- •Lesson 1. Full-time student
- •4. Answer these questions.
- •5. Work with your partner and translate the text into Russian.
- •6. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous in the following sentences.
- •7. Study this information about two courses and find similarities and differences between them.
- •8. Write sentences describing similarities and differences you have found using the example structures.
- •9. Matthew Smith is a student of electronics at a college of further education. Here is his weekly timetable. Try to answer these questions.
- •10. Listen to the interview with Matt Smith and complete the information missing in the table.
- •11. Now listen again and answer the questions.
- •12. Read the script of the conversation at the end of the book and find English equivalents to the following words.
- •13. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words. Use your dictionary if you need.
- •4. Match the abbreviations and their full forms. Translate them into Russian.
- •6. Work with your partner and translate the given paragraphs into Russian.
- •7. Use Active or Passive voice in the following sentences.
- •8. Translate these sentences from the text into Russian paying particular attention to the translation of Passive forms.
- •9. Read and translate the text about electronics diagrams. Understanding Electronics Diagrams
- •10. Find the answers to these questions.
- •15. Now look at the basic units of the circuit and translate the text into Russian.
- •16. Fill in the gaps in this description of the tuned circuit shown in Fig. 2. Each gap represents one word. Use the words from the box.
- •17. Write the description of the following diagram. Does it answer the following questions?
- •3. Answer these questions. Use the information from the text above.
- •4. Work with your partner and find in the text the English equivalents to the words.
- •5. Match the terms and their definitions.
- •6. Complete the tables. Use the words from the text. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words.
- •8. Here are some circuit symbols. Label them and describe their function.
- •9. Study the block diagram of a battery charger. Match each component or unit with its function in a battery charger.
- •3. You are going to read a text about computers. Check that you know these words and expressions from the text.
- •4. Read the information about personal computers and choose the best heading for each paragraph (1 – 8). There is extra heading which you don’t need to use.
- •Personal Computer
- •5. Answer the questions.
- •6. Read the statements and decide if they are true (t) or false (f). Prove your answers.
- •7. Work with the partner and find English equivalents in the text above.
- •8. Match the words from the columns and translate the word combinations.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Complete the sentences with the words and expressions from the box.
- •12. Make sentences from the following words beginning with the word in bold.
- •13. Complete the table with a suitable part of speech.
- •14. Choose the words from the box and put them into Past Simple form to complete the sentences.
- •15. Write 8-10 sentences about what you did or didn’t do yesterday.
- •16. Find in the first three paragraphs the examples of using which. Explain its necessity in each case. Are they an essential part of the sentence?
- •17. Link these pairs of sentences using which. You may omit words and make whatever changes you think are necessary in the word order and punctuation of the sentences.
- •18. Write the translation of paragraphs 5 and 6. Lesson 5. Types of computers.
- •1. Answer the questions.
- •2. You are going to read the text about different types of computers. Make sure you know these words and phrases.
- •3. Read the text and complete the sentences after the text with the types of computers.
- •10 Types of Computers.
- •2. Desktop
- •3. Laptop
- •4. Netbook
- •6. Work station
- •4. Are the following sentences true (t) or false (f)?
- •5. Find in the text some more examples of comparison.
- •6. Find 4 incorrect sentences and correct them. Mistakes are all connected with comparison.
- •7. Write your own sentences comparing different types of computers.
- •8. What type of computer is the best for students? Prepare a short talk and include the following aspects:
- •9. Read the information about laptops and choose the best heading (a- f) for each paragraph (1-5). There is one extra heading which you don’t need to use.
- •10. Answer these questions.
- •11. Are the statements true (t) or false (f)? Prove your answer.
- •12. Complete the table. Use the information about laptops above.
- •13. Match the pictures and the names of the laptops.
- •14. These are examples of advantages and disadvantages of laptops. Can you separate them into two groups?
- •Vocabulary.
- •15. Find English equivalents in the information above about laptops.
- •16. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •17. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •18. Complete the tables. Translate all words.
- •19. Complete the sentences with the following words and expressions.
- •20. Write the Russian translation of paragraph 4 or 5.
