first and second thoracic vertebrae |
(5), the internal jugular vein (6) joins with the |
groove. |
|
(18), enters the apex of the thorax and traverses the |
subclavian vein (7) to form the brachiocephalic vein |
Only in transverse section is the extreme thinness |
|
apices of the upper lobes of the lungs (13, 23). |
(see Axial section 4). |
of the blade of the scapula (43) appreciated fully. |
|
There are considerable differences between the |
The intercostal neurovascular bundle (12) is |
One CT (A) is displayed at soft tissue settings |
|
section and CT images at this level because the CT |
seen well. Note that it comprises the intercostal |
(window level and width of grey scale), the other |
|
is performed with the arms elevated alongside the |
vein, artery and nerve from above downwards; |
CT (B) at lung windows. |
|
head in order to reduce artefacts from the humeri. |
the nerve corresponds to the number of its |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
107 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Male – 3 section Axial
THORAX

108
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
47 |
|
|
3 |
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
21 |
18 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
43 |
|
44 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
49 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
30 |
|
|
|||
41 |
42 |
15 |
|
11 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
33 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
36 |
35 |
|
28 |
|
34 |
1 |
Pectoralis major |
15 |
Upper lobe of right lung |
28 |
Scapula |
38 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
2 |
Manubrium of sternum |
16 |
Right vagus nerve (X) |
29 |
Subscapularis |
39 |
Body of third thoracic vertebra |
3 |
Sternothyroid |
17 |
Right brachiocephalic vein |
30 |
Second rib |
40 |
Axillary nerve |
4 |
Sternoclavicular joint |
18 |
Brachiocephalic artery |
31 |
Intercostal artery and vein and |
41 |
Radial nerve |
5 |
First rib |
19 |
Left common carotid artery |
|
nerve |
42 |
Ulnar nerve |
6 |
Internal thoracic artery |
20 |
Left brachiocephalic vein |
32 |
External and internal intercostal |
43 |
Median nerve |
7 |
Left phrenic nerve |
21 |
Right phrenic nerve |
|
muscles |
44 |
Right axillary artery |
8 |
Left vagus nerve (X) |
22 |
Pectoralis minor |
33 |
Third rib |
45 |
Right axillary vein |
9 |
Upper lobe of left lung |
23 |
Coracobrachialis and biceps (short |
34 |
Trapezius |
46 |
Axillary fat |
10 Thoracic duct |
|
head) |
35 |
Rhomboideus major |
47 |
Pectoral branch of the |
|
11 Oesophagus |
24 |
Long head of biceps tendon |
36 |
Erector spinae |
|
acromiothoracic artery and vein |
|
12 Left subclavian artery |
25 |
Deltoid |
37 |
Fourth rib with articulation of its |
48 |
Cephalic vein |
|
13 Left recurrent laryngeal nerve |
26 |
Infraspinatus |
|
head with body of third thoracic |
49 |
Shaft of humerus |
|
14 Trachea |
27 |
Suprascapular artery and vein |
|
vertebra transverse process |
|
|
|
THORAX
Male – 4 section Axial

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
6 |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
18 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
Right |
Left |
|
|
14 |
12 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
15 |
|
11 |
9 |
|
15 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
Posterior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
36 |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
T3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
View |
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
section Axial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– 4 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|
Male |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Notes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THORAX |
The contents of the upper mediastinum – including the |
This section also shows the walls and contents of the axilla. |
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
oesophagus, trachea and great vessels – are demonstrated |
|
Note that the cephalic vein (48) runs in the deltopectoral |
|
|
|||||
in this section, which traverses the manubrium and the third |
groove between the medial edge of deltoid and the lateral |
|
|
||||||
thoracic vertebra; these are also shown in Axial section 5. |
edge of pectoralis major. |
|
|
|
|||||
109

|
110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
|
30 |
|
|
25 |
27 |
|
36 |
|
|
31 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
49 |
28 |
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
26 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
||||
|
16 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
37 |
|
32 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
43 |
|
38 |
39 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
42 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
41 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
8 |
|
|
46 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
9 |
47 |
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 Manubriosternal joint (angle of |
14 |
Part of intervertebral disc between |
|
26 |
Left vagus nerve (X) |
|
41 |
Circumflex scapular artery and vein |
||||||
|
Louis) |
|
fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae |
|
27 |
Left phrenic nerve |
|
42 |
Subscapularis |
|
|||||
|
2 Internal thoracic artery and vein |
15 |
Part of body of fourth thoracic |
|
28 |
Pretracheal lymph node |
|
43 |
Serratus anterior |
|
|||||
|
3 Thymic residue within anterior |
|
vertebra |
|
29 |
Superior vena cava |
|
44 |
Body of scapula |
|
|||||
|
mediastinal fat |
16 |
Azygos vein |
|
30 |
Right phrenic nerve |
|
45 |
Teres minor |
|
|||||
|
4 Second rib |
17 |
Apical segment lower lobe lung |
|
31 |
Pectoralis major |
|
|
46 |
Infraspinatus |
|
||||
|
5 Intercostal |
|
separated by oblique fissure from |
|
32 |
Deltoid |
|
|
47 |
Rhomboideus |
|
||||
|
6 Third rib |
|
(18) |
|
33 |
Shaft of humerus |
|
|
48 |
Trapezius |
|
||||
|
7 Fourth rib |
18 |
Upper lobe of lung |
|
34 |
Biceps – long head |
|
49 |
Axillary vein |
|
|||||
|
8 Fifth rib |
19 |
Oesophagus |
|
35 |
Biceps – short head and |
|
50 |
Axillary artery |
|
|||||
|
9 Fifth costotransverse joint |
20 |
Trachea at bifurcation |
|
|
coracobrachialis |
|
|
51 |
Cephalic vein |
|
||||
10 Erector spinae |
21 |
Recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
36 |
Pectoralis minor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
11 Transverse process of fifth thoracic |
22 |
Left subclavian artery orifice |
|
37 |
Subscapular artery vein and nerve |
|
52 |
Oblique fissure |
|
||||||
|
vertebra |
23 |
Aortic arch |
|
38 |
Latissimus dorsi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
12 Spinal cord within dural sheath |
24 |
Left common carotid artery orifice |
|
39 |
Triceps – lateral head |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13 Sympathetic chain |
25 |
Brachiocephalic artery orifice |
|
40 |
Triceps – long head |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
THORAX
Male – 5 section Axial

