
- •Lesson 1. Full-time student
- •4. Answer these questions.
- •5. Work with your partner and translate the text into Russian.
- •6. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous in the following sentences.
- •7. Study this information about two courses and find similarities and differences between them.
- •8. Write sentences describing similarities and differences you have found using the example structures.
- •9. Matthew Smith is a student of electronics at a college of further education. Here is his weekly timetable. Try to answer these questions.
- •10. Listen to the interview with Matt Smith and complete the information missing in the table.
- •11. Now listen again and answer the questions.
- •12. Read the script of the conversation at the end of the book and find English equivalents to the following words.
- •13. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words. Use your dictionary if you need.
- •4. Match the abbreviations and their full forms. Translate them into Russian.
- •6. Work with your partner and translate the given paragraphs into Russian.
- •7. Use Active or Passive voice in the following sentences.
- •8. Translate these sentences from the text into Russian paying particular attention to the translation of Passive forms.
- •9. Read and translate the text about electronics diagrams. Understanding Electronics Diagrams
- •10. Find the answers to these questions.
- •15. Now look at the basic units of the circuit and translate the text into Russian.
- •16. Fill in the gaps in this description of the tuned circuit shown in Fig. 2. Each gap represents one word. Use the words from the box.
- •17. Write the description of the following diagram. Does it answer the following questions?
- •3. Answer these questions. Use the information from the text above.
- •4. Work with your partner and find in the text the English equivalents to the words.
- •5. Match the terms and their definitions.
- •6. Complete the tables. Use the words from the text. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words.
- •8. Here are some circuit symbols. Label them and describe their function.
- •9. Study the block diagram of a battery charger. Match each component or unit with its function in a battery charger.
- •3. You are going to read a text about computers. Check that you know these words and expressions from the text.
- •4. Read the information about personal computers and choose the best heading for each paragraph (1 – 8). There is extra heading which you don’t need to use.
- •Personal Computer
- •5. Answer the questions.
- •6. Read the statements and decide if they are true (t) or false (f). Prove your answers.
- •7. Work with the partner and find English equivalents in the text above.
- •8. Match the words from the columns and translate the word combinations.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Complete the sentences with the words and expressions from the box.
- •12. Make sentences from the following words beginning with the word in bold.
- •13. Complete the table with a suitable part of speech.
- •14. Choose the words from the box and put them into Past Simple form to complete the sentences.
- •15. Write 8-10 sentences about what you did or didn’t do yesterday.
- •16. Find in the first three paragraphs the examples of using which. Explain its necessity in each case. Are they an essential part of the sentence?
- •17. Link these pairs of sentences using which. You may omit words and make whatever changes you think are necessary in the word order and punctuation of the sentences.
- •18. Write the translation of paragraphs 5 and 6. Lesson 5. Types of computers.
- •1. Answer the questions.
- •2. You are going to read the text about different types of computers. Make sure you know these words and phrases.
- •3. Read the text and complete the sentences after the text with the types of computers.
- •10 Types of Computers.
- •2. Desktop
- •3. Laptop
- •4. Netbook
- •6. Work station
- •4. Are the following sentences true (t) or false (f)?
- •5. Find in the text some more examples of comparison.
- •6. Find 4 incorrect sentences and correct them. Mistakes are all connected with comparison.
- •7. Write your own sentences comparing different types of computers.
- •8. What type of computer is the best for students? Prepare a short talk and include the following aspects:
- •9. Read the information about laptops and choose the best heading (a- f) for each paragraph (1-5). There is one extra heading which you don’t need to use.
- •10. Answer these questions.
- •11. Are the statements true (t) or false (f)? Prove your answer.
- •12. Complete the table. Use the information about laptops above.
- •13. Match the pictures and the names of the laptops.
- •14. These are examples of advantages and disadvantages of laptops. Can you separate them into two groups?
- •Vocabulary.
- •15. Find English equivalents in the information above about laptops.
- •16. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •17. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •18. Complete the tables. Translate all words.
- •19. Complete the sentences with the following words and expressions.
- •20. Write the Russian translation of paragraph 4 or 5.
