- •2. Phonetics and its branches.
- •3. Phonetics and a speech sound. Human speech and its stages.
- •4. Language and speech.
- •5. The theoretical and practical aspects of Phonetics.
- •The notion of the phoneme. The phoneme and its main aspects.
- •Relationship between the phoneme and its allophones.
- •The main trends in phoneme theory.
- •1.The notion of the phoneme. The phoneme and its allophones.
- •2.Relationship between the phoneme and its allophones.
- •3. The main trends in phoneme theory.
- •1. The three parts of Phonology as corresponding to the three levels of Linguistic analysis.
- •2. The distributional method in phonology
- •3. The semantic method in phonology
- •Lecture 4.
- •2. Paradigmatic and syntagmatic approaches as the principle aspects of phonological system.
- •3. Synchronic, diachronic and socio-linguistic factors in phonological system.
- •The phonetic structure of a language.
- •1) Type of obstruction;
- •2) Place of obstruction and the active organ of speech;
- •3) Force of articulation.
- •4. The position of the soft palate.
- •1. The place of noise.
- •2. The manner of articulation.
- •2. Constrictive;
- •3. Occlusive-constrictive (affricates);
- •4. Rolled;
- •3. The place of articulation.
- •1. Labial;
- •2. Lingual;
- •3. Glottal;
- •3. Differences in the Articulation Bases of English and Russian Consonants and their Peculiarities
- •It is a reference point which is fixed and unchanged, established within the total range of vowel quality to which any other vowel sound can be directly related.
- •2. Classification of English vowels.
- •1. Classification of the vowels according to the position of the tongue.
- •2. Classification of English vowels according to the position of the lips.
- •3. Classification of English vowels according to length.
- •4. Classification of English vowels according to the degree of tenseness.
- •3. Stability of articulation. English diphthongs.
- •Articulatory Transitions
- •Peculiarities of the cc, cv, vc, VV Articulatory Transitions in English and in Russian
- •Unstressed Vocalism
- •Lecture 8 the principle types of english pronunciation. The teaching norm. Rp and ga
- •Diphthongs
- •Lecture 9.
- •2. Types of Syllables.
- •3. Syllable Formation and Syllable Division.
- •Scale of Sonority
- •4. Vocoids and contoids.
- •2. Types of word stress. Factors, kinds and degrees of word stress.
- •Qualitative type of stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel under stress.
- •Recessive tendency, 2. Rhythmic tendency, 3.Retentive tendency and 4. Semantic factor.
- •3.Rules of word stress. Stress in compounds.
- •Verb noun adjective
- •4. The functional aspect of word stress.
- •5. Strong and weak forms. Degrees of reduction.
- •6 Sentence stress.
- •2. The structural elements of prosody.
- •3. Intonation Patterns.
- •4. Fundamental Intonation Patterns and their Use.
- •2. Extralinguistic situation and its main constituents:
- •3. The problem of classification of phonetic styles.
- •2. Academic style.
- •Publicistic style.
- •4. Informational style.
- •5. Declamatory style.
- •Список вопросов к экзамену/зачету по теоретической фонетике.
- •Задания для самостоятельной работы
- •2. Declamatory style:
- •Plan of phonostylistic analysis.