31 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
20 |
23 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|||
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
12 |
|
17 |
42 |
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
46 |
|
|
A |
|
|
47 |
|
A |
||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 18
18


 18
18 
52
52
B |
17 |
17 |
B |
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
Right 
 Left
Left
Posterior
T4–5
View
■ Notes
This section passes through the important anatomical |
contents, and the posterior mediastinum, behind |
are present in the lung parenchyma adjacent to a |
level of the manubriosternal joint, the angle of Louis |
the pericardium. |
fissure. |
(1). At this joint articulate the second costal cartilage |
The trachea bifurcates at this level (20). In the |
Pretracheal nodes (28) may become enlarged due |
and rib (4), and it is from here that the ribs can be |
living upright subject, however, the bifurcation may |
to a wide variety of disease processes. They are |
conveniently counted in clinical practice. Posteriorly |
be as low as the level of T6, particularly in deep |
accessible for biopsy via mediastinoscopy. |
this plane passes through the T4/5 intervertebral disc |
inspiration. |
Subscapularis (42) arises not only from the |
(14). |
The cranial portions of the oblique fissures of the |
periosteum of the medial two-thirds of the |
This plane demarcates the junction between the |
lungs (17, 52) are traversed on this section. The |
subscapular fossa of the scapula but also from |
superior and the lower mediastinum, the latter of |
normal oblique fissures are often not seen on |
tendinous laminae in the muscle itself, which are |
which is subdivided into the anterior mediastinum, |
conventional CT images of the lung parenchyma. |
attached to prominent transverse ridges on the |
in front of the pericardium, the middle |
The position can be inferred, however (see CT b) by |
subscapular fossa. This is shown clearly in this |
mediastinum, occupied by the pericardium and its |
the paucity of blood vessels; only small terminal vessels |
section. |
|
|
|
Male – 5 section Axial
THORAX
111

112
51 48
50
46
45
42
41
40
2
|
|
55 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
53 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
49 |
52 |
16 |
|
25 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
47 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
19 |
18 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
12 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
26 |
31 |
|
|
29 |
4 |
|
30 |
|
27 |
28 |
16 |
|
||
22 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
15 |
6 |
|
14 |
7 |
|
8 |
|
1 |
Body of sternum |
13 |
Intercostal artery and vein |
29 |
Pulmonary vein tributary |
44 |
Ulnar nerve |
2 |
Internal thoracic artery and vein |
14 |
Lower lobe of lung |
30 |
Segmental bronchus |
45 |
Radial nerve |
3 |
Thymic residue within anterior |
15 |
Oblique fissure |
31 |
Left phrenic nerve with |
46 |
Latissimus dorsi tendon |
|
mediastinal fat |
16 |
Upper lobe of lung |
|
pericardiacophrenic artery |
47 |
Axillary artery and vein |
4 |
Third rib |
17 |
Descending aorta |
32 |
Ascending aorta |
48 |
Biceps and coracobrachialis |
5 |
Fouth rib |
18 |
Thoracic duct |
33 |
Superior vena cava |
49 |
Median nerve |
6 |
Intercostal muscle |
19 |
Azygos vein |
34 |
Right phrenic nerve |
50 |
Shaft of humerus |
7 |
Fifth rib |
20 |
Oesophagus |
35 |
Trapezius |
51 |
Deltoid |
8 |
Sixth rib |
21 |
Lymph node |
36 |
Rhomboideus major |
52 |
Serratus anterior |
9 |
Transverse process of sixth thoracic |
22 |
Left vagus nerve (X) |
37 |
Infraspinatus |
53 |
Lateral thoracic artery and vein |
|
vertebra |
23 |
Left main bronchus |
38 |
Scapula |
54 |
Pectoralis minor |
10 Spinal cord within dural sheath |
24 |
Right intermediate bronchus |
39 |
Subscapularis |
55 |
Pectoralis major |
|
11 Part of intervertebral disc between |
25 |
Right pulmonary artery |
40 |
Teres major |
|
|
|
|
fifth and sixth thoracic vertebrae |
26 |
Pulmonary trunk |
41 |
Triceps – long head |
56 |
Superior pulmonary vein |
12 Part of body of fifth thoracic |
27 |
Left pulmonary artery |
42 |
Triceps – lateral head |
57 |
Left basal pulmonary artery |
|
|
vertebra |
28 |
Pulmonary artery branch |
43 |
Subscapular artery and vein |
58 |
Breast |
THORAX
Male – 6 section Axial

58 |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
16 |
33 |
32 |
26 |
16 |
|
|
|||
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
25 |
56 |
52 |
|
24 20 |
|||
|
23 57 |
|
||
|
|
|
17 |
38 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
10 |
|
37 |
A |
35 |
A |
|
|
16 
|
|
|
16 |
|
15 |
24 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
20 |
15 |
|
|
|
14 |
14 |
|
B |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
Right 
 Left
Left
Posterior
T5–6
View
■ Notes
This section, traversing the upper body of the |
At the left hilum, the superior pulmonary vein |
accompany the segmental and subsegmental |
sternum (1) and the lower part of the body of the |
(56) lies anterior to the bronchus (23), which in turn |
bronchi (30) usually lie dorsolaterally to these |
fifth thoracic vertebra (12), passes through the great |
lies anterior to the left basal pulmonary artery (57). |
structures; each pulmonary segment receives an |
arterial trunks as these emerge from the heart, the |
On the right side, the vein (56) lies anterior to the |
independent arterial supply. The bronchi usually |
pulmonary trunk (26) and the ascending aorta (32). |
right pulmonary artery, which lies anterior to the |
separate the dorsolateral pulmonary artery branch |
On the CT image, the left main bronchus gives off |
right intermediate bronchus (24). |
from the ventromedially situated pulmonary vein |
its common upper lobe/lingular branch at this level. |
In this subject, the right (25) and left (27) |
tributary (29). Peripherally, many pulmonary venous |
On the right, the upper lobe bronchus has already |
pulmonary arteries lie in the same axial plane. In |
tributaries run between, and drain adjacent, |
originated more cranially (on both CT images and |
most subjects, the left pulmonary artery is at a more |
pulmonary segments. Thus, an individual |
section); hence, the term ‘intermediate bronchus’ |
cranial level than the right – hence the discrepancy |
bronchopulmonary segment will have its own |
(24) is applied to that portion of the right bronchus |
between the section and CT image appearances. |
bronchus and artery but not an individual |
between its upper lobe and middle lobe branches. |
The branches of the pulmonary artery (28) that |
pulmonary venous drainage. |
|
|
|
Male – 6 section Axial
THORAX
113

