
- •Statistical analysis of the data on your pc
- •Medical statistics. Basic terms and concepts
- •Information (from Lat. Informatio - «clarification, presentation, awareness") - information about anything, regardless of its format.
- •The organization of medical and statistical research
- •Necessary terms
- •Standard deviation
- •Normal distribution
- •Medians and percentiles
- •Is the standard deviation of all possible sample average of the volume, which is called the standard error of the mean, depends on the standard deviation of the population, and on the sample size.
- •Conclusions
The organization of medical and statistical research
In carrying out scientific research in medicine researcher is faced with the social and biological phenomena that have random, probabilistic nature. The study of regularities inherent in such phenomena, produced by the methods of mathematical statistics and requires the presence of a certain, sometimes quite substantial, the number of observations. Organization of the collection, quantitative and statistical analysis of medical observations are called "health-statistical research."
The content of medical and statistical research is divided into four successive stages:
• 1st - planning and research programs;
• 2nd - statistical observation;
• 3rd - statistical grouping and summary of observations;
• 4th - statistical processing and analysis of the materials,
design of the study results.
Necessary terms
The object of observation - a set of units, which must be collected statistical data, delimited by the territorial, administrative, time and other characteristics
The observation unit - the primary element that make up the object of study, to be carefully defined in accordance with the purpose and objectives of the study.
Surveillance program - a list of features that characterize the observation unit with qualitative and quantitative parties and subject to statistical registration: gender, age, occupation of the patient, the diagnosis, the cause of the disease, the nature of the treatment, the timing of the relapse, the characteristic nasal breathing and so on. N. In drawing up the program selected only those features that are needed to answer the theme and purpose of work certain questions. The practice of increasing the number of signs "just in case" complicates the processing of the collected data, extend the duration of work, and sometimes hides its meaning.
Type of observation time of the meeting can be one-time or ongoing. Most medical phenomena observed continuously as they arise (the cases of diseases, injuries, complications, death of the therapeutic and preventive measures, and so on. D.), And therefore subject to the current account. In some cases, the clinical and statistical and other medical research carried out one-time observation t. E. Check the data at a specific point in time (for example, the census of patients).
Through the coverage of units of the object and does not distinguish between a solid continuous observation. When continuous monitoring records all units constituting the object of observation, with no continuous, partial observation is taken only some of these units (sample), in which then judge all the properties of the object.
The main methods of collecting health statistics are the direct observation of materials (for example, registration of doctors clinic patients with vasomotor rhinitis), survey and reporting method.
Grouping
Results grouping of statistical material on individual characteristics and their different combinations are expressed in statistical tables. Statistical table is a rational form of systematization of statistical data.
Typological grouping, the purpose of which is to divide the target population into homogeneous groups according to the main types of events (for example, the distribution of patients in classes, groups and forms of the disease).
Relative values
The resulting reports, and grouping of materials research may be presented as a spreadsheet or statistical variation series having magnitudes. As a rule, these absolute data are insufficient for a comprehensive analysis of the phenomenon under study, and because researchers have resorted to generalize the calculation of statistical indicators: relative and average values.
Relative values - the ratio of two numbers representing different population or part of a set of observations.
Statistical processing of an ordered series
The study of health effects, search inherent laws, usually associated with repetition (sometimes multiple) homogeneous observations or experiments. The researchers are not interested in individual observations, and their generalized characteristics that help to understand the typical features of the phenomena being studied. Analyzing the results of several series of observations or experiments, the researcher finds differences in the frequency of interest to its features, if these symptoms quality, or value of attributes, if they can be quantified. In all cases, the detection of characteristic values spread the researcher needs to figure out how significant this scatter, accidental or not and what are the factors that determine it. To solve these problems need to make a variational series and calculate its generalized characteristics.
Every set of individual objects, differing from each other and at the same time similar in some significant respects, constitute the so-called population. For example, children born in the country for any period of time. The most common body called the General. It is theoretically infinitely large collection of all units that it can be attributed.
A group of elements that you want to study to answer the research question, called the general population. Very often, the researchers plan to study and draw conclusions about a large population, but in the end, to save time and money, or simply because they see no other way out, they see only a narrow set of. This can lead to big trouble when summing up. For example, imagine that a university teacher wants to determine how television advertising makes consumers buy products. This study is based on a group of his own students who participate in the survey to get five extra points to offset. Perhaps this is a convenient sample, but the results can not be attributed to any other set of these in addition to students, because the study other aggregate were not provided
The composition of the aggregate includes various members or units of the aggregate. The total number of units in the population called the volume of aggregate. Each unit together distinct characteristics. For example, children born - weight, height, etc. Each feature takes different values in different units in the population. The differences in the values of the characteristic between individual units together is called the variation or dispersion.
The concept of "sign varies" means that the sign takes different values in different units in the population. For example, height or weight in children born in the country for any period of time.
Options - this particular value of the random variable Xi, ie value is influenced by many random factors.
Set consisting of a small number of units called sampling (sampling). Researcher usually has to do with the sample.
Often, researchers want to find out something about the population, but they do not have the time or money to study each element of this set. Then what do they do? They select a small number of elements together, study them, and use this information to draw a conclusion about the whole population. This is called the sample.
How to describe the data
descriptive statistics
AVERAGE
If we are interested in values characteristic of most objects are close to their average and is equally likely to deviate from it in the up or down, the best performance together will be very mean and standard deviation. In contrast, when the feature value asymmetrically distributed relative to the average, the collection better described using the median and percentiles.

Fig. 1. Distribution of Martians on growth. Each circle corresponds to the Martian. Please note that the Martians medium height (about 40 cm), and most of all that tall as much as shorties - distribution is symmetric.

Fig. 2. Distribution of Venusians on growth. Venusians below Martians spread is smaller. However, the form of distribution that resembles a bell, Venusians and Martians are similar to each other.
Growth of most any member close to the middle of the distribution, rather than removed from it significantly and equally likely to be both above and below the midpoint. Distribution in the figures have a similar shape and approximately determined the same formula.
Characteristics of the provisions distribution on the real line is called the mean. Average jointly designated by the Greek letter μ (read "mu") and is calculated as follows:

Equivalent mathematical expression has the form
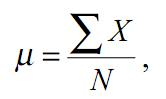
where X - value of the sign, N - number of members of the population. Most Greek letter Σ (read "sigma") refers to the amount.
