
- •Syllabus
- •Well completion design
- •High Technology Wells
- •Production from oil rims
- •Intrawell gas lift
- •Alternating gas production
- •Improving sweep efficiency in a system of injection and production wells
- •Example
- •Problem setup
- •Drainage Strategy
- •Well completion scenario
- •Simulation Results: Cumulative oil production with ICVs and its incremental volumes as compared with ordinary completion wells
- •Discounted effect, ICVs performance
- •Position of ICV in one of the wells
- •Well perforation
- •Sand Control
- •Syllabus
- •Examples of developing materials with improved erosion resistance

Section 3
Sand Control
Part II - Well completion design

Syllabus
Sand control
Problems in production from unconsolidated sands
−Sand influx and productivity of a well
−Sand failure mechanisms: sand bridging, sand arching
Gravel packing
−Gravel size selection
−Porosity and permeability of gravel packs
−Liner of screen selection
−Gravel placement
Gravel packing in deviated and horizontal wells
Part II - Well completion design
Sand management in StatoilHydro
Part II - Well completion design

Sand management
Elements in Sand Management
1.Rock mechanical data acquisition
2.Sand production prediction
3.Sand control
4.Erosion risk management
Part II - Well completion design

Sand management
Rock mechanical data acquisition
Part II - Well completion design

Rock mechanical data acquisition for sand prediction
High quality data acquisition is the basis for all rock mechanics, including
•Sand prediction
•Stress in the formation
•Mechanical properties of the formation
Part II - Well completion design
Rock mechanical data acquisition for sand prediction
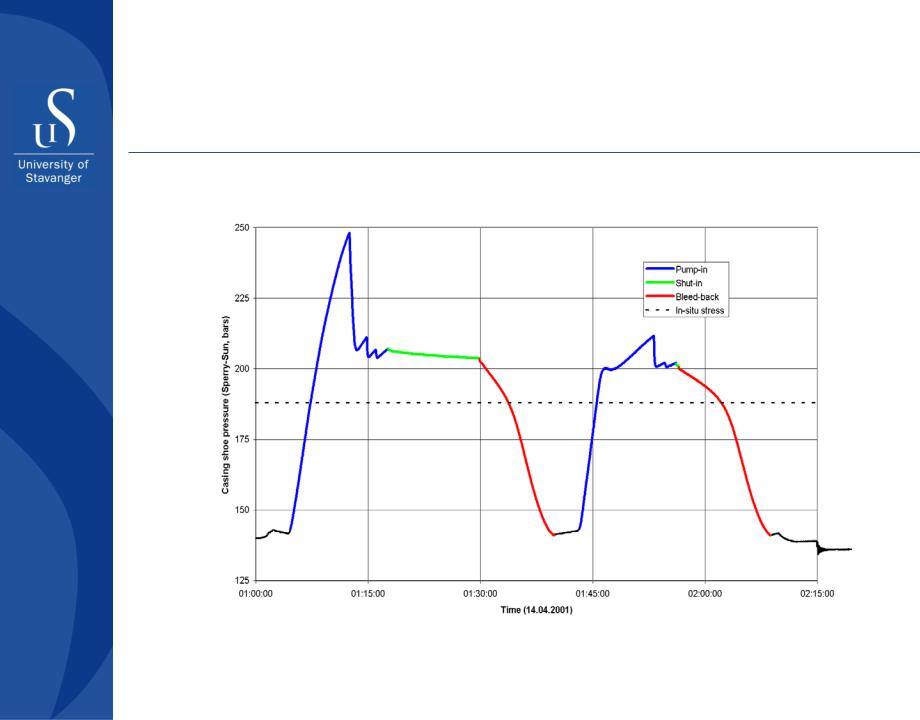
XLOT to derive magnitude of minor horizontal stress
Part II - Well completion design

Rock mechanical data acquisition for sand prediction
Stress direction based on breakout and drilling induced fractures from image logs
Direction of major horizontal stress in the Tampen area in the North Sea.
Blue dots indicate wells where no breakout or drilling induced fractures were found.
Part II - Well completion design