114
27
|
|
49 |
|
|
61 |
60 |
50 |
51 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
54 |
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
55 |
53 |
26 |
|
|
|
||
59 |
|
|
|
|
56 |
57 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
25
58
1 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
42 |
|
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
45 |
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
7 |
|
||
|
|
36 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
38 |
26 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
||
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
9 |
|
11 |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
30 |
|
28 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
29 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
24 |
|
25 |
|
16 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
21 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
||
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
||
1 |
Third costal cartilage with |
15 |
Scapula |
26 |
Upper lobe of lung |
40 |
Left pulmonary artery |
50 |
Coracobrachialis |
|
adjacent sternocostal joint |
16 |
Subscapularis |
27 |
Middle lobe of right lung |
|
branch to lingula |
51 |
Axillary artery and vein |
|
(see Notes) |
17 |
Fifth rib |
28 |
Descending aorta |
41 |
Superior vena cava |
52 |
Medial cutaneous nerves |
2 |
Body of sternum |
18 |
Rhomboideus major |
29 |
Azygos vein |
42 |
Artefactual gap within the |
|
of arm and forearm |
3 |
Internal thoracic artery |
19 |
Trapezius |
30 |
Thoracic duct |
|
pericardial space |
53 |
Basilic vein |
|
and vein |
20 |
Erector spinae |
31 |
Oesophagus |
43 |
Ascending aorta, with |
54 |
Median nerve |
4 |
Partially calcified third |
21 |
Sixth rib, with adjacent |
32 |
Left vagal plexus |
|
orifice of left coronary |
55 |
Ulnar nerve |
|
costal cartilage |
|
costotransverse joint to |
33 |
Right vagal plexus |
|
artery (arrowed) |
56 |
Triceps – medial head |
5 |
Pectoralis major |
|
transverse process of sixth |
34 |
Right superior pulmonary |
44 |
Left ventricle wall |
57 |
Radial nerve with |
6 |
Pectoralis minor |
|
thoracic vertebra |
|
vein |
45 |
Coronary artery (left |
|
profunda brachii artery |
7 |
Third rib |
22 |
Spinal cord within dural |
35 |
Left superior pulmonary |
|
anterior interventricular |
|
and vein |
8 |
Intercostal muscle |
|
sheath |
|
vein |
|
branch) |
58 |
Triceps – long head |
9 |
Fourth rib |
23 |
Thoracic sympathetic chain |
36 |
Left atrium |
46 |
Infundibulum of right |
59 |
Triceps – lateral head |
10 Serratus anterior |
24 |
Body of sixth thoracic |
37 |
Left auricle (atrial |
|
ventricle with pulmonary |
60 |
Shaft of humerus |
|
11 Subscapular artery vein |
|
vertebra, with part of |
|
appendage) |
|
valves |
61 |
Deltoid |
|
|
and nerve |
|
intervertebral disc |
38 |
Left pulmonary vein |
47 |
Fibrous pericardium |
|
|
12 Teres major |
|
between the sixth and |
|
tributary to lingula |
48 |
Right auricle (atrial |
62 |
Hemiazygos vein |
|
13 Latissimus dorsi |
|
seventh thoracic vertebrae |
39 |
Left bronchus segmental |
|
appendage) |
63 |
Right coronary artery |
|
14 Infraspinatus |
25 |
Lower lobe of lung |
|
branch to lingula |
49 |
Biceps |
64 |
Oblique fissure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THORAX
Male – 7 section Axial

|
2 |
|
|
|
27 |
46 |
|
|
63 |
||
|
48 |
||
|
43 |
||
|
|
||
10 |
|
36 |
|
31 |
28 |
||
|
|||
|
25 |
29 |
|
13 |
62 |
||
|
|
A
27
25
B
45
26
25
A
26
64
 25
25 

B
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
|
||
Right |
|
|
Left |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Posterior |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
T6–7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
View |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Notes
The plane of this section traverses the lower part of |
components of the joint. In some or all of these |
infundibulum of the right ventricle and demonstrates |
the body of the sixth thoracic vertebra (24). |
joints, however, an arrangement may be found |
the pulmonary valves (46). |
Anteriorly, it passes through the body of the |
similar to that of the first joint. |
On the CT image, both the ascending aorta (43) |
sternum (2) at the level of the third costal cartilage |
The presence of a pericardial effusion in this |
and the region of the pulmonary valves (46) have |
(1). Note the adjacent sternocostal joint. These vary; |
subject has produced an artefactual gap in the |
indistinct outlines due to pulsation (compliance) of |
the first lacks a synovial cavity, its costal cartilage |
superior reflection of the pericardial space (42). The |
their walls during the 1-s data-acquisition time. (See |
being attached by fibrocartilage to the manubrium. |
aorta at its origin (43) shows the orifice of the left |
also the ascending aorta on the left-hand image in |
The second to seventh joints are usually synovial (as |
coronary artery. The descending aorta (28) is |
Axial section 6.) |
in this subject), with the fibrocartilaginous articular |
normally more circular in outline than in this subject. |
|
surfaces on both the chondral and the sternal |
Note that this section passes through the |
|
|
|
|
Male – 7 section Axial
THORAX
115

