
- •Unit 1 the construction-related engineering profession
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about the history of civil engineering.
- •Early christian and byzantine architecture
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about and early Christian and Byzantine architecture.
- •Orders of architecture
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about orders of architecture.
- •Mortars
- •6 Give a literary translation of §§7 – 10.
- •7 Fill in the table using the information from the text:
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about mortars.
- •Unit 5 glass
- •6 Match the information given to the paragraphs in the text:
- •7 Give a literary translation of §§ 9, 10.
- •8 You’ve misheard the information. Make it more exact, putting questions:
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about the staircases.
- •Unit 6 stairs
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about the staircases.
- •Unit 7 doors
- •7 You’ve misheard the information from the previous assignment. Make it more exact, putting questions:
- •In a paragraph of 70-100 words, and using your own words, as far as possible, summarize what the text tells us about the types of doors.
- •Unit 8 green and sustainable buildings
- •2A) Transcribe the following words:
- •Nanotechnology in building construction
- •3Read the text again and answer the questions that follow (1-8):
- •4Match the columns:
- •5A) Find the synonyms in the text and rephrase the sentences using the given expressions:
- •6 Explain the words in bold from the text and make up sentences of your own. Use English-English dictionaries to help you.
- •7 Give the English equivalents to the following and use 5 of them in small situations:
- •8Fill in the gaps with derivatives of the words in capitals:
- •9Group work: choose five questions from the list below, find and presentinformation:
Unit 8 green and sustainable buildings
|
|
|
|
Figure 8.1 LEED Green Buildings
Explain how the following words and expressions are connected with “green building”:
nanotechnology, sustainable, environmentally friendly, self-cleaning coatings, energy-saving production, air purification, lower water consumption.
2A) Transcribe the following words:
Urgent, issues, acidification, conductivity, nano-enhanced, energy-conserving, versatility, toxicity, nanoparticles, unique, convergence.
b) In what context do you think the following words and phrases will appear in the text?
• thenano era • at the molecular level • nanotubes •nanotechnology • a boom • accrue • coatings and insulating materials • purification •declining coast
Read the text and check your answers:
Nanotechnology in building construction
Green is a nice color. It also is a buzzword that’s being used rather freely whenever people want to claim that their product or service is environmentally friendly.
Sustainability means designing structures that take advantage of technological advancements to create eco-friendly products.
Green building is one of the most urgent environmental issues of our time. But for the building industry to achieve its potential as the leader in sustainable development, new materials are urgently needed. a new frontier is opening in building materials as nanotechnology introduces new products and new possibilities.
By working at the molecular level, nanotechnology opens up new possibilities in material design. In the nanoscale world where quantum physics rules, objects can change color, shape, and phase much more easily than at the macroscale. Fundamental properties like strength, surface-to-mass ratio, conductivity, and elasticity can be designed in to create dramatically different materials.
Many nano-enhanced products and processes now on the market can help create more sustainable, energy-conserving buildings, providing materials that reduce waste and toxic outputs as well as dependence on non-renewable resources. Other products still in development offer even more promise for dramatically improving the environmental and energy performance of buildings. Nano-enabled advances for energy conservation in architecture include new materials like carbon nanotubes (can be up to 250 times stronger than steel and 10 times lighter, as well as electrically and thermally conductive (Fig. 8.2) and insulating nanocoatings, as well as new processes including photocatalysis. Nanomaterials can improve the strength, durability, and versatility of structural and non-structural materials, reduce material toxicity, and improve building insulation.
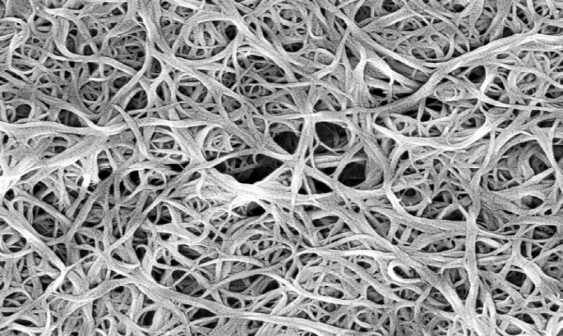
Figure 8.2 Carbon Nanotubes
Nanoparticles have unique mechanical, electrical, optical and reactive properties distinct from larger particles. Their study (nanoscience) and manipulation (nanotechnology) also open up the convergence of synthetic and biological materials.
The examples of some of these materials are aerogel, thin-film insulation, self-cleaning coatings, air purification, and water purification.
Current nanomaterials and nano-products show demonstrable environmental improvements including energy savings and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources, as well as reduced waste, toxicity and carbon emissions. Some can even absorb and break down airborne pollutants. The benefits of nanotechnology for green building will accrue first from coatings and insulating materials available today, followed by advances in solar technology, lighting, air and water purification, and, eventually, structural materials and fire protection.