Sand management
Sand production prediction
Part II - Well completion design
Sand production prediction
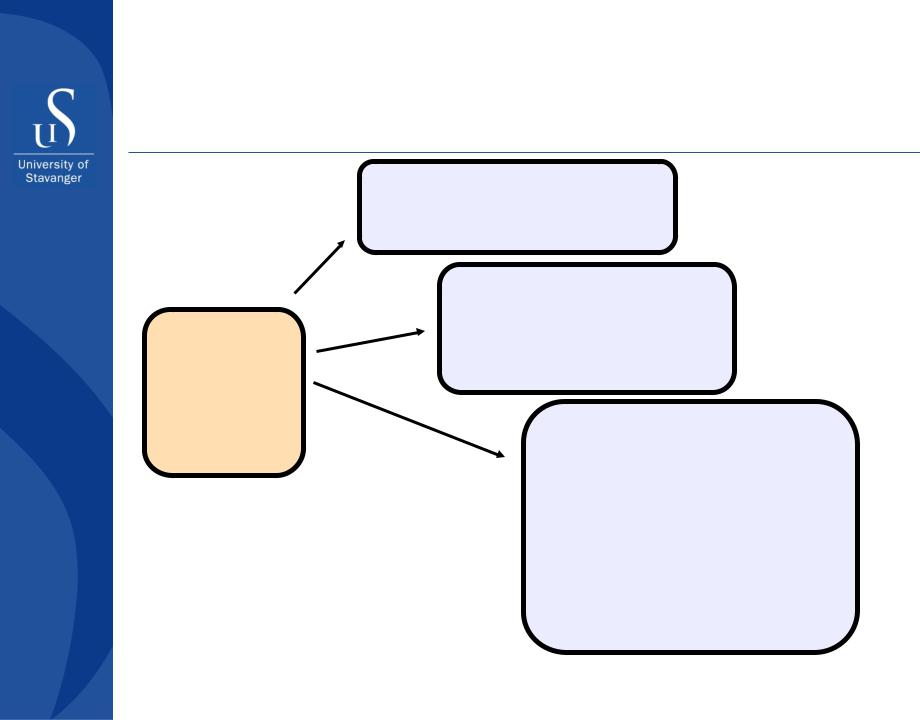
A key element in sand management
No sand production expected |
Strong reservoir |
independent of well direction |
|
and perforation strategy |
|
Possible outcome of sand
prediction
Sand production can be |
Medium |
|
avoided by a carefully |
|
|
chosen well direction or |
|
|
perforation strategy |
|
|
Independent of perforation |
|
|
strategy, the well will produce |
|
|
sand if the rate is above |
|
Weak |
maximum sand-free rate |
||
Strategy:
Use sand prediction in design, avoid sand control when possible
Use mechanical sand control or produce at maximum acceptable sand rate