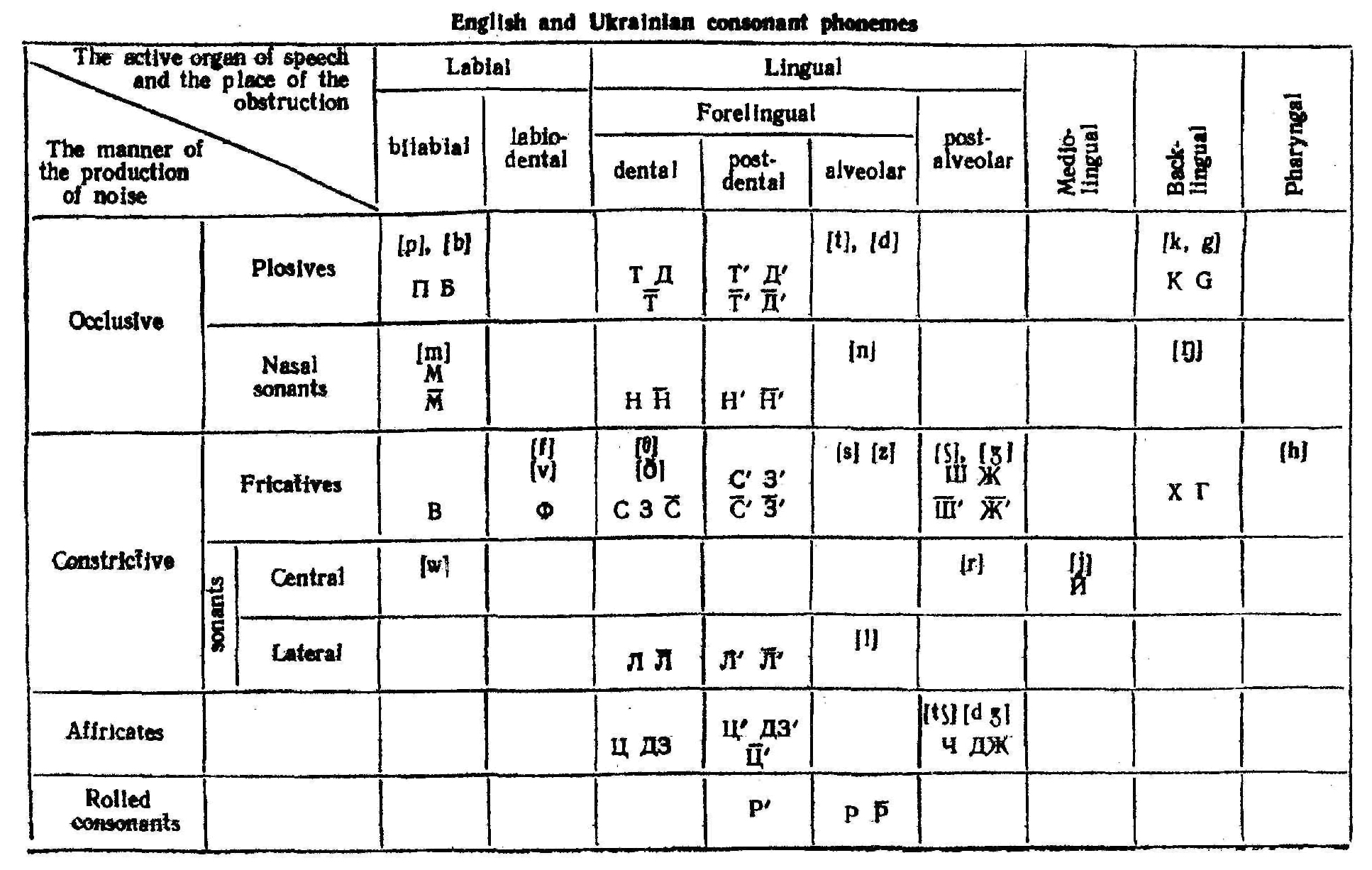
3. The place of articulation.
The place of articulation is determined by the active organ of speech against the point of articulation. There may be one place of articulation or focus, or two places of articulation or focus when active organs of speech contact with two points of articulation. In the first case consonants are called unicentral, in the second they are bicentral.
According to the position of the active organ of speech against the point of articulation (i.e. the place of articulation) consonants may be:
1. Labial;
2. Lingual;
3. Glottal;
Labial consonants are made by the lips. They may be bilabial and labio-dental. Bilabial consonants are produced when both lips are active. Labio-dental consonants are articulated with the lower lip against the edge of the upper teeth.
Lingual consonants are classified into forelingual, mediolingual and backlingual.
Forelingual consonants are articulated with the tip of the blade of the tongue. They differ in the position of the tip of the tongue. According to its work they may be: apical, if the tip of the tongue is active;
dorsal, if the blade of the tongue takes part in the articulation, the tip being passive and lowered;
cacuminal, if the tip of the tongue is at the back part of the teeth ridge, but a depression is formed in the blade of the tongue;
According to the place of obstruction forelingual consonants may be:
interdental;
dental;
alveolar;
post-alveolar;
palato-alveolar.