- •4. Read the information again and answer the questions in pairs.
- •5. Read the statements and decide if they are true (t) or false (f). Prove your answer.
- •6. Find English equivalents in the information above.
- •7. Match the words from the two columns to have the word combinations. They all are in the information about peripherals.
- •8. Complete the tables. The necessary words are in the text. Translate all words.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Complete the sentences with the words from the box.
- •11. Explain these compound nouns.
- •3. Read the text and say about the main difference between analogue and digital recording of sound. Sound recording and reproduction
- •4. Answer the following questions.
- •5. Choose the best answer for the following definitions.
- •6. Match the following terms with their definitions.
- •8. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple in the following sentences.
- •9. Write 6-7 sentences about your experience using Present Perfect or Past Simple forms of the verbs.
- •10. Words and expressions to know.
- •11. Look at the diagram and answer these questions.
- •12. Read the information below and translate it into Russian. Mp3 Files
- •13. Answer the questions.
- •14. Explain how each of these actions happen. The explanations are available in the information above.
- •15. There are seven blanks. Complete them. Use the words from the box (Three of them are extra). Explain your choice.
- •16. Match the words from the two columns and translate the word combinations. All of them are from the information above.
- •17. Complete the information of how to make a recording by putting each of the verbs in brackets in the correct form.
- •18. Write the translation of the paragraphs beginning with “mp3 completes with another audio file format…” and the next one. Lesson 8. Sound engineer
- •1. Steve is a sound engineer. He describes his work and how you can make your own recordings of live music. The recording is in two parts:
- •2. Listen to Part 1 and answer the questions:
- •3. As you listen to Part 2, answer the following questions:
- •4. Listen again to the complete interview and answer these more difficult questions:
- •5. Which form will you use in these sentences – Past Simple or “used to”?
- •9. Answer these questions. Read the information above again if you need.
- •10. Make sentences from the words.
- •11. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech they belong to. Translate all words.
- •12. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •13. Match the words from the two columns and translate the word combinations. All of them are from the information above.
- •14. Fill in the gaps. Use the words from the box.
- •15. Which word is odd according to their meaning and use in every line? Explain your choice.
- •16. Give some advice to a sound engineer: write a list of thing to do and not to do. Use information from the text and any information of your own. When you have finished, discuss them in the class.
- •4. Answer these questions about remote controls.
- •5. Complete the table. Use the information from the text.
- •6. Read paragraph 6 again to complete the gaps in the flowchart, which shows how the remote control transmitter works.
- •7. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech the words belong to.
- •8. Match the words from two columns. Use the information above.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Go back to the flowchart you made in task 6. Write sentences to link stages 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6, using the time clauses.
- •3.Read the information about different kinds of alarms and alarm systems. What alarms and alarm systems do you think people use more often than the others? Alarms and Alarm Systems
- •4. Try to answer these questions.
- •5. Match the names of alarms or alarm systems and their examples or descriptions.
- •6. Find English equivalents in the information above.
- •7. Find the words with a similar meaning.
- •8. Find the words with an opposite meaning.
- •9. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech. The necessary words are in the text. Translate all words.
- •10. Match words from two columns to have word combinations. The information about alarms and alarm systems can help you.
- •11. Match the actions in Column a with an appropriate consequence from Column b. Then join each action and consequence using an if-sentence and making changes if it is necessary.
- •12. Think about these situations and what you will do in each of them. Then talk to your partner and find out his ideas.
- •13. Translate the paragraph which your teacher will give you.
- •14. Read and translate the text. Three stages of a simple alarm system.
- •15. Use the information from the text to complete the tables and answer the questions.
- •16. Study this simple circuit and answer the questions below it.
- •16. Write the text explaining how the door-alarm circuit works.
- •17. Write the translation of the paragraphs beginning with “The ldr forms the potential divider… “ and the next one.
- •17. What words or word combinations in the text “Alarms and alarm systems” do these grammar links refer to?
- •4. Try to answer these questions. Use the information from the text.
- •5. Are the statement true (t) or false (f)? Prove your answer. Use the information above.