Part II - Well completion design
Sand production prediction methodology
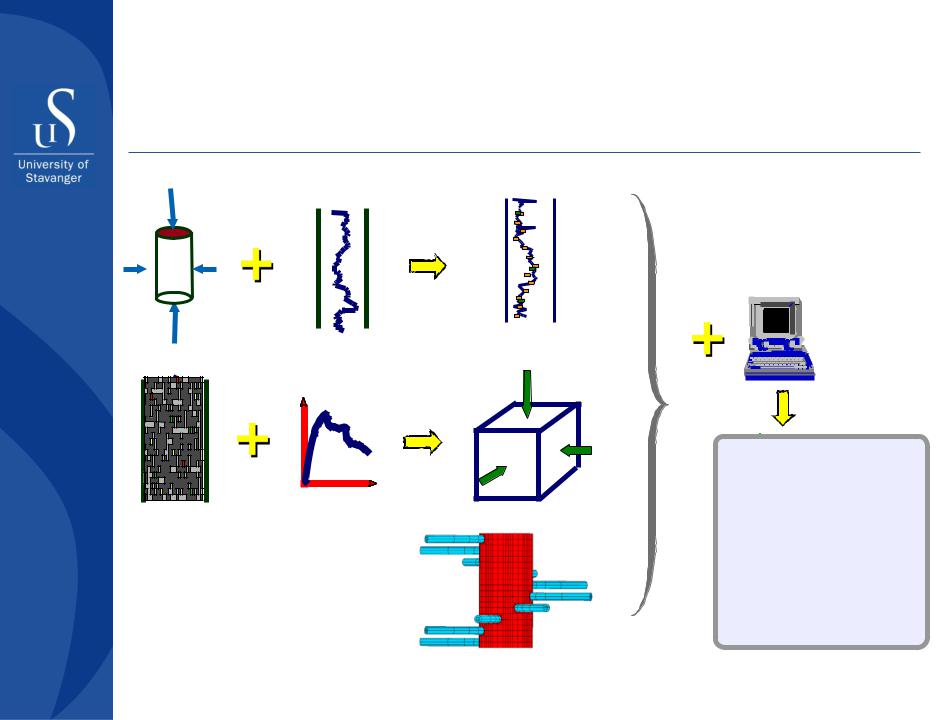
Strength testing |
Borehole logs |
Formation strength |
Stability simulation by use of FEM
Image log |
Minifrac or XLOT |
Stress state |
Pressure
Time |
Geometry/boundary conditions
Sand production potential as a function of perforation geometry, reservoir depletion and drawdown
Part II - Well completion design
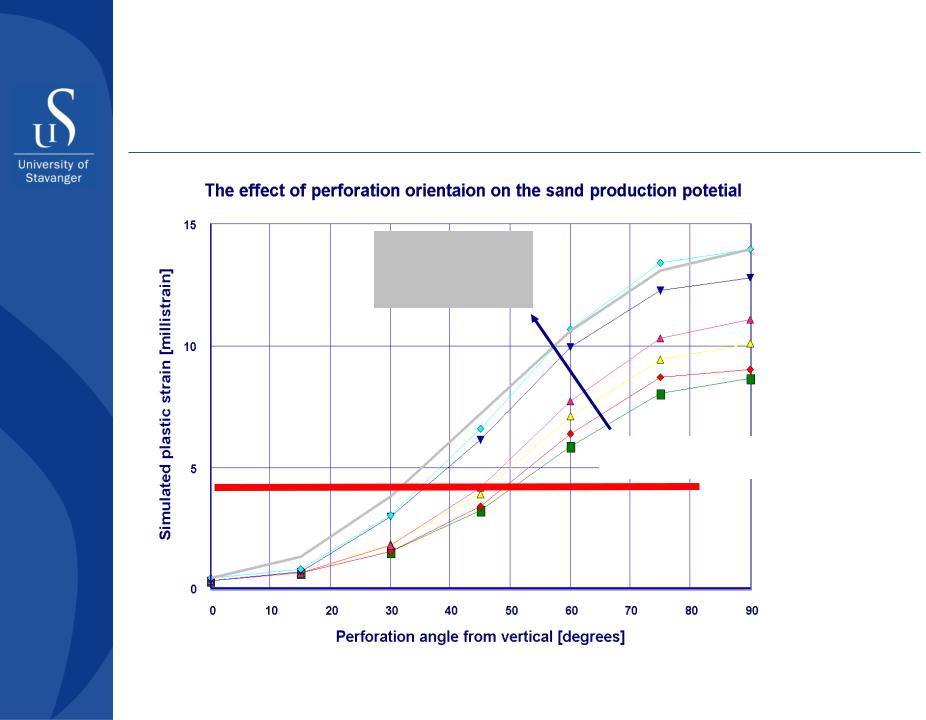
Sand production prediction
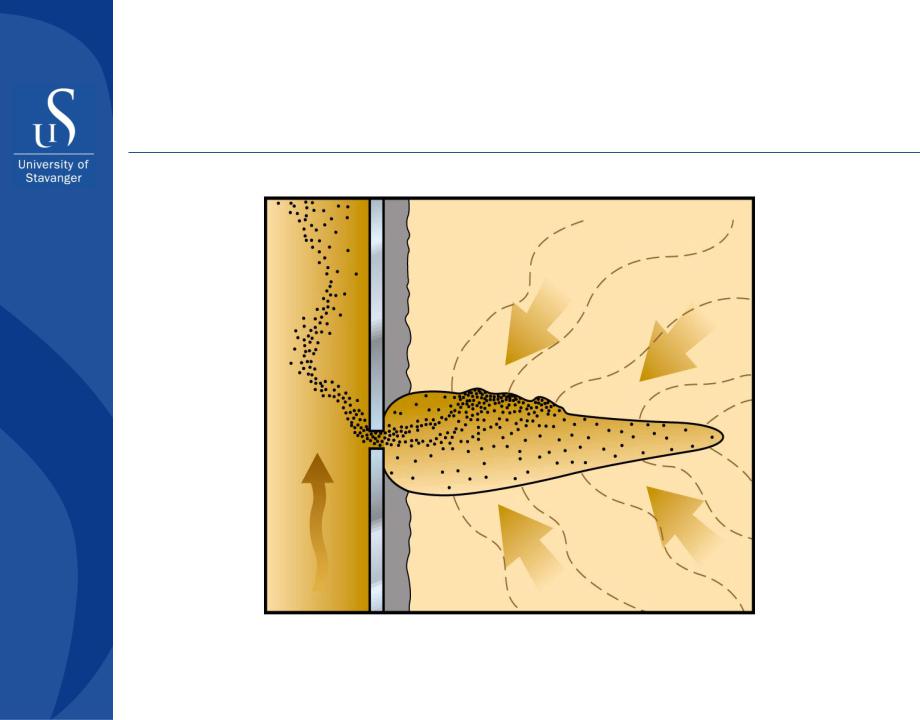
Effect of perforation orientation in a horizontal well
Increasing drawdown and depletion
Expected sand production above red line
Part II - Well completion design

