
- •Business plan for the new venture Master Thesis
- •Valovaya str.,
- •Declaration of Authorship
- •Abstract
- •Contents
- •1. Introduction………………………………………………………………………………..6
- •2 Theoretical Framework…………………………………………………………………..11
- •4.1. World’s industry outlook…………………………………………………………….….37
- •4.2. Economic trends affecting consulting services in Russia…………………………….…58
- •4.3. Types of consulting firms in Russia…………………………………………………….39
- •6.2 Target customer segments………………………………………………………………...71
- •8. Financial Plan………………………………………………………………………………78
- •6. Conclusion and recommended future work…………………………………………….85
- •7. Appendix a……………………………………………………………………………….88
- •1. Introduction
- •Background
- •1.2 Purpose and objectives of the Master thesis Purpose
- •Objectives of the Master thesis:
- •1.3 Methods and approaches of mastering business plan
- •Data collection
- •1.4 Outline of the Master thesis
- •2. Theoretical framework
- •2.1 Entrepreneurship in business services
- •2.1.1 Entrepreneurial qualities
- •2.1.2 The new venture decision making
- •2.1.3 The new venture creation process
- •2.1.4 Stages of company growth
- •Identify and Define a Market Niche
- •2.2 Management structure in consulting business and types of consulting activities
- •2.3 Tools to create business plan of the new enterprise
- •3. Company idea
- •3.1 Motivation for establishing the new business entity
- •3.2 Positioning concept of the company
- •4. Market analyses
- •4.1. World’s industry outlook
- •4.2. Economic trends affecting consulting services in Russia
- •4.3. Types of consulting firms in Russia
- •4.4 Qualitative evaluation of consulting services
- •4.5 Market capacity and market growth
- •4.6. Main factors of competition
- •5. Business Plan
- •1. Executive Summary
- •1.1 Vision and Mission
- •Vision Statement
- •1.2 Core competences
- •1.3 Management Team
- •1.4 Legal form of company Ownership
- •1.5 Service Targeting
- •1.6 Financial Summary
- •1.6.1. Financial objective
- •Products Through of experience of Marktune consultants have been practicing marketing management, financial management, human resources management and information technologies management consulting.
- •4. Competitor Analysis
- •5. Swot Analysis
- •6. Marketing Plan
- •6.1 Marketing Objectives
- •6.2 Target customer segments
- •6.3 Size of the market and market share of Marktune
- •6.4 Marketing Strategies
- •6.4.1 Products
- •6.4.2 Price
- •6.4.3 Distribution
- •6.4.4 Promotion
- •Investment in Advertising and Promotion
- •7. Key Strategic Issues
- •8. Financial Plan
- •8.1 Start-up costs
- •8.2 Sales Forecast
- •8.3 Organization Structure Chart
- •8.4 Projected financial statements
- •8.5 Business Ratios
- •6. Conclusion and recommended future work
- •7. Appendix a
- •Magazine articles
- •40 Http://www.Raexpert.Ru/ratings/consulting/2009/
- •41 Http://www.Raexpert.Ru/ratings/consulting/2009/
2.1.2 The new venture decision making
Important part of the entrepreneurial decision making is entrepreneurial learning that minimise risks of failure. Entrepreneurial learning is concerned with how people construct new meaning in the process of recognising and acting on opportunities, and organizing managing ventures. However, the new venture is accompanied by entrepreneurial heuristics – the thumb-rules guiding the management decisions involved in the start-up and management of the new venture.
Role of learning and heuristics developing by Rauf M.S. and Zainullah M.9 in venture creation can be depicted in the figure, along with the following two statements:
Statements 1: If accumulated knowledge is higher or comparable to threshold knowledge, then the entrepreneurs is prepared to create a venture.
Statement 2: The level of Threshold Knowledge is controlled or adjusted by the individual’s heuristics.