116
|
|
46 |
|
|
57 |
|
47 |
|
|
52 |
49 |
48 |
||
|
||||
|
|
|||
56 |
51 |
|
50 |
|
|
53 |
|
||
|
|
|
||
55 |
|
|
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
41 |
39 |
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
40 |
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
42 |
|
|
34 |
|
36 |
|
|
|
31 |
29 |
33 |
|
|
||
|
|
28 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
43 |
19 |
21 |
|
|
20 |
||
|
44 |
|
|
45
17
18
18
16
15 |
14 |
13
12
4
5
37
32
6
27
26
25
7
24
23
8
9
11
10
1 |
Internal thoracic artery |
16 |
Spinal cord within dural |
29 |
Interatrial septum |
39 |
Right coronary artery |
50 |
Basilic vein |
|
and vein |
|
sheath |
30 |
Phrenic nerve with |
40 |
Right auricle (atrial |
51 |
Ulnar nerve |
2 |
Body of sternum |
17 |
Intervertebral disc |
|
pericardiacophrenic artery |
|
appendage) |
52 |
Shaft of humerus |
3 |
Fourth costal cartilage |
|
between seventh and |
|
and vein |
41 |
Fibrous pericardium |
53 |
Triceps – short head |
4 |
Pectoralis major |
|
eighth thoracic vertebrae |
31 |
Middle lobe of right lung |
42 |
Nerve to serratus anterior |
54 |
Triceps – long head |
5 |
Fourth rib |
18 |
Lower lobe of lung |
32 |
Wall of left ventricle |
43 |
Intercostal neurovascular |
55 |
Triceps – lateral head |
6 |
Fifth rib |
19 |
Azygos vein |
33 |
Mitral valve |
|
bundle |
56 |
Radial nerve with |
7 |
Sixth rib |
20 |
Descending aorta |
34 |
Vestibule of left ventricle |
44 |
Innermost intercostal |
|
profunda brachii artery |
8 |
Serratus anterior |
21 |
Thoracic duct |
|
(outflow tract) leading to |
45 |
External and internal |
|
and vein |
9 |
Latissimus dorsi |
22 |
Oesophagus |
|
root of aorta |
|
intercostal muscles |
57 |
Deltoid |
10 Scapula inferior angle |
23 |
Pulmonary artery branch |
35 |
Divided cusp of aortic |
46 |
Biceps |
|
|
|
11 Seventh rib |
24 |
Branches of left lower lobe |
|
valve |
47 |
Median nerve with |
|
|
|
12 Trapezius |
|
bronchus |
36 |
Right atrium |
|
musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
|
13 Erector spinae |
25 |
Pulmonary vein tributaries |
37 |
Anterior interventricular |
|
(lateral to it) |
|
|
|
14 Eighth rib |
26 |
Oblique fissure |
|
(descending) branch of left |
48 |
Brachial artery with two |
|
|
|
15 Lamina of seventh thoracic |
27 |
Upper lobe of left lung |
|
coronary artery |
|
venae comitantes |
|
|
|
|
vertebra |
28 |
Left atrium |
38 |
Right ventricle cavity |
49 |
Coracobrachialis |
|
|
THORAX
Male – 8 section Axial

|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
38 |
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
39 |
27 |
|
|
|
34 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
8 |
18 |
22 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
9 |
|
19 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
A |
|
12 |
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
18 |
|
|
18 |
B |
|
B |
|
|
|
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
Anterior |
|
|
Right 
 Left
Left
Axial |
Posterior |
|
|
computed |
|
tomogram |
|
(CT) |
T7–8 |
View
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Notes
This section lies at the level of the intervertebral disc |
oesophagus (22), separated by the pericardium. The |
mortem thrombus in the right atrium (36). The |
between the seventh and eighth thoracic vertebrae |
left ventricle (32) forms the bulk of the left border of |
septum is normally straighter. |
(17) and passes through the body of the sternum (2) |
the heart, and the right ventricle (38) constitutes the |
The lower four or five digitations of serratus |
at the level of the fourth costal cartilage (3). All four |
major component of the anterior cardiac surface. |
anterior (8) converge to insert on the costal aspect |
cardiac chambers can be seen and their relationships |
In this subject, the left ventricular wall (32) |
of the inferior angle of the scapula. This component |
to each other appreciated. Note that the right |
becomes thinner in the region of the apex of the left |
of the muscle, together with the trapezius, |
atrium (36) forms the right border of the heart. The |
ventricle, due to a previous myocardial infarction. |
powerfully pulls the inferior angle of the scapula |
left atrium (28) is the major contribution to the base |
The interatrial septum (29) has a rather curious |
forwards and upwards in raising the arm above the |
of the heart and lies immediately anterior to the |
convexity. This has been caused by extensive post- |
head. |
|
|
|
Male – 8 section Axial
THORAX
117
|
118 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
17 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
9 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
14 13 |
|
11 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
15 |
|
21 |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
37 |
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
39 |
38 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 Fifth costal cartilage |
14 |
Left atrium |
|
27 |
Serratus anterior |
|
|
40 Azygos vein |
|||
|
2 Sternocostal joint |
15 |
Coronary sinus |
|
28 |
Eighth rib |
|
|
|
41 Thoracic duct |
||
|
3 Internal thoracic artery and vein |
16 |
Right atrium |
|
29 |
Trapezius |
|
|
|
42 Oesophageal vagal plexus |
||
|
4 Body of sternum |
17 |
Fibrous pericardium |
|
30 |
Erector spinae |
|
|
43 Oesophagus |
|||
|
5 Pectoralis major |
18 |
Left phrenic nerve, with |
|
31 |
Spine of eighth thoracic vertebra |
44 Dome of right hemidiaphragm |
|||||
|
6 Papillary muscle |
|
pericardiacophrenic artery and vein |
32 |
Lamina of eighth thoracic vertebra |
45 Apex of right lobe liver |
||||||
|
7 Chordae tendinae within right |
19 |
Fifth rib |
|
33 |
Ninth rib |
|
|
|
46 Right phrenic nerve, with |
||
|
ventricular cavity |
20 |
Upper lobe of left lung (lingula) |
34 |
Right sympathetic chain |
|
pericardiacophrenic artery and vein |
|||||
|
8 Triscupid valve |
21 |
Oblique fissure |
|
35 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
47 Middle lobe of right lung |
|||||
|
9 Interventricular septum |
22 |
Sixth rib |
|
36 |
Intervertebral disc between eighth |
|
|||||
10 Left ventricular cavity |
23 |
Lower lobe of lung |
|
|
and ninth thoracic vertebrae |
|
48 Inferior vena cava |
|||||
11 Normal left ventricular wall |
24 |
Seventh rib |
|
37 |
Aorta |
|
|
|
49 Right ventricular cavity |
|||
12 Thinned left ventricular wall |
25 |
Lateral thoracic artery and vein |
38 |
Origin of eighth intercostal artery |
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||
13 Mitral valve |
26 |
Latissimus dorsi |
|
39 |
Hemiazygos vein |
|
|
|
||||
THORAX
Male – 9 section Axial