Sand management
Sand control
Part II - Well completion design

Sand control
Statoil practice the last decade
Mechanical sand control installed in more than 200 Statoil wells since 1994:
•25% Cased hole gravel pack
•25% Stand alone screen in open hole
•50% Open hole gravel pack
•A couple of frac packs (both cased hole and open hole)
Statoil’s present sand control strategy:
•Open hole completions to reduce risk of plugging
•Frac pack to stimulate productivity in stratified reservoirs
Part II - Well completion design
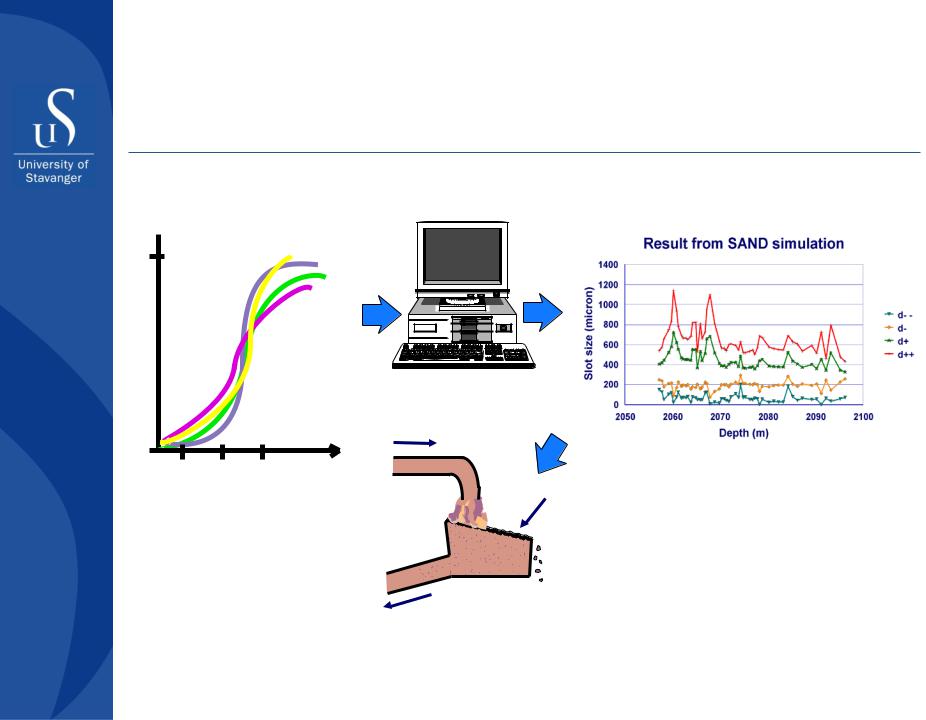
Sand control
Sizing screen for open hole application
|
Particle size |
|
|
100 |
distribution of |
Computer |
|
formation |
|||
% |
program |
||
|
|||
|
|
SAND |
0% |
|
|
0,01 |
0,1 |
1,0 |
|
|
Shake |
|
|
r |
|
|
scree |
|
|
n |
Screen slot size to be selected between d- and d+
Sand-screen slot size dictate mud conditioning
Part II - Well completion design

