
- •Price and output determination under the perfect competition. Profit maximization under perfect competition. Firms behavior under perfect competition.
- •Basic characteristics of perfect competition.
- •T otal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •A verage and marginal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Last week was said!!!
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •Oligopoly.
- •The basic characteristics of an oligopoly:
- •Explicit collusions:
- •Rules of thumb models.
- •Kinked d-curve. Assumptions:
- •Maximax strategy (optimistic approach). Ex:
- •Cournot model / duopoly (2 firms in industry) 1830s.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Market equilibrium in different market structures.
- •Algebraic explanation of the Cournot model.
- •Stackelberg model (quantity leadership model).
- •Contestable markets model.
- •Oligopoly and public.
- •Monopolistic competition.
- •Major characteristics:
- •Lr equilibrium
- •Minuses”-”.
- •Derived dem. For ec. Resources.
- •Equilibrium of the firm on the resource market.
- •Sr equilibrium:
- •Lr equilibrium(all factors are variable):
- •Wage determination under Perfect competition.
- •Wage determination under imperfect competition.
- •The theory of distribution of income II. Capital(k) and Land.
- •Concepts of capital.
- •Measuring k.
- •How does the firm invest?
- •Sell bills/bonds to the households.
- •Sr rentals include:
- •Demand and Supply for k purchase.
- •Fairness and effectiveness
- •Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- •Distr. Of income and wealth characteristics:
- •Pareto efficiency and Edgeworth box.
- •Edgeworth box
- •Pareto efficiency allocation:
- •P rinciple possibility of losses compensation.Icks
- •There are positive and negative external effects, divided into 4 groups:
- •Taxes (Pigourian taxes)
- •Sell the right to pollute for example.
- •Public goods –
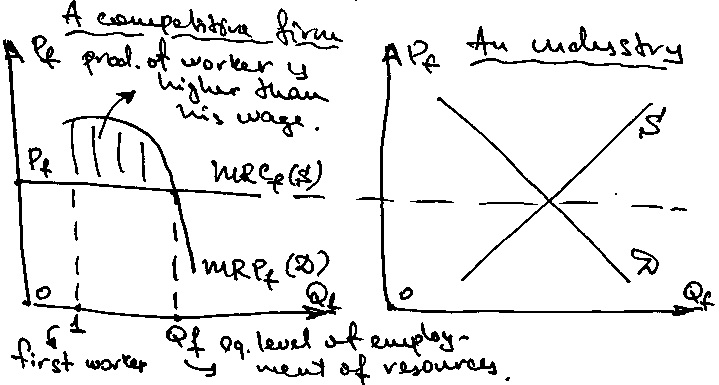
Derived dem. For ec. Resources.
Dem. for ec. rsources depends upon:
The dem. for good produced with this resource
The price of the good
Productivity of the resource(productivity↑ demand↑)
Prices of other resources(complementary and substitute)
Results of the usage of one additional unit of a factor:
additional product(MPf – marg. product of a factor)
add. revenue((marg. revenue product of a factor)MRPf = MR * MPf)
add. value((value of marg. product of a factor)VMPf = Pgood * MPf)
!!! In perf. competition Pgood = MR, so MRPf = VMPf
!!! Under imperfect compet. P > MR, so VMPf > MRPf
Equilibrium of the firm on the resource market.
Sr equilibrium:
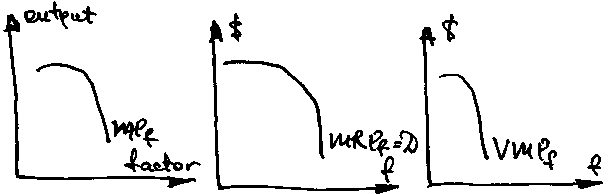 In
the SR a firm confronts the law of diminishing marg. productivity
of a variable factor.
In
the SR a firm confronts the law of diminishing marg. productivity
of a variable factor.MRC – marg. revenue cost – the cost of employing on more unit of a var. factor.
MC – marg. cost – cost of producing of one more unit of a product.
The dem. for resources will be realized by the firm until MRPf ≥ MRCf, and equilibrium MRPf = MRCf
If we assume a perf. compet. market structure . MRCf = Pf a firm is a price-tajer price of hiring a new worker will be equal to the av. market wage.
MRCf = Pf – eq. rule for perfectly comp. markets.
!!! (Neo)Classical schools used this theory to conclude that owners of resources are awarded according to the MProductivity of resources.
Lr equilibrium(all factors are variable):
Two or more factors can be used; all the units of labor and cap. are identical
Both factors are substitutes and compliments(used together)
Substitution and output effects of a price change.
Assume(L,K - factors):
Pk↑
Costs↑ Output↓ DL↓ and QDk↓ - output effect
Labour relative costs↓, though DL↑; DK↓ PL=const – substitution effect
!!! Both effects are negative(P↑ Q↓)
!!! Cross-effects work in the opposite direction(разные изменения от одного)
!!! In some cases factors are complement no substitution effect(only output(scale) effect)
![]() -- cost min