Interdental consonants or interdentals are made with the tip of the tongue projected between the teeth;
Dental consonants or dentals are produced with the blade of the tongue against the upper teeth;
Alveolar consonants or alveolars are articulated with the tip of the tongue against the upper teeth ridge;
Post-alveolar consonants or post alveolars are made when the tip or the blade of the tongue is against the back part of the teeth ridge or just behind it;
Palato-alveolar consonants or palato-alveolars are made with the tip or the blade of the tongue against the teeth ridge and the front part of the tongue raised towards the hard palate, thus having two places of articulation.
Mediolingual consonants are produced with the front part of the tongue. They are always palatal. Palatal consonants or palatals are made with the front part of the tongue raised high to the hard palate;
Backlingual consonants are also called velar, because they are produced with the back part of the tongue raised towards the soft palate (Lat. velum)
3. The glottal consonant [h] is articulated in the glottis.
4. According to the position of the soft palate: oral, nasal.
When the soft palate is raised and the air gets into pharynx (from the lungs) and then into the mouth cavity, the oral consonants are produced. When the soft palate is lowered and the air on its way passes through the nasal cavity, the nasal consonants are produced.
2. The system of English consonant phonemes as compared with the system of Ukrainian and Russian consonant phonemes.
English consonants differ from the Ukrainian consonants in many points.
1. The number of consonant phonemes is not the same in the two languages.
There are 24 consonant phonemes in the English language. In the Ukrainian language there are 47 consonant phonemes (16 of them are long).
2. Both Ukrainian and English consonant phonemes are classified according to the obstruction and according to the work of the vocal chords.
These features of articulation are considered to be phonematically independent in the two languages.
3. In the Ukrainian language there are short and long consonant phonemes.
Therefore we say that length of consonants is also phonematically an independent feature of articulation in Ukrainian. This feature of articulation does not exist in English, as there are no long consonant phonemes in the English language.
4. In Ukrainian there are non-palatalized and palatalized consonant phonemes.
Therefore we may say that palatalization is also phonematically an in
dependent feature of articulation in the Ukrainian language. Palatalized consonant phonemes do not exist in English. Dark or clear variants of the English [l] depend upon the position of the sound in the word.
5.English voiceless plosive consonants [p], [t], [k] are aspirated, while there are no aspirated consonants in the Ukrainian language.
6. According to the active organ causing the obstruction, there are the following groups of consonants in the Ukrainian language labial (bilabial and labio-dental) and lingual (forelingual, mediolingual, backlingual). In the English language besides the above mentioned groups there exists a group of pharyngeal consonants to which English [h] belongs.
7. The distribution of English and Ukrainian consonant phoneme among the groups of consonants is also different. The Ukrainian group of forelingual consonants includes palatalized and long phoneme and the phonemes [Ц], [ДЗ]. In its turn the English group of forelingual consonants includes the phonemes [ ], [ ] which do not exist in the Ukrainian language. The group of English backlingual consonants includes the phonemes [k], [g], [ ], while in Ukrainian [ ] does not exist, but at the same time there are two additional Ukrainian backlingual constrictive consonants [Х], [Г].
8. There is also a difference between the phonematic system of English and Ukrainian consonants in the articulation of similar consonants, i.e. consonants united by some common feature of articulation. Thus, in pronouncing Ukrainian forelingual consonant the place of obstruction is generally nearer to the front upper teeth than in the corresponding English consonants. The Ukrainian [Т], [Л], [Н], [С], [З], for example, are dental according to the passive organs of speech, while the English [t], [d], [n], [s], [z] are alveolar, the Ukrainian [Р] is alveolar, the English [r] is post-alveolar, etc.
9. The shape of the tongue in pronouncing English and Ukrainian forelingual consonants is different. English forelingual consonants are usually apical, while the Ukrainian ones are as a rule cacuminal.
10. Lip articulation differs in pronouncing English and Ukrainian consonants. In Ukrainian pronunciation there is no noticeable tension of the lips, though there is a considerable protrusion.