Sand control
Testing the mechanical strength of screens
Part II - Well completion design
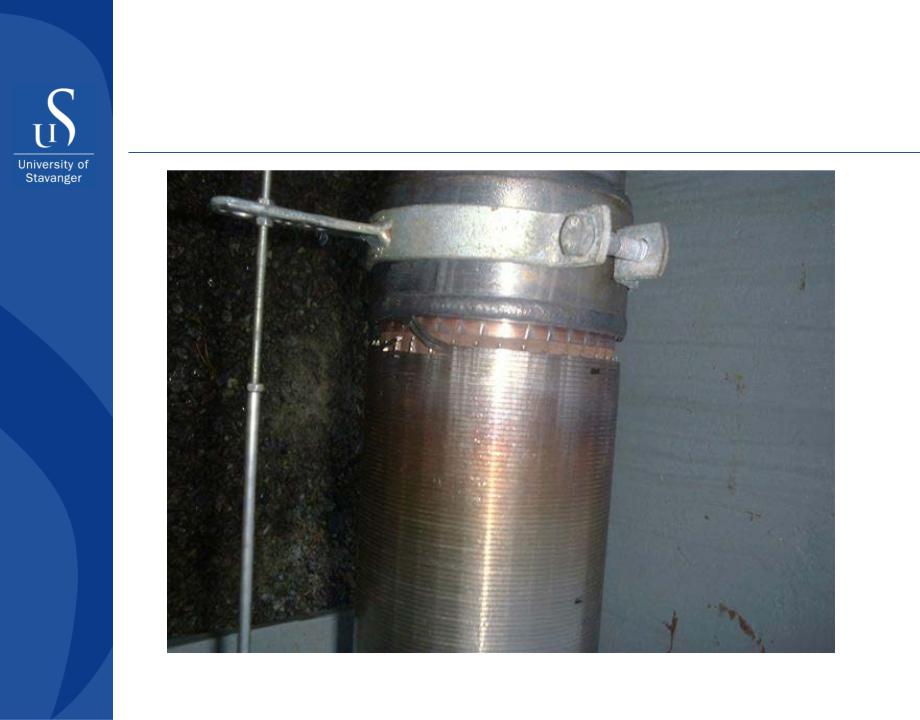

Sand control
Failure mode of certain types of wire wrapped screens
Part II - Well completion design