■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
47 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
Anterior |
|||
49 |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
16 |
10 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
Right |
|
|
Left |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
15 |
43 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
37 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Posterior |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
26 |
|
35 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T8–9
|
A |
|
|
|
|
View |
|
|
|
B |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
||||
■ Notes
This section traverses the intervertebral disc between the |
Note how only a tiny portion of the left atrium (14) is |
eighth and ninth thoracic vertebrae (36) and slices through |
present on this section. This demonstrates that the left |
the dome of the right hemidiaphragm (44) and a sliver of |
atrium is situated more cranially than the other three |
the underlying right lobe of the liver (45). |
cardiac chambers. |
In this section, there is considerable thinning and |
The terminal fibres of the right phrenic nerve (46) usually |
discoloration of the left ventricular wall at the apex (12), |
pass through the vena caval opening in the diaphragm but |
consistent with infarction associated with left anterior |
may traverse the muscle itself. |
descending (interventricular) coronary arterial disease. |
|
Male – 9 section Axial
THORAX
119

120
1 Pectoralis major
2 Internal thoracic artery and vein
3 External oblique
4 Extrapericardial pad of fat
5 Left ventricle
6 Interventricular septum
7 Right ventricle
8 Tricuspid valve
9 Coronary sinus
10Diaphragm
11Fibrous pericardium
12Line of fusion of diaphragm and
pericardium
|
41 |
42 |
2 |
|
40 |
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
11 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
33 |
32 |
38 |
|
30 |
|
34 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
28 |
37 |
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
23 |
|
36 |
|
22 |
35
21
1
3
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
13
|
14 |
|
15 |
25 |
17 |
|
16 |
24 |
|
18
20
19
13 |
Upper lobe of left lung (lingula) |
|
between ninth and tenth thoracic |
35 |
Tenth rib |
14 |
Left dome of diaphragm |
|
vertebrae |
36 |
Ninth rib |
15 |
Spleen |
24 |
Left sympathetic chain |
37 |
Eighth rib |
16 |
Lower lobe of lung |
25 |
Hemiazygos vein |
38 |
Seventh rib |
17 |
Serratus anterior |
26 |
Azygos vein |
39 |
Sixth rib |
18 |
Latissimus dorsi |
27 |
Thoracic duct |
40 |
Middle lobe of right lung |
19 |
Trapezius |
28 |
Aorta |
41 |
Sixth costal cartilage |
20 |
Erector spinae |
29 |
Oesophagus |
42 |
Fifth costal cartilage |
21 |
Tip of spine of eighth thoracic |
30 |
Left vagus nerve (X) |
43 |
Sternum |
|
vertebra |
31 |
Right vagus nerve (X) |
|
|
22 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
32 |
Inferior vena cava |
44 |
Oblique fissure |
23 |
Body of ninth thoracic vertebra, |
33 |
Right hepatic vein |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
with part of intervertebral disc |
34 |
Right lobe of liver |
|
|
THORAX
Male – 10 section Axial

10
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
16 |
34 |
32 |
|
15 |
|
29 |
|||
|
33 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
14 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
16 |
22 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
 20
20
A
A
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
|
|
■ Orientation |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
44 |
|
|
Anterior |
|
||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
Right |
|
|
|
Left |
|
16 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
Posterior |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B
B
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Notes
This section is at the level of the body of the ninth thoracic vertebra (23) and traverses the dome of the left diaphragm (14). The cranial portion of the spleen (15) is, therefore, revealed.
The fusion of the diaphragm (10) with the base of the fibrous pericardium (11) is shown clearly at this point.
The massive size of the hepatic veins as they drain into the inferior vena cava (32) is well demonstrated in this section, which passes through the right hepatic vein at its termination (33).
The aorta (28) at this level has become the immediate posterior relation of the oesophagus (29), just as it is about to pass through its hiatus in the diaphragm (10).
■ Section level
T9–10
View
Male – 10 section Axial
THORAX
121

122
17
1
16
46
24
15
38
14 |
33 |
|
|
|
34 |
13 |
32 |
31
23
12
18 19 20
43
42
39
40
37
36
29
28 |
25 |
27 26
11 10
9
8 7
1
46
2
41
3
44
21
45
35
22
30
23
5
4
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
1 |
Breast |
14 |
Fifth rib |
29 |
Oesophagus |
41 |
Left ventricle |
2 |
Pectoralis major |
15 |
Fourth rib |
30 |
Mediastinal lymph node |
42 |
Right ventricle |
3 |
Intercostal muscles |
16 |
Third rib |
31 |
Pulmonary arterial branch in lower |
43 |
Right coronary artery |
4 |
Latissimus dorsi |
17 |
Third costal cartilage |
|
lobe |
44 |
Left phrenic nerve |
5 |
Serratus anterior |
18 |
Third sternocostal joint |
32 |
Bronchus – segmental branch in |
45 |
Fibrous pericardium |
6 |
Trapezius |
19 |
Sternum |
|
lower lobe |
46 |
Extrapericardial fat pad |
7 |
Erector spinae |
20 |
Internal thoracic artery and vein |
33 |
Orifice of right inferior pulmonary |
|
|
8 |
Spine of seventh thoracic vertebra |
21 |
Upper lobe of left lung (lingula) |
|
vein |
47 |
Ascending aorta |
9 |
Spinal cord within dural sheath |
22 |
Left oblique fissure |
34 |
Right inferior pulmonary vein |
48 |
Descending aorta |
10 Part of intervertebral disc between |
23 |
Lower lobe of lung |
35 |
Coronary sinus |
49 |
Pulmonary trunk |
|
|
the seventh and eighth thoracic |
24 |
Middle lobe of right lung |
36 |
Left atrium |
50 |
Right pulmonary artery |
|
vertebrae |
25 |
Aorta |
37 |
Interatrial septum |
51 |
Superior vena cava |
11 Body of seventh thoracic vertebra |
26 |
Azygos vein |
38 |
Right atrium |
52 |
Left basal pulmonary artery |
|
12 Seventh rib |
27 |
Right sympathetic chain |
39 |
Tricuspid valve |
53 |
Upper lobe of right lung |
|
13 Sixth rib |
28 |
Thoracic duct |
40 |
Aortic valve |
54 |
Carcinoma right breast |
|
THORAX
Female – 1 section Axial