- •4. Read the information again and answer the questions in pairs.
- •5. Read the statements and decide if they are true (t) or false (f). Prove your answer.
- •6. Find English equivalents in the information above.
- •7. Match the words from the two columns to have the word combinations. They all are in the information about peripherals.
- •8. Complete the tables. The necessary words are in the text. Translate all words.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Complete the sentences with the words from the box.
- •11. Explain these compound nouns.
- •3. Read the text and say about the main difference between analogue and digital recording of sound. Sound recording and reproduction
- •4. Answer the following questions.
- •5. Choose the best answer for the following definitions.
- •6. Match the following terms with their definitions.
- •8. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple in the following sentences.
- •9. Write 6-7 sentences about your experience using Present Perfect or Past Simple forms of the verbs.
- •10. Words and expressions to know.
- •11. Look at the diagram and answer these questions.
- •12. Read the information below and translate it into Russian. Mp3 Files
- •13. Answer the questions.
- •14. Explain how each of these actions happen. The explanations are available in the information above.
- •15. There are seven blanks. Complete them. Use the words from the box (Three of them are extra). Explain your choice.
- •16. Match the words from the two columns and translate the word combinations. All of them are from the information above.
- •17. Complete the information of how to make a recording by putting each of the verbs in brackets in the correct form.
- •18. Write the translation of the paragraphs beginning with “mp3 completes with another audio file format…” and the next one. Lesson 8. Sound engineer
- •1. Steve is a sound engineer. He describes his work and how you can make your own recordings of live music. The recording is in two parts:
- •2. Listen to Part 1 and answer the questions:
- •3. As you listen to Part 2, answer the following questions:
- •4. Listen again to the complete interview and answer these more difficult questions:
- •5. Which form will you use in these sentences – Past Simple or “used to”?
- •9. Answer these questions. Read the information above again if you need.
- •10. Make sentences from the words.
- •11. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech they belong to. Translate all words.
- •12. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •13. Match the words from the two columns and translate the word combinations. All of them are from the information above.
- •14. Fill in the gaps. Use the words from the box.
- •15. Which word is odd according to their meaning and use in every line? Explain your choice.
- •16. Give some advice to a sound engineer: write a list of thing to do and not to do. Use information from the text and any information of your own. When you have finished, discuss them in the class.
- •4. Answer these questions about remote controls.
- •5. Complete the table. Use the information from the text.
- •6. Read paragraph 6 again to complete the gaps in the flowchart, which shows how the remote control transmitter works.
- •7. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech the words belong to.
- •8. Match the words from two columns. Use the information above.
- •9. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •10. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •11. Go back to the flowchart you made in task 6. Write sentences to link stages 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6, using the time clauses.
- •3.Read the information about different kinds of alarms and alarm systems. What alarms and alarm systems do you think people use more often than the others? Alarms and Alarm Systems
- •4. Try to answer these questions.
- •5. Match the names of alarms or alarm systems and their examples or descriptions.
- •6. Find English equivalents in the information above.
- •7. Find the words with a similar meaning.
- •8. Find the words with an opposite meaning.
- •9. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech. The necessary words are in the text. Translate all words.
- •10. Match words from two columns to have word combinations. The information about alarms and alarm systems can help you.
- •11. Match the actions in Column a with an appropriate consequence from Column b. Then join each action and consequence using an if-sentence and making changes if it is necessary.
- •12. Think about these situations and what you will do in each of them. Then talk to your partner and find out his ideas.
- •13. Translate the paragraph which your teacher will give you.
- •14. Read and translate the text. Three stages of a simple alarm system.
- •15. Use the information from the text to complete the tables and answer the questions.
- •16. Study this simple circuit and answer the questions below it.
- •16. Write the text explaining how the door-alarm circuit works.
- •17. Write the translation of the paragraphs beginning with “The ldr forms the potential divider… “ and the next one.
- •17. What words or word combinations in the text “Alarms and alarm systems” do these grammar links refer to?
- •4. Try to answer these questions. Use the information from the text.
