
- •I only
- •The firm faces an inelastic demand curve
- •A single firm can influence price
- •Price down and quantity up.
- •It could decrease output to increase revenues.
- •Coincides with the demand curve
- •Higher Lower
- •The monopoly will have to be subsidized to continue operating.
- •None of the above.
- •None of the above.
- •None of the above
- •None of the above
- •None of the above.
- •None of the above.
It is experiencing economies of scale in production.
It is maximizing total revenue.
It is producing where demand is price elastic.
It could lower price to increase profits.
It could decrease output to increase revenues.
11. For a perfectly discriminating monopoly, the Marginal Revenue Curve
lies below the demand curve
lies above the demand curve
Coincides with the demand curve
crosses the demand curve and is steeper than it
crosses the demand curve and is flatter than it
12. A monopolist has the same costs and the same market demand curve as a perfectly competitive industry. Compared to a perfectly competitive industry, which of the following will be true of the monopolist's price and output?
Monopolist's Price Monopolist's Output
Higher Higher
Higher Lower
Higher The same
Lower Higher
Lower Lower
13. If a monopolist is selling its 50th unit of output for $40, its marginal revenue:
May be either greater or less than $40
Is equal to $40
Is greater than $40
Is equal to zero
Is no more than $40
14. According to the diagram, the monopolist will produce ___ and the price will be ___
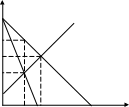
P
$13
MC
$10
$7
$5
MR D
5 10 20 Q
20 units; less than $7
5 units; $10
10 units; $5
10 units; $7
5 units; $5
15. According to the diagram, the loss of consumer surplus from being a monopoly market rather than a competitive market is (assuming that MC and the Demand curves are linear)
22.5;
12.5;
15;
7.5;
10.
16. Which of the following will result when a monopoly firm operating under conditions of declining unit cost sells its output at a uniform price equal to marginal cost?
The monopoly will make economic profits.
The monopoly will have to be subsidized to continue operating.
The monopoly will realize a rate of profit equal to that of a competitive return.
The monopoly will hire inputs above the level at which the value of their marginal product equals the marginal factor cost.
The monopoly will hire inputs below the level at which the value of their marginal product equals the marginal factor cost.
19.It costs a lot of money to become an electricity supplier. However, it is extremely cheap to run the business afterwards. Such a firm is likely to:
I. exhibit economies of scale
II. have constant marginal cost as output rises
III. become a monopoly
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III
(E) II and III
D
20.A monopolist can maximize profits by:
(A) producing where MR=MC and setting price according to the demand curve
(B) setting the price as high as possible
(C) setting the price where the difference between price and marginal cost is the highest
(D) producing where marginal cost equal the price of the good
(E) producing where the price elasticity of demand is equal to one.
A
21.In the game described by the payoffs matrix below the dominant strategy:
(A) is to produce high output for each firm
(B) is to produce low output for each firm
(C) for one firm depends on the strategy taken by the other firm
(D) exists only for firm 1
(E) does not exist for either firm.
|
Firm 2 produces high output |
Firm 2 produces low output |
Firm 1 produces high output |
180; 180 |
230; 150 |
Firm 1 produces low output |
150; 230 |
205; 205 |
A
22.Given a downward sloping demand curve, a market that moves from competition to a multiplant monopoly will:
I. produce a deadweight loss (pure waste)
II. see a decrease in total surplus
III. see a decrease in producer surplus
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I, II and III
(E) I and II only
E
23.If a single firm can produce industry output at a lower cost than any other number of firms using the same technology, this is called:
(A) a natural monopoly
(B) the marginal output rule
(C) diseconomies of scale
(D) more than one answer is correct
(E) none of the above
A
24.Assuming that marginal costs are zero, the equilibrium point in a profit-maximizing monopoly occurs where:
(A) demand is inelastic
(B) demand is elastic
(C) demand is unit elastic
(D) marginal revenue is highest
(E) cannot tell from the information given
C
25.Given the downward sloping demand and the upward sloping marginal cost curves, if a per unit tax is imposed on a monopoly, a monopoly will ___________the price of its good and the total revenue (including the tax) will __________ :
(A) decrease; decrease
(B) decrease; increase
(C) increase; increase
(D) increase; decrease
(E) cannot tell from the information given
D
26.In the long run, the monopoly and monopolistically competitive equilibrium are the same in that:
(A) price is greater than marginal cost
(B) price is greater than average cost
(C) marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
(D) firms always earn normal profit
(E) more than one answer is correct
A
26.In the long run, the perfectly competitive equilibrium and monopolistically competitive equilibrium are the same in that:
(A) price is greater than marginal cost
(B) price is greater than average cost
(C) marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost
(D) firms always earn normal profit
(E) more than one answer is correct
D
27.According to the oligopoly kinked demand curve, with the P* being the price in the kink:
I. if one firm attempts to set the price below the P* level, its rivals will not change their prices
II. if one firm attempts to set the price below the P* level, its rivals will do the same
III. if one firm attempts to set the price above the P* level, its rivals will not change their prices
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I and III only
D
28.When suppliers jointly act like a monopolist by restricting output and raising price, they are said to form:
(A) monopolistic competition
(B) a monopsony
(C) a natural monopoly
(D) a cartel
(E) none of the above
D
29.Which of the following best explains why the demand curve for a factor of production such as labor slopes downward?
(A) The law of diminishing returns
(B) The law of comparative advantage
(C) Economies of scale
(D) The superior bargaining position of workers compared to employers
(E) The poor bargaining position of workers compared to employers
A
30. A firm finds that the slope of the marginal product of labour curve for the corresponding amount of labour used is zero. It follows that in the short run:
I. hiring additional workers will increase output
II. hiring additional workers will decrease output
III. decreasing the number of workers will decrease output
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
(E) II and III only
B
31.Which of the following factors will shift the demand curve for labour to the right?