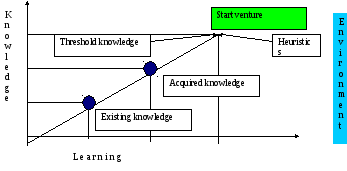
Figure 2. Decision about a creation of the new venture10
In real situation, entrepreneurs may make a number of entrepreneurial decisions to start a business even when many information related to a specific market, products or certain industry are scarce or even unavailable. Additionally, these decisions are made under significant time pressure. So, under such uncertain conditions, heuristics can be an effective and efficient guide for entrepreneurs to make decisions11. Therefore, entrepreneurial decision-making is considered as a skill which is used by entrepreneurs to perform different entrepreneurial tasks (e.g., discovering or exploiting opportunity, venture creation). Created business plan helps to increase acquired knowledge to the maximum level and reduce uncertainness while opening a new firm.
To describe psychological aspect of the decision making and managing activities while opening of the new venture and making new strategic steps in existing business that explains entrepreneurial heuristics. Author operates with notions Mega focus and Factual focus. Mega focus targets entrepreneurs to more opportunistic behaviour and entrepreneurial heuristics. Mega focus is associated with risk taking technique. Factual focus targets entrepreneurs to more critical cognitive approach that simplifies acquired knowledge and generates positive business experience. One of the main fields of the factual focus is business learning itself.
2.1.3 The new venture creation process
Three main elements make up the new venture. They are the company itself, entrepreneurs and the location, successful businesses have characteristics in common which can be evaluated, altered and influenced. (1) They are opportunity driven (2) they are led by a founder or by an entrepreneurial team (3) they are creative and have restricted resources.
The new venture creation is balanced between three main entities that guarantee the entrepreneurial success; these entities are opportunity, resources and the team. The entrepreneurial team of the Marktune intends to manage the new venture since management will be moving in a dynamic environment. Furthermore, to have an understanding and a balance in the process; the business plan will set the communication code between this three driving forces.
The first force is opportunity, ensures that the new venture creation process does not start with money, strategy or the team; it starts with an opportunity that is described in business plan. Business environment is emerging and respectful to the new ideas where creativity and communication are encouraged. Opportunity identification generates the business context where value is added. Opportunity can be measured by parameters such as the size of the market, the demand or the market structure; these parameters produce the factors that differentiate an opportunity from only having an idea.
The next entry in the diagram is the resources, which can be defined as a procedure or a mean to accomplish a task; every business idea needs a correct organization of its resources so it can be exploited into a true opportunity. The resources needed in the venture are explained in the business plan, e.g. the financial resources needed along with the business assets and the required people. Furthermore, it is more valuable for a successful business venture, to have control and possession of the right resources rather than own a large resource pool with little control.
The team is the last driving force that completes the diagram; this means having the right people working efficiently. This usually begins with a leader that establishes an entrepreneurial organization and culture based on skills such as dealing against adversity, integrity, honesty and dependability. These characteristics need to become a commitment as a team for motivation and tolerating ambiguity stresses the importance of a high level team in building a successful venture. He ensures that is better to have a grade A team with a grade B idea rather than a grade B team with an A grade idea. Usually, every member of the managerial team accumulates five to ten years or more of general management and industry experience. Criteria of the new venture success is linked to thoughtful preparation and planning before taking the first steps with start-up.
The model of entrepreneurial process (Figure 3) should be balanced, and any change in the size of the entities might place the venture in a risky position. If the opportunity grows, and the resources become scarce, the whole model will be weakened and an injection of capital will be needed to maintain the company’s health.
ENTREPRENEURIAL TEAM Lead Entrepreneur
Founding Management Team Apprenticeship and Career Strategy Experience and Know-How Management Skill and Competencies Acquirable Characteristics
Role Demands and Trade-Offs Personal Goals and Values Mental Attitudes and Philosophy THE OPPORTUNITY
Market: Finding, Shaping, Creating The Window: Scheduling
Implementation Requirements
Screening and Evaluating
The Economics: How Forgiving and
Rewarding? Risk vs. Rewards Yield tactics
Matching NESESSARY RESOURCES The expansion Team The Business Plan and Strategy
Financing
Outside Professional Resources Minimizing and Controlling vs. Maximizing
and Owning












Figure 3. New Venture Creation: The Driving Forces12