- •5. Are the statement true (t) or false (f)? Prove your answer. Use the information above.
- •6. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the part of speech. Translate all words. Use your dictionary if it is necessary.
- •7. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •8. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •9. Match the words from the two columns to have word combinations. Read the information about the Internet above again.
- •10. Complete the sentences. Use the words from the box.
- •11. Read the examples of cmc and complete this table.
- •12. Use can/can’t or should/shouldn’t in the following sentences.
- •13. Write some sentences to tell what you should/shouldn’t do to keep data on your computer safe.
- •14.Write the translation of paragraph 4.
- •15. Rewrite each of these sentences like this.
- •16. Complete these sentences with the correct form of the verb: infinitive or –ing form.
- •Lesson 12. Webpage creators
- •8. Now read the interview in the Appendix and find English equivalents in the information above and in the interview.
- •9. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech the words belong to.
- •10. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •11. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •12. Match the words to have word combinations.
- •13. Read the information. What is the difference between the terms ‘Internet’ and ‘World Wide Web’?
- •14. Answer the questions about your future.
- •15. Complete the gaps in this interview with will or would or the reduced forms ’ll and ’d where appropriate.
- •16. Here is a part of an interview with Alex. Fill in the blanks with will or would or the reduced forms ’ll and ’d where appropriate.
- •17. Answer the questions with the 2nd conditional sentences.
- •4. Complete the tables. Pay attention to the parts of speech the words belong to.
- •5. Match the words with a similar meaning.
- •6. Match the words with an opposite meaning.
- •7. Match the words to have word combinations. Look through the information about the anatomy of a virus if it’s necessary.
- •8. Some verbs beginning or ending with en have a causative meaning. Replace the words in italics in these sentences with the appropriate form of en verb from this list.
- •2. Putting the events in sequence and using a causative verb.
- •3. Using a when clause.
- •9. Describe how these viruses work in short texts, using different links.
- •10. Find one more example of virus and write about its work.
- •4.Work with your partner and make a list of benefits or challenges connected with Smart Home systems.
- •5.Check that you know these words and phrases from the second text.
- •6.Read the text and complete the table about technologies used in Home networking.
- •Smart Home Software and Technology
- •7.Answer the questions on the text.
- •9. Link these pairs of actions. Use short ways when this is possible.
- •The Interviewer and the Full-time Student
- •Webpage Creator
16. Here is a part of an interview with Alex. Fill in the blanks with will or would or the reduced forms ’ll and ’d where appropriate.
|
I: A: I: A:
I: A: I: A: I: A: |
What (1) _____ you do when you leave college? I hope to work in local television. What kind of work (2) _____ you like to do? I (3) _____ like to be a sound technician. That (4) _____ give me a chance to work with a camera team on location. Is there any other kind of work you (5) _____ enjoy? Maybe working for a recording studio. But it all depends on my exams. When (6) _____ you take your finals? In June. And how soon after that (7) _____ you start applying for jobs? I’ve already started. |
Writing.
17. Answer the questions with the 2nd conditional sentences.
1. What would you do if you won a lot of money?
2. What would you do if you got a very expensive present from your close friend?
3. What would be different in your life if you were a man/woman?
18. Write a text about how you imagine your future career
- where you would like to live and why
- where you would like to work and why
- what sort of work you would like to have
- experience and skills you have
- how you imagine your working day
- etc.
Lesson 13. virus
Lead-in.
1. a) What are the most common computing problems of yours? Mark them from 1 to 6 (1 is the most common one). How do you cope with these problems?
b) Can you tell about any virus?
|
Viruses Monitor problems Mouse problems |
Computer hangs Printer problems Computer crashes |
Reading and Vocabulary.
