
- •Activity 1.1.1: Using Google Earth™ to View the World
- •Activity 1.4.5: Identifying Top Security Vulnerabilities
- •Lab 1.6.1: Using Collaboration Tools— IRC and IM
- •Lab 1.6.2: Using Collaboration Tools—Wikis and Web Logs
- •1.7.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Introduction to Packet Tracer
- •Activity 2.2.5: Using NeoTrace™ to View Internetworks
- •Lab 2.6.1: Topology Orientation and Building a Small Network
- •Lab 2.6.2: Using Wireshark™ to View Protocol Data Units
- •2.7.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Examining Packets
- •Activity 3.4.1: Data Stream Capture
- •Lab 3.4.2: Managing a Web Server
- •Lab 3.4.3: E-mail Services and Protocols
- •Lab 4.5.1: Observing TCP and UDP using Netstat
- •Lab 4.5.2: TCP/IP Transport Layer Protocols, TCP and UDP
- •Lab 4.5.3: Application and Transport Layer Protocols Examination
- •Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Device’s Gateway
- •Lab 5.5.2: Examining a Route
- •5.6.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Routing IP Packets
- •Lab 6.7.1: Ping and Traceroute
- •Lab 6.7.2: Examining ICMP Packets
- •Activity 6.7.3: IPv4 Address Subnetting Part 1
- •Activity 6.7.4: IPv4 Address Subnetting Part 2
- •Lab 6.7.5: Subnet and Router Configuration
- •Lab 7.5.2: Frame Examination
- •7.6.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Data Link Layer Issues
- •Lab 8.4.1: Media Connectors Lab Activity
- •Lab 9.8.1: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- •Lab 9.8.2: Cisco Switch MAC Table Examination
- •Lab 9.8.3: Intermediary Device as an End Device
- •9.9.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Switched Ethernet
- •Lab 10.3.2: How Many Networks?
- •Lab 10.6.1: Creating a Small Lab Topology
- •Lab 10.6.2: Establishing a Console Session with HyperTerminal
- •Lab 10.6.3: Establishing a Console Session with Minicom
- •11.4.3.3: Network Latency Documentation with Ping
- •Lab 11.5.1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration
- •Lab 11.5.2: Managing Device Configuration
- •Lab 11.5.3: Configure Host Computers for IP Networking
- •Lab 11.5.4: Network Testing
- •Lab 11.5.5: Network Documentation with Utility Commands
- •Lab 11.5.6: Final Case Study - Datagram Analysis with Wireshark
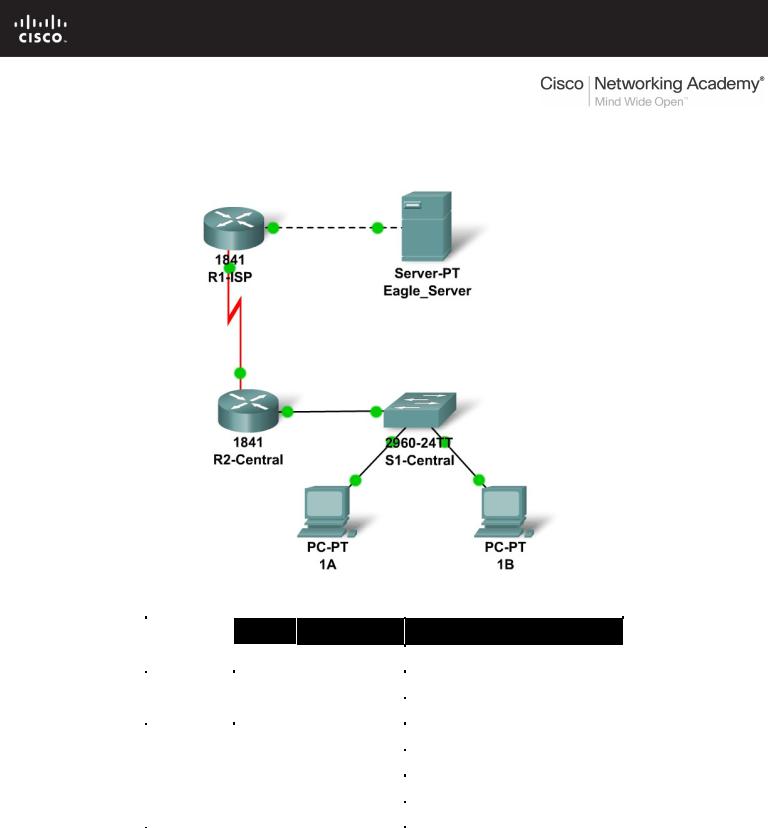
9.9.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Switched Ethernet
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1-ISP |
Fa0/0 |
192.168.111.134 |
255.255.255.248 |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
||
S0/0/0 |
192.168.111.138 |
255.255.255.252 |
N/A |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
R2-Central |
Fa0/0 |
|
|
192.168.111.138 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
S0/0/0 |
192.168.111.137 |
255.255.255.252 |
192.168.111.138 |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC 1A |
NIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC 1B |
NIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eagle Server |
NIC |
192.168.111.133 |
255.255.255.248 |
192.168.111.134 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 1 of 3 |

CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Ethernet |
9.9.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Switched Ethernet |
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
•Determine IP subnet planning
•Repair Ethernet-related network issues.
•Test the network
Background
You have been asked to repair some problems in the network model related to the Ethernet LAN connected to R2-Central.
Task 1: IP Subnet Planning.
You have been given an IP address block of 192.168.111.0 /24. You must provide for the three existing networks.
Subnet assignments are:
•1st subnet, existing student LAN, up to 100 hosts; (Fa0/0 on R2-Central)
•2rd subnet, existing ISP LAN, up to 5 hosts; (already configured)
•3rd subnet, existing WAN, point-to-point link; (already configured)
Interface IP addresses:
•The server, R1-ISP, and R2-Central's serial interface have already been configured.
•For R2-Central's Fa0/0 interface, use the highest usable address on the existing student LAN subnet.
•For hosts 1A and 1B, use the first 2 IP addresses (two lowest usable addresses) on the existing student LAN subnet.
•For Hosts 1A and 1B, the DNS server is 192.168.111.133 /29.
•The next hop router (to which the default route should point), R1-ISP, has an IP address of 192.168.111.138 /30.
Task 2: Repair Problems with the Ethernet Switched LAN.
•PC 1B has a wireless card and cannot be connected to the switch; add the Fast Ethernet Interface card PT-HOST-NM-1CFE to PC 1B.
•Connect this newly installed Fast Ethernet NIC to the Fa0/2 interface on the switch.
•Connect PC 1A to the Fa0/1 interface on the switch.
•Connect the Fa0/24 interface on the switch to the R2-Central Fa0/0 interface.
Apparently the Ethernet speed and duplex settings for the R2-Central Fa0/0 interface, the S1Central switch interfaces (Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/24), and the PC 1A interfaces are incorrect. Set all Ethernet interfaces to auto negotiate speed and duplex (which will achieve Full Duplex, 100 Mbps operation, if both ends of the link can support it). For all devices, make sure the power is on to the device and to the interfaces (make sure the Ethernet interfaces are not shut down). Add IP addresses to the router Fa0/0 interface and to the two PCs-- highest usable subnet address assigned to the gateway; two lowest usable addresses to the PCs. The static route on the R2Central should be a default static route which points via R1-ISP's serial interface IP address. These procedures were explained in the Chapter 5 and 6 Skills Integration Challenges.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 2 of 3 |

CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Ethernet |
9.9.1: Skills Integration Challenge-Switched Ethernet |
Task 3: Test the Network.
Use ping, trace, web traffic, and the Inspect tool to trace packet flow in simulation mode, with HTTP, DNS, TCP, UDP, ICMP, and ARP viewable, to test your understanding of how the network is operating.
Reflection
The two Layer 2 (and Layer 1 technologies) in this model are a serial connection (between the routers) and the Ethernet LANs (for the ISP server and with S1-Central switch). Compare and contrast the serial connection with Ethernet. In a future course you will learn much more about switched Ethernet technologies.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 3 of 3 |

Lab 10.3.2: How Many Networks?
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
•Determine the number of subnets.
•Design an appropriate addressing scheme.
•Assign addresses and subnet mask pairs to device interfaces.
•Examine the use of the available network address space.
Scenario
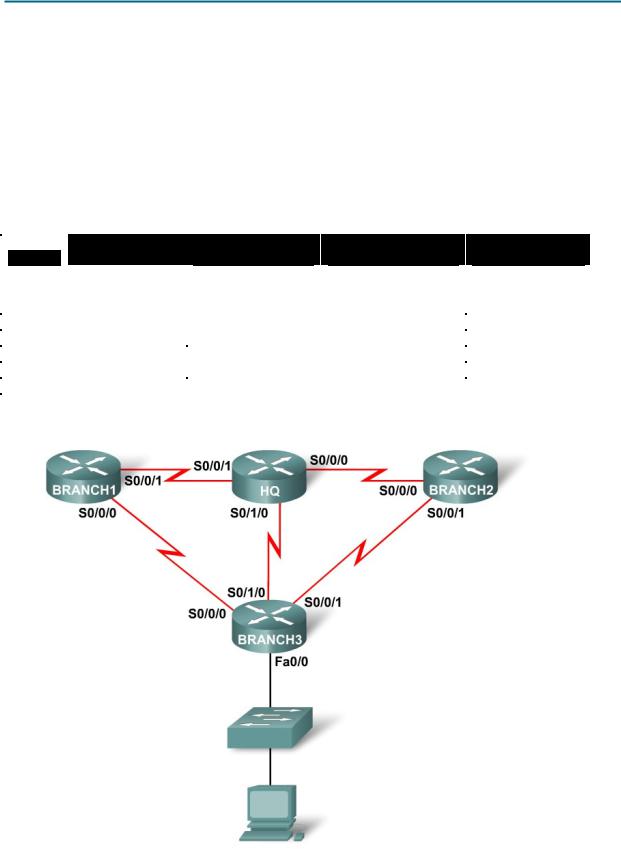
In this lab, you have been given the network address 192.168.26.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP addressing for the networks shown in the Topology Diagrams. You must determine the number of networks needed then design an appropriate addressing scheme. Place the correct address and mask in the Addressing Table. In this example, the number of hosts is not important. You are only required to determine the number of subnets per topology example.
Topology Diagram A
Task 1: Determine the Number of Subnets in the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: How many networks are there? ____
Step 2: How many bits should you borrow to create the required number of subnets? ____
Step 3: How many usable host addresses and usable subnets did this give you? ____
Step 4: What is the new subnet mask in decimal form? _____________________________
Step 5: How many subnets are available for future use? ____
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 1 of 6 |

CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Planning and Cabling Networks |
Lab 10.3.2 How Many Networks? |
Task 2: Record Subnet Information.
Step 1: Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
|
Subnet |
Subnet Address |
First Usable |
Last Usable |
Broadcast |
|
Number |
Host Address |
Host Address |
Address |
|
|
|
||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
Topology Diagram B
Fa0/0 |
Fa0/0 |
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 2 of 6 |
CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Planning and Cabling Networks |
Lab 10.3.2 How Many Networks? |
Task 1: Determine the Number of Subnets in the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: How many networks are there? ____
Step 2: How many bits should you borrow to create the required number of subnets? ____
Step 3: How many usable host addresses and usable subnets did this give you? ____
Step 4: What is the new subnet mask in decimal form? _____________________________
Step 5: How many subnets are available for future use? ____
Task 2: Record Subnet Information.
Step 1: Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
|
Subnet |
Subnet Address |
First Usable |
Last Usable |
Broadcast |
|
Number |
Host Address |
Host Address |
Address |
|
|
|
||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
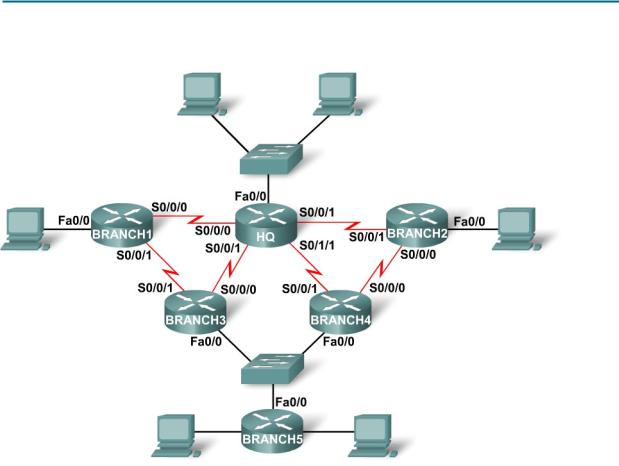
Topology Diagram C
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 3 of 6 |

CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Planning and Cabling Networks |
Lab 10.3.2 How Many Networks? |
Task 1: Determine the Number of Subnets in the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: How many networks are there? ____
Step 2: How many bits should you borrow to create the required number of subnets? ____
Step 3: How many usable host addresses and usable subnets did this give you? ____
Step 4: What is the new subnet mask in decimal form? _____________________________
Step 5: How many subnets are available for future use? ____
Task 2: Record Subnet Information.
Step 1: Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
|
Subnet |
Subnet Address |
First Usable |
Last Usable |
Broadcast |
|
Number |
Host Address |
Host Address |
Address |
|
|
|
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 4 of 6 |
CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Planning and Cabling Networks |
Lab 10.3.2 How Many Networks? |
Topology Diagram D
Fa1/0
Task 1: Determine the Number of Subnets in the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: How many networks are there? ____
Step 2: How many bits should you borrow to create the required number of subnets? ____
Step 3: How many usable host addresses and usable subnets did this give you? ____
Step 4: What is the new subnet mask in decimal form? _____________________________
Step 5: How many subnets are available for future use? ____
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 5 of 6 |
CCNA Exploration |
|
Network Fundamentals: Planning and Cabling Networks |
Lab 10.3.2 How Many Networks? |
Task 2: Record Subnet Information.
Step 1: Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
|
Subnet |
Subnet Address |
First Usable |
Last Usable |
Broadcast |
|
Number |
Host Address |
Host Address |
Address |
|
|
|
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Reflection
What information is needed when determining an appropriate addressing scheme for a network?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. |
Page 6 of 6 |