Sand management
Erosion risk management
Part II - Well completion design

Erosion risk management
Examples of choke erosion
Part II - Well completion design
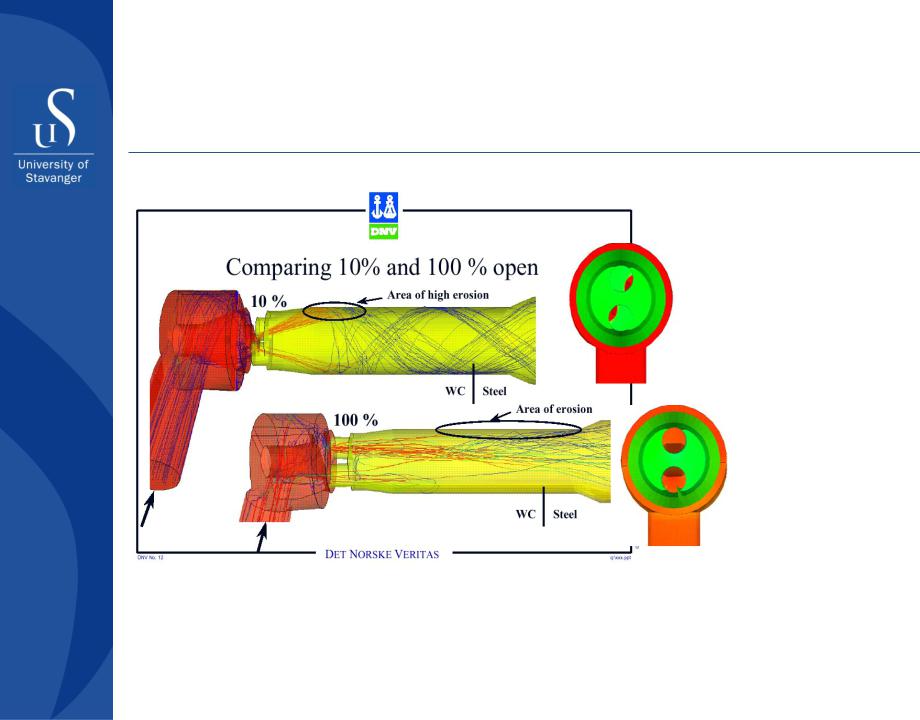
Erosion risk management
Examples of erosion modeling by CFD
Simulations show that wells with high gas production and small choke opening will experience concentrated erosion where the outlet jets hit the pipe wall (upper figure).
By changing to choke discs with smaller holes that can be operated fully, or close to fully open, the erosion rate will be dramatically reduced (lower figure).
Part II - Well completion design
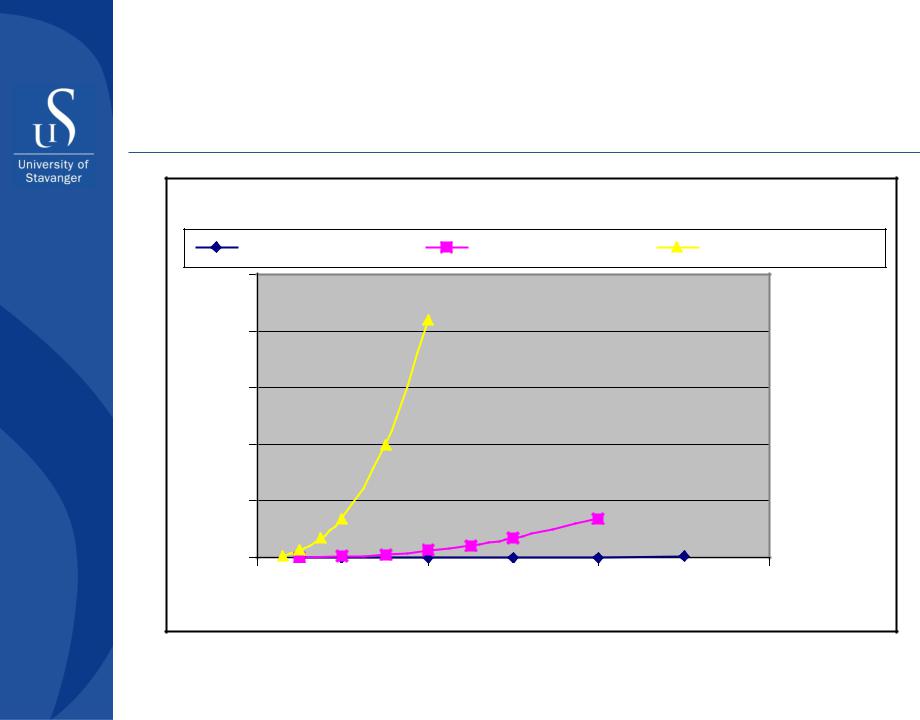
Erosion risk management
Erosion prediction for 6” pipe bend
|
|
WC=0, p=55bar, 1.5D bend, 0.3 mm particles |
||
|
GOR=100Sm³/Sm³ |
GOR=500Sm³/Sm³ |
GOR=1500Sm³/Sm³ |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
sand) |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mm/tonn |
0.3 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
Erosion |
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
2000 |
4000 |
6000 |
|
|
Production rate (Sm³/day oil+water) |
|
|
Part II - Well completion design