54 |
|
|
|
53 |
|
|
|
|
47 |
49 |
21 |
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
52 |
|
29 |
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
26 |
23 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|
■ Notes |
|
|
|
This section of a female subject passes through the body of |
tissue becomes atrophied. The inner wall of the left |
the seventh thoracic vertebra (11) and through the third |
ventricle, immediately proximal to the aortic valve (40), is |
sternocostal joint (18). Note the general smaller |
smooth-walled and termed the aortic vestibule. |
configuration of the female thorax and the smaller, less |
This CT image shows a patient with a large carcinoma of |
bulky muscles. |
the right breast, which has ulcerated and extended into, |
The breast (1) contains the mammary gland. This extends |
and infiltrated, a wide area of adjacent skin. The |
vertically from the second to the sixth rib and transversely |
anatomical level is considerably more cranial than the |
from the side of the sternum to near the mid-axillary line. |
cadaveric section; it corresponds closely to that shown in |
The gland is situated within the superficial fascia and is |
Axial section 6 of the male thorax. |
separated from the fascia covering pectoralis major, |
Note that in this section, the margin of the mass of left |
serratus anterior and the external oblique muscle by loose |
ventricular muscle (41) has been cut across; there is |
areolar tissue. In old age, as in this subject, the glandular |
infarction in the anterior free wall. |
|
|
■ Section level
T7–8
View
■ Orientation
Anterior
Right 
 Left
Left
Posterior
Female – 1 section Axial
THORAX
123

|
|
Selected images – Heart |
|
THORAX |
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
||||
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
19 |
8 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
6 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
12 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
||
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
2 |
4 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
B |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
||
Images A–B |
7 |
Tricuspid valve |
10 |
Left atrioventricular |
15 |
Aorta |
|
|
|
8 |
Right atrioventricular |
|
groove for circumflex |
16 |
Oesophagus |
1 |
Right atrium |
|
groove for right |
|
branch of left |
17 |
Thoracic vertebra |
2 |
Right ventricle |
|
coronary artery |
|
coronary artery |
18 |
Right coronary artery |
3 |
Left atrium |
9 |
Interventricular |
11 |
Mitral valve |
19 |
Left coronary artery |
4 |
Left ventricle |
|
groove for anterior |
12 |
Anterior leaflet of |
|
|
5 |
Interatrial septum |
|
branch of left |
|
mitral valve |
|
|
6 |
Interventricular |
|
coronary artery |
13 |
Papillary muscle |
|
|
|
septum |
|
|
14 |
Pulmonary vein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Notes
|
|
Multidetector CT with rapid data acquisition has |
|
|
opened up huge opportunities for imaging the heart |
|
|
and great vessels. If the data for a whole revolution of |
|
|
the CT gantry can be acquired in less than 400 ms, |
|
|
then a considerable amount of information can be |
|
|
obtained in the relatively quiescent period of the |
|
|
cardiac cycle. If the patient’s heart rate is slow and |
|
|
regular, then a succession of images can be obtained |
|
|
during one breath-hold at the same phase of the |
|
|
cardiac cycle; these can be combined and a three- |
|
|
dimensional dataset created. This can provide |
|
|
exceptional anatomical (and, increasingly, functional) |
124 |
|
|
|
information. |
|
|
|
The four-chamber view (A) is a multiplanar two- |
|
|
|
dimensional reconstruction so that all four chambers can be seen on one oblique image. This is a standard view used in many imaging investigations, including CT, ultrasound and MRI. It allows direct comparison of the left and right sides of the heart. It elegantly shows the interventricular septum. The close relationship of the oesophagus to the posterior aspect of the left atrium explains the advantages of transoesophageal echocardiography.
The coloured three-dimensional surface rendered view of the ventricles and coronary arteries provides a good general overview but, in practice, the coronary arteries (B) are better displayed and analysed using more selective analysis tools.

Selected images – Heart |
|
|
THORAX |
|
|
|
|
|
C
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
■ Orientation |
|
■ Orientation |
||
|
Anterior |
|
|
Superior |
Right |
|
Left |
Right |
Left |
A |
Posterior |
|
B C |
Inferior |
20 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
8 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
5 |
|
|
15 |
|
12 |
|
18 |
14 |
17 |
|
C
Image C
1 First rib (right)
2 Second rib
3 Third rib
4 Fourth rib
5 Fifth rib
6 Clavicle
7 Sternoclaviclar joint
8 Sternum – manubrium
9 Sternum – body
10Hyoid bone
11Left subclavian vein
12Right atrium
13Right atrial appendage
14Right ventricle
15Right ventricular outflow tract
16Pulmonary trunk
17Left ventricle
18Left anterior descending – branch of left coronary artery
19Right coronary artery
20Right subclavian artery
■ Notes
This edited 3D view of the chest (C) has been |
the contrast medium and are well shown. It is just |
presented as a collage whereby the skin and |
possible to see the right subclavian artery (20) |
subcutaneous tissues have been ‘peeled away’ to |
between the right first rib (1) and the right clavicle |
expose the internal structures of the chest. By using |
(6). The coronary vessels are well shown with the left |
different window widths and colouring, it has been |
anterior descending artery (LAD, 18) seen in the |
possible to demonstrate some lung detail in areas, |
interventricular groove and the right coronary artery |
which have not been obscured by overlying |
(19) seen in the right atrioventricular groove. Note the |
structures. These images were obtained during a long |
way that the 2nd rib (2) leads to the sterno-manubrial |
bolus injection of dilute iodinated contrast medium |
angle (of Louis). Of course the chondral part of the |
via the left arm. Hence the left subclavian vein (11) is |
rib, which articulates with the sternomanubrial joint, |
well demonstrated but not the right. The heart, great |
is not sufficiently calcified to be seen at these |
vessels and coronary arteries are rendered opaque by |
settings. |
|
|
125