- •6. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words. Use your dictionary if it is necessary.
- •7. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •8. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •9. Match the words from the two columns to have word combinations. Read the information about the Internet above again.
- •10. Complete the sentences. Use the words from the box.
- •11. Read the examples of cmc and complete this table.
- •12. Use can/can’t or should/shouldn’t in the following sentences.
- •13. Write some sentences to tell what you should/shouldn’t do to keep data on your computer safe.
- •14.Write the translation of paragraph 4.
- •15. Rewrite each of these sentences like this.
- •16. Complete these sentences with the correct form of the verb: infinitive or –ing form.
- •Lesson 12. Webpage creators
- •8. Now read the interview in the Appendix and find English equivalents in the information above and in the interview.
- •9. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech the words belong to.
- •10. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •11. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •12. Match the words to have word combinations.
- •13. Read the information. What is the difference between the terms ‘Internet’ and ‘World Wide Web’?
- •14. Answer the questions about your future.
- •15. Complete the gaps in this interview with will or would or the reduced forms ’ll and ’d where appropriate.
- •16. Here is a part of an interview with Alex. Fill in the blanks with will or would or the reduced forms ’ll and ’d where appropriate.
- •17. Answer the questions with the 2nd conditional sentences.
- •4. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech the words belong to.
- •5. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •6. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •7. Match the words to have word combinations. Look through the information about the anatomy of a virus if it’s necessary.
- •8. Some verbs beginning or ending with en have a causative meaning. Replace the words in italics in these sentences with the appropriate form of en verb from this list.
- •2. Putting the events in sequence and using a causative verb.
- •3. Using a when clause.
- •9. Describe how these viruses work in short texts, using different links.
- •10. Find one more example of virus and write about its work.
- •4.Work with your partner and make a list of benefits or challenges connected with Smart Home systems.
- •5.Check that you know these words and phrases from the second text.
- •6.Read the text and complete the table about technologies used in Home networking.
- •Smart Home Software and Technology
- •7.Answer the questions on the text.
- •9. Link these pairs of actions. Use short ways when this is possible.
- •The Interviewer and the Full-time Student
- •Webpage Creator
15. Use the information from the text to complete the tables and answer the questions.
Complete this table
|
Sensing device |
Used to detect |
|
LDR |
|
|
|
heat |
|
|
sound |
What effect does light have on an LDR?
What is the purpose of RV1 in Fig. 2 ?
Use words from the text to complete the following table
|
Term |
Opposite |
|
cut-off |
saturation |
|
fixed resistor |
|
|
increases |
|
|
energize |
|
|
slow |
|
|
to cause |
|
|
forward bias |
|
How is the transistor in Fig. 2 protected from a large back EMF?
16. Study this simple circuit and answer the questions below it.
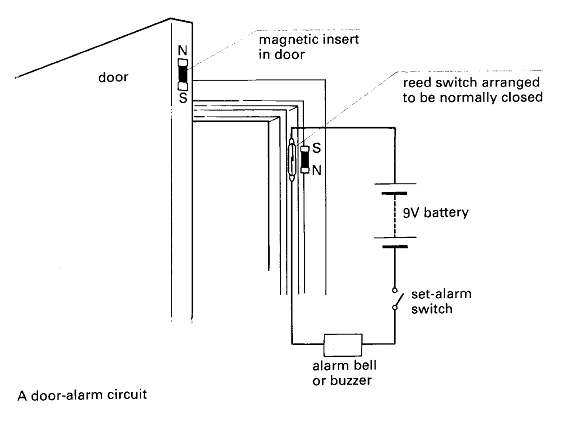
What are the components?
How are they connected?
What is the state of the system when the door is closed?
What happens if the door is opened?
Why does this happen?
Writing.
16. Write the text explaining how the door-alarm circuit works.
17. Write the translation of the paragraphs beginning with “The ldr forms the potential divider… “ and the next one.
Language Study. Grammar links
Sentences in all texts are held together by grammar links. Note the links in this paragraph about metal detectors.
