
- •Price and output determination under the perfect competition. Profit maximization under perfect competition. Firms behavior under perfect competition.
- •Basic characteristics of perfect competition.
- •T otal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •A verage and marginal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Last week was said!!!
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •Oligopoly.
- •The basic characteristics of an oligopoly:
- •Explicit collusions:
- •Rules of thumb models.
- •Kinked d-curve. Assumptions:
- •Maximax strategy (optimistic approach). Ex:
- •Cournot model / duopoly (2 firms in industry) 1830s.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Market equilibrium in different market structures.
- •Algebraic explanation of the Cournot model.
- •Stackelberg model (quantity leadership model).
- •Contestable markets model.
- •Oligopoly and public.
- •Monopolistic competition.
- •Major characteristics:
- •Lr equilibrium
- •Minuses”-”.
- •Derived dem. For ec. Resources.
- •Equilibrium of the firm on the resource market.
- •Sr equilibrium:
- •Lr equilibrium(all factors are variable):
- •Wage determination under Perfect competition.
- •Wage determination under imperfect competition.
- •The theory of distribution of income II. Capital(k) and Land.
- •Concepts of capital.
- •Measuring k.
- •How does the firm invest?
- •Sell bills/bonds to the households.
- •Sr rentals include:
- •Demand and Supply for k purchase.
- •Fairness and effectiveness
- •Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- •Distr. Of income and wealth characteristics:
- •Pareto efficiency and Edgeworth box.
- •Edgeworth box
- •Pareto efficiency allocation:
- •P rinciple possibility of losses compensation.Icks
- •There are positive and negative external effects, divided into 4 groups:
- •Taxes (Pigourian taxes)
- •Sell the right to pollute for example.
- •Public goods –
Price and output determination under the perfect competition. Profit maximization under perfect competition. Firms behavior under perfect competition.
Basic characteristics of perfect competition.
There are 4 basic market structures: Perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly(pure).
All market structures are distinguished by 5 characteristics. We apply them to perfect competition:
There are very many consumers/producers and an individual supply to the market of a single firm is insignificant in comparison with industrial supply. SO:
Firms and households have no price control. They can’t influence the market price, they take it => they are price-takers.
There are no restrictions to the entry of new firms to the industry (free entry/exit).
The product is homogeneous, there are no trademarks.
T
 he
demand curve for a product of a firm is a horizontal line:
he
demand curve for a product of a firm is a horizontal line:
There is no sense for the firm to charge a lower price as it can sell all it produces at the current market price. And it’s impossible to charge a higher price, as there are lots of rivals and the Demand for this firm’s product will fall to zero.
T otal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
TR = P ∙ Q
Max TП the Max vertical distance between TR and TC curves.
TR>TC – Economic profit.
TR<TC – Ec losses.
TR=TC – normal profit (cost of staying in business).
If in SR Ec profit is earned the LR decision is to EXPAND.
If in SR Ec losses occur, the LR decision is to contract of even to shutdown and exit.
A verage and marginal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
D-curve coincides with MR/AR curves.
MR is the revenue received from each additional unit of good.
AR is the Revenue per unit of output. AR= TR/Q.
MR=MC – general rule for all firms.
MR=P for perfect competition. P=MC – general rule for perfect competition – the rule of allocative efficiency. When the equality is true the producers produce goods most wanted by the society. This is the main rule of profit MAX or losses MIN.
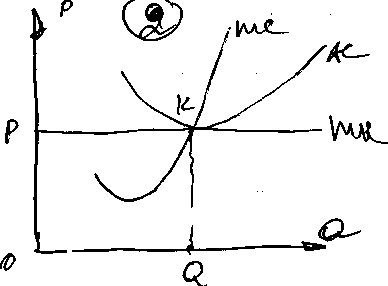
On the graph: TR = P∙Q= OPKQ
TC = AC∙Q = OMLQ
ТП = TR – TC = PKLM or:
ТП = АП∙Q = (P-AC) ∙Q=PKLM
The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.

Last week was said!!!
P↓ = bottom level of MR. AC = P TR = TC(OPKQ) in this case a firm earns normal profit.
P↓ price line is between AC and AVC curves(AVC<P<AC) a firm suffers ec. losses(TR<TC(OKLQ)), KLMP – ec. losses).
MR = MC – rile of profit maximization(or losses minimisation)
 !!!
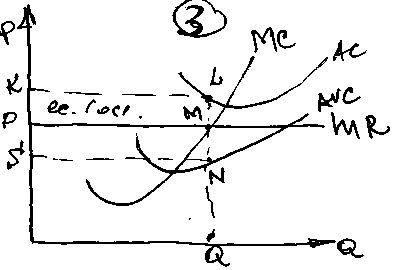
If a firm continues production in the SR, it suffers econ. losses =
PKLM; if in the SR firm decides to close down, its losses = TFC =
SKLN)
!!!
If a firm continues production in the SR, it suffers econ. losses =
PKLM; if in the SR firm decides to close down, its losses = TFC =
SKLN)TC = OKLQ
TVC = OSNQ KS = LN =AFC
TFC = SKLN
Conclusion: losses can be min, if the firm continues production in the SR. IT’s so, as P>AVC it compensates AVC and some part of the AFC(PS- отрезок).
Losses are minimized, due to the profit on operation(POO) – SPMN and POO = (P –AVC)*Q
!!!OR POO = PQ – AVC*q = TR – TVC
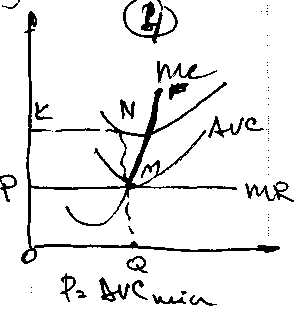
P touches AVC shut down point(M).
If a firm prod in the SR it’ll suffer losses(TFC = PKNM), even if it’ll shut down(losses are the same).
!!! There is no output below the P-line the MC-curve of the firm above AVC-curve illustrates the supply(MF) of the firm in the SR.