126
|
|
7 |
|
10 |
|
|
8 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
9 |
11 |
|
21 |
11 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
||||
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
6 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
20 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
22 |
|
16 |
|
A |
A |
|
|
|
18 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
||
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
B |
|
|
|
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|||
Axial computed tomogram (CT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7
9 21
4
2
20
112
16
19
C 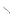 C
C
Axial computed tomogram (CT)
THORAX
CTs Axial – Mediastinum – images Selected

Images A–D |
12 |
Aortic arch (with fleck of |
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
||
|
|
|
calcification in wall in image C) |
|
|
|
1 |
Trachea |
13 |
Ascending aorta |
Anterior |
|
|
2 |
Right brachiocephalic vein |
14 |
Descending aorta |
|
||
|
|
|||||
3 |
Brachiocephalic artery |
15 |
Left pulmonary artery |
|
|
|
4 |
Left brachiocephalic vein |
16 |
Oesophagus |
|
|
|
5 |
Left common carotid artery |
17 |
Superior vena cava |
Right |
Left |
|
6 |
Left subclavian artery |
18 |
Azygos vein |
|||
|
|
|||||
7 |
Manubrium of sternum |
19 |
Right superior intercostal vein |
|
|
|
8 |
Body of sternum |
20 |
Fat in pretracheal space |
|
|
|
9 |
Internal thoracic artery and vein |
21 |
Fat in anterior mediastinal |
Posterior |
|
|
10 Pectoralis major |
|
space (with thymic remnant) |
|
|||
|
|
|
||||
11 Pectoralis minor |
22 |
Azygos-oesophageal recess |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
View |
|
■ Notes
This patient has copious mediastinal fat, which |
structure (partial volume effect). The space |
the cardinal veins, is of immense importance when |
makes the normal structures very conspicuous. |
immediately caudal to the aortic arch and cranial to |
the vena cava becomes blocked for any reason |
Enlarged lymph nodes would show up well in such |
the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery is known as |
(usually by a tumour). For example, in superior vena |
a patient (see Axial section 6). If such nodes lie in |
the subaortic fossa or aortopulmonary window. The |
cava obstruction caused by mediastinal nodal |
the pretracheal space (20), then biopsy material can |
ligamentum arteriosum (the obliterated ductus |
enlargement secondary to carcinoma of the |
be obtained via mediastinoscopy. |
arteriosus passing from the left pulmonary artery to |
bronchus, the venous return from the head, neck |
The trachea (1) is bifurcating on image D; this |
the aorta) runs through this space. This fossa may |
and arms will go via collateral veins around the |
point is known as the carina. The left pulmonary |
also contain enlarged lymph nodes. |
scapula and retrogradely in the intercostal veins into |
artery (15) lies at a more cranial level than the right; |
The azygos vein (18) can be seen approaching |
the azygos and thence back to the heart, bypassing |
it is just entering part of the section shown on |
the posterior aspect of the superior vena cava (17) |
the obstruction in the superior mediastinum. |
image D. It appears indistinct because only part of |
on image D. This venous system, which developed |
|
the thickness of the slice is occupied by the |
at an early stage of embryological development of |
|
|
|
|
CTs Axial – Mediastinum – images Selected
THORAX
127

128
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
12 13 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
12 |
|
|
|
14 |
16 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
25 |
21 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
18 |
|||
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
23/24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
26 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
39 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
28 |
|
||||||
|
40 |
|
32 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
41 |
34 |
|
35 |
|
|||
|
41 |
|
39 |
|
|
41 |
34 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
A |
42 |
|
45 |
|
B |
|
|
45 |
|
46 |
|
C |
43 |
|
|
45 |
|
37 |
46 |
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
A |
|
B |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coronal magnetic resonance image (MRI) |
|
|
|
|||
Coronal magnetic resonance image (MRI) Coronal magnetic resonance image (MRI) |
||||||
THORAX
MRIs Coronal – images Selected

1 |
Falx cerebri |
25 |
Brachiocephalic vein |
2 |
Lateral ventricle |
26 |
Carina (bifurcation of trachea into |
3 |
Third ventricle |
|
two main bronchi) |
4 |
Lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure) |
27 |
Aortic arch |
5 |
Tentorium cerebelli |
28 |
Superior vena cava |
6 |
Cerebellum |
29 |
Left pulmonary artery |
7 |
Sternocleidomastoid |
30 |
Right pulmonary artery |
8 |
Spinal cord |
31 |
Main pulmonary artery |
9 |
Second cervical vertebra (axis) |
32 |
Left superior pulmonary vein |
10 |
Parotid gland |
33 |
Left atrium |
11 |
Scalene muscles |
34 |
Right atrium |
12 |
Clavicle |
35 |
Left ventricle |
13 |
Acromioclavicular joint |
36 |
Ascending aorta |
14 |
Glenoid fossa of scapula |
37 |
Descending aorta |
15 |
Acromion process of scapula |
38 |
Inferior vena cava |
16 |
Humeral head |
39 |
Left lung |
17 |
Coracoid process of scapula |
40 |
Right lung |
18 |
Deltoid |
41 |
Liver |
19 |
Trachea |
42 |
Right hepatic vein |
20 |
Thyroid gland |
43 |
Middle hepatic vein |
21 |
Internal jugular vein |
44 |
Left hepatic vein |
22 |
Subclavian vein |
45 |
Stomach |
23 |
Axillary vessels |
46 |
Spleen |
24 |
Brachial plexus and resulting |
47 |
Vertebral artery |
|
nerves |
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Orientation |
■ Section level |
|
|
|
|
Superior |
A B C |
|
|
|
|
View
Right 
 Left
Left
Inferior
■ Notes
These three T1-weighted coronal magnetic |
depend much on the degree of thoracic spine |
cancer, the axilla may be affected both by nodal |
resonance images are included to show the overall |
kyphosis, body habitus and degree of inspiration. |
metastases and by the effects of radiotherapy. |
relations of the head, neck, thorax and upper |
The relations in this relatively obese subject are fairly |
These can cause either neurological symptoms in |
abdomen. Only rarely would such a large field of |
representative. |
the arm or lymphoedema. Coronal images of the |
view be used in clinical practice, as the anatomical |
A wide field of view is used when trying to |
two axillae together can be very helpful in this |
spatial resolution is inevitably compromised. Of |
compare structures on the two sides. The brachial |
differentiation, which can be difficult on clinical |
course, the exact relations on the coronal plane |
plexus (image B, 24) is a case in point. In breast |
grounds. |
129
MRIs Coronal – images Selected
THORAX