(1) Metal detectors are used to locate hidden metal objects such as water pipes. (2) They contain a search coil and a control box. (3) The coil is mounted in the search head. (4) When an AC voltage from the box is applied to the coil, a magnetic field is created around it. (5) In turn this induces a current in any metal object the head passes over.
This paragraph illustrates some common grammar links:
Nouns become pronouns:
Metal detectors (1) becomes they (2).
Repeated nouns change from a to the and sometimes words are dropped:
A search coil (2) becomes the coil (3).
Clause and even sentences become this or that:
A magnetic field created around it (4) becomes this (5).
17. What words or word combinations in the text “Alarms and alarm systems” do these grammar links refer to?
1. … to eliminate it. (para 1)
2. The primary use of these clocks … (para 2)
3. … and its contents. (para 4)
4. … such as earthquakes or tornadoes. (para 5)
5. … that provides sensor power… (para 6)
6. … which a person may use … (para 9)
18. Find the words in bold in the text “Three stages of a simple alarm system” and write out the words or phrases they refer to.
lesson 11. The internet
Lead-in.
1. Answer the questions in pairs.
|
1.How often do you surf the Internet?
2.What do you usually do on the Internet?
3.What are your favorite websites? What sites don’t you like? Why?
4. Have you ever designed your website?
|
|
Reading and Vocabulary.
2. You are going to read the text about the Internet. Make sure you know these words and expressions.
|
worldwide to link to carry path to stay in touch with to knock out to route to treat as initial definite merger |
commonplace quarter of Earth’s population message delay satellite to reshape instant retail outlet artisans and traders supply chain entire |
3.Read the information about the Internet and match the headings (A – F) and the paragraphs (1 – 5). There is one extra heading which you don’t need to use.
A. The Stages of Development of the Internet
B. Common Information
C. The Use of the Internet
D. The Internet services
E. The future of he Internet
F. Terminology
The Internet
1. The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks to serve billions of users worldwide. It consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks which are linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services. Information sent over the Internet takes the shortest path available from one computer to another. Because of this, any computers on the Internet will be able to stay in touch with each other. If some computers on the network are knocked out, information will just route around them.
2. ‘Internet’ is a short form of the technical term ‘internetwork’, the result of interconnecting computer networks with special gateways or routers. The Internet is also often referred to as ‘the Net’. The term ‘the Internet’ is treated as a proper noun and written with an initial capital letter and the definite article. In the media and popular culture there is a trend to treat it as a generic term or common noun and thus write it as "the internet", without capitalization. Some people think that the word should be capitalized as a noun but not capitalized as an adjective.
3. The origins of the Internet reach back to research of the 1960s when the United States had private military interests to build distributed computer networks. The opening of the network to commercial interest began in the 1980s. It led to worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies, and the merger of a lot of networks. In the 1990s an international network resulted in its popularization and incorporation into virtually every aspect of modern human life. By 1996 usage of the word ‘Internet’ had become commonplace. Nowadays more than a quarter of Earth's population uses the services of the Internet.
4. The most popular Internet service is e-mail (electronic mail). The most of the people, who have access to the Internet, use the Network only for sending and receiving e-mail messages. However, other popular services are available on the Internet: reading Usenet News, using the World Wide Web, Telnet, FTP, IRC, ICQ and Gopher. Most computer-mediated communication (CMC) is asynchronous. The participants are not on line at the same time and there are delays between messages. The examples of asynchronous communication are mobile phone messages, chat rooms and e-mail. Synchronous CMC depends on participants being on line at the same time. There may be a few seconds delay – like a satellite phone. The examples of synchronous communication are Internet Relay Chat, audio and video conferencing.
5. Most traditional communications media including telephone, music, film, and television are reshaped by the Internet, giving birth to new services. Newspaper, book and other print publishing are adapting to Web site technology, or are reshaped into blogging and web feeds. The Internet enables or accelerates new forms of human communication through instant messaging, Internet forums, and social networking. Online shopping booms both for major retail outlets and small artisans and traders. Business and financial services on the Internet affect supply chains across entire industries.

