- •The money you spent on airplane tickets.
- •Firm a works more efficiently than firm b
- •None of the above
- •There are no idle resources in the economy.
- •Robinson should specialize in tanks, leaving jets for Friday
- •Only b is true
- •Both factors should bring the firm the same marginal product per dollar spent on them
- •An oligopoly
- •The long run supply curve would not depend on the actual number of firms in the industry
- •A natural monopoly
- •None of the above
- •The world market for cell phones.
- •Equilibrium quantity could increase
- •A and d are correct
- •A perfectly discriminating monopoly
- •The marginal productivity of capital declines with the quantity of capital
- •The marginal revenue product of labor will decrease.
- •Decrease if the quantities of b and c are left unchanged, but not necessarily to decrease if b and c quantities are also increased.
- •Cause a reduction in marginal product.
- •No change in deadweight losses
The electricity market.
The market for mobile phone operators’ services in Russia.
The world market for cell phones.
The market for Treasury bonds (in absence of large players).
The Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange (MICEX).
The following three questions refer to this graph:
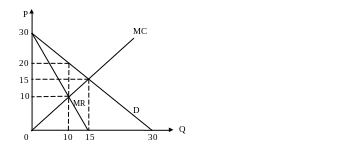
At the profit-maximizing level of output, total variable costs of this firm would equal:
10
100
112,5
50
15
If this were a non-price-discriminating multi-plant monopoly, the deadweight loss from this market’s monopolization would equal:
5
50
25
75
12,5
If this monopoly could perfectly price discriminate, the consumer surplus would equal:
50
100
112,5
225
0
Consider a monopolized market in a state of equilibrium (Pm, Qm). The government introduces a price ceiling Pmax, Pmax < Pm. As a direct consequence of that…
Equilibrium quantity could increase
Equilibrium quantity would decrease, but consumer surplus will increase
There would be excess supply in this market
The quantity sold by the now regulated monopoly will be Pareto-optimal
None of the above
In a “prisoner’s dilemma” type of game:
Each player is individually rational
Nash equilibrium is Pareto-optimal
Either player has a unilateral incentive to play his dominated strategy, instead of his dominant one
If both players play their dominated strategies, their payoffs are higher than in Nash equilibrium
A and d are correct
The largest amount of output that a firm can produce with a given combination of inputs is determined by the
-
A.
marginal product of labor
B.
gains from specialization
C.
cost function
D.
production function
E.
input-output function
Which of the following is a COMMON feature of perfectly competitive, monopolistically competitive and monopolistic markets?
In long run equilibria, for every firm i, P = min(LRACi (qi))
Government regulation could bring the equilibrium quantity closer to the socially optimal one
In long run equilibria, P = LRACi(qi) for every firm i.
If a firm produces positive output qi, it must be that MR(qi) MC(qi)
P > MR
Assume that the industry initially consisted of many plants producing a homogeneous good (i.e., was perfectly competitive). A series of mergers and takeovers have led to a change in its market structure. Social welfare would suffer the least, if that new market structure were:
A monopolistic competition
A non-price-discriminating monopoly
An oligopoly (assuming there are no price wars)
A perfectly discriminating monopoly
A natural monopoly
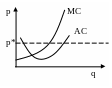
The following graph illustrates the position of a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry, which is now in a state of short-run equilibrium. According to the graph, what should this firm do?
|
continue selling its output at p* no matter what: the industry is actually in LR equilibrium.
immediately decrease the price it charges: this may draw off potential competition
temporarily increase the price it charges: this way it will at least get some profit before new competitors come
try to reach a collusion with other firms in this industry – together they may be able to retain their current profits and bar entry for new firms
in the short run– nothing.
The long-run supply curve of a perfectly competitive industry:
Is obtained as a horizontal sum of all short-run supply curves
Is relatively steeper than the short-run supply curve
Is typically horizontal – but can also be U-shaped
Must be upward-sloping
No right answer
Which of the following is an example of an externality-producing activity?
A chemical plant cleans a local river from pollution by extracting some of the poisonous substances for its production
A group of students bypasses the queue in the canteen joining their friends
A student snores loudly during a Microeconomics seminar
All of the above
None of the above
A competitive equilibrium is Pareto efficient unless
average cost curves are downward sloping for all firms in one unregulated industry
income distribution is not equitable
the government imposes per unit taxes
the government imposes per unit subsidies
more than one answer is correct.
Consider a competitive industry creating a negative externality in production that increases nonlinearly with the output produced. In this case:
A per-unit tax can restore efficiency
Direct bargaining can restore efficiency
A quota can restore efficiency
I
II
III
II and III
I, II and III
Which of the following is not a factor of production?
land
labor
capital
money
All of the above
Demand for capital is downward sloping because