THORAX Selected images – Chest CT
|
A |
|
B |
|
|
|
Coronal computed tomogram (CT) |
Coronal computed tomogram (CT) |
|||
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
2 |
5 |
18 |
|
|
6 |
|||
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
A |
|
B |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
C |
|
D |
|
|
|
Sagittal computed tomogram (CT) |
Sagittal computed tomogram (CT) |
|||
|
Left Lung |
|
Right Lung |
|
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
13 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
130 |
C |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

Selected images – Chest CT |
|
|
THORAX |
|
|
|
|
|
■ Orientation |
|
■ Orientation |
|
|
|
Superior |
Superior |
|
Right |
Left |
Anterior |
Posterior |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
B E |
Inferior |
C |
D |
Inferior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
E |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Trachea |
|
12 |
Lingula (on the left) |
||
Reconstructed 3D computed |
2 |
Right main bronchus |
13 |
Lower lobe |
|||||||
3 |
Right upper lobe bronchus |
14 |
Middle lobe (on the right) |
||||||||
tomogram (CT) |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
4 |
Bronchus intermedius |
15 |
Oblique fissure |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Left main bronchus |
16 |
Horizontal fissure (on the |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Left upper lobe/lingular |
|
right) |
|
||
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
bronchus |
17 |
Aortic knuckle |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Left lower lobe bronchus |
18 |
Left pulmonary artery |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Left upper lobe bronchus |
19 |
Oesophagus (containing |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Left upper lobe lingular |
|
some swallowed air) |
|||
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
bronchus |
20 |
Carina – the bifurcation of |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
3 |
2 |
5 |
|
8 |
10 Right lower lobe bronchus |
|
the trachea |
||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
6 |
9 |
11 Upper lobe |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Notes
A spiral CT dataset of the chest at full inspiration has |
lowest image is a three-dimensional reconstruction |
been obtained on a multidetector CT system. Next, |
just extracting out the airways and accentuating the |
the individual thin slices have been loaded together to |
interface between air and soft tissue – this provides a |
form a three-dimensional volume with each voxel |
graphic map of the anatomy of the trachea and main |
isometric so that the x, y and z resolutions of the |
bronchi. These images elegantly show the more |
resulting pixels are identical. This three-dimensional |
vertical nature of the right main bronchus (2) – hence |
dataset can be analysed in a variety of ways. |
the peanut and the endotracheal tube tend to enter |
The first two images show coronal multiplanar |
the right side preferentially. They also show the |
reconstructions viewed at lung settings to show the |
greater length of the left main bronchus (5); on the |
anatomy of the airways in this plane. The middle |
right, the takeoff for the upper lobe bronchus can be |
images shows sagittal reconstructions to demonstrate |
very close to the carina (20, the point of bifurcation |
the lobes and fissures of the left and right lungs. The |
of the trachea into two main bronchi). |
|
|
131
|
|
Selected images – Arterial system |
|
THORAX |
|
|
|
|
A
B
132

Selected images – Arterial system |
|
|
THORAX |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
9 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
11 |
12 |
|
10 |
|
3 |
|
|
8 |
13 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
15 |
14 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
6 |
4 |
|
4 |
B
7
A
1 |
Heart |
9 Twelfth thoracic vertebra |
|
■ Orientation |
|
|||
2 |
Ascending aorta |
10 |
First lumbar vertebra |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Abdominal aorta |
11 |
Coeliac artery |
|
|
Superior |
|
|
4 |
Common iliac artery |
12 |
Splenic artery |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
External iliac artery |
13 |
Hepatic artery |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Common femoral artery |
14 |
Superior mesenteric artery |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Superficial femoral artery |
|
and arcade |
|
Right |
|
|
Left |
8 |
Kidney and pelvicalyceal |
15 |
Cholecystectomy clips |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
system |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inferior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
■ Notes
These two surface rendered 3D angiograms have |
On the right image the patient has had a previous |
|
||
been obtained on a modern CT system following the |
laproscopic cholecystectomy and the clips (15) can |
|
||
injection of standard iodinated contrast medium. The |
readily be identified as very dense structures overlying |
|
||
CT data were acquired during the aortic phase of the |
the right kidney and close to the hepatic artery (13). |
|
||
passage of contrast medium through the body and |
Note the way the aorta changes in calibre at the L1 |
|
||
the images subsequently manipulated on the |
level; it is smaller inferior to the coeliac artery, |
|
||
workstation. |
superior mensenteric artery and the two renal |
|
||
On the left image the global view allows the |
arteries. The superior mensenteric arcade is beautifully |
|
||
relationship of the heart, aorta, iliac and femoral |
demonstrated (14). The tortuosity of the iliac vessels is |
|
||
vessels to be appreciated in relation to the skeletal |
normal in middle age and above. The renal and |
|
||
structures. A test dose of contrast medium has been |
splenic parenchyma are only faintly seen in this early |
|
||
given sometime before and this accounts for the |
phase. |
|
|
|
133 |
||||
dense iodine being excreted from the kidneys and |
|
|
||
pelvicalyceal system (8). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