2. You are going to read the text about computer viruses. Check that you know these words and expressions.
|
simple to cause harm to patch to enable to run to load into memory resident to continue to remain dormant |
a variety of relative to display destructive to replace to return to hide trigger to take place payload fair |
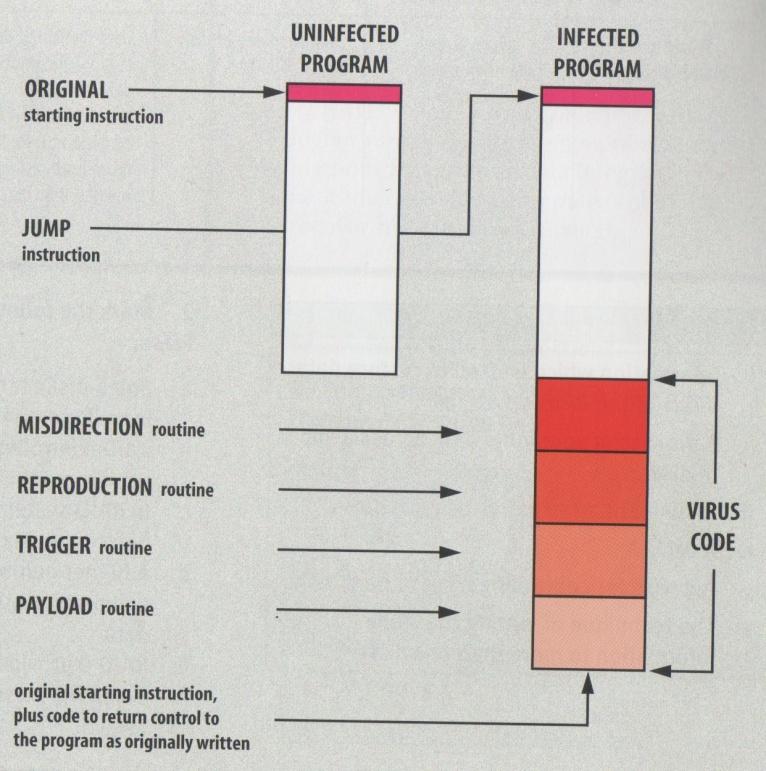
3.Read the information about the anatomy of a virus and answer the questions after the text.
The Anatomy of a Virus
A biological virus is a very small, simple organism that infects living cells, known as the host, by attaching itself to them and using them to reproduce itself. This often causes harm to the host cells.
Similarly, a computer virus is a very small program routine that infects a computer system and uses its resources to reproduce itself. It often does this by patching the operating system to enable it to detect program files, such as COM or EXE files. It then copies itself into those files. This sometimes causes harm to the host computer system.
When the user runs an infected program, it is loaded into memory carrying the virus. The virus uses a common programming technique to stay resident in memory. It can then use a reproduction routine to infect other programs. This process continues until the computer is switched off.
The virus may also contain a payload that remains dormant until a trigger event activates it, such as the user pressing a particular key. The payload can have a variety of forms. It might do something relatively harmless such as displaying a message on the monitor screen or it might do something more destructive such as deleting files on the hard disk.
When it infects a file, the virus replaces the first instruction in the host program with a command that changes the normal execution sequence. This type of command is known as a JUMP command and causes the virus instructions to be executed before the host program. The virus then returns control to the host program which then continues with its normal sequence of instructions and is executed in the normal way.
|
To be a virus, a program only needs to have a reproduction routine that enables it to infect other programs. Viruses can, however, have four main parts. A misdirection routine that enables it to hide itself; a reproduction routine that allows it to copy itself to other programs; a trigger that causes the payload to be activated at a particular time or when a particular event takes place; and a payload that may be a fairly harmless joke or may be very destructive. A program that has a payload but does not have a reproduction routine is known as a Trojan. |
|
1. How are computer viruses like biological viruses?
2. What is the effect of a virus patching the operating system?
3. Why are some viruses designed to be loaded into memory?
4. What examples of payload does the writer provide?
5. What kind of programs do viruses often attach to?
6. What is the function of the Jump instruction?
7. What are the main parts of the virus code?
8. What is the last act of the virus?
9. Match each virus routine to its function.
-
Routine
Function
1 misdirection
2 reproduction
3 trigger
4 payload
a) does the damage
b) attaches a copy of itself to another program
c) hides the presence of the code
d) decides when and how to activate the payload
10. How does a Trojan differ from a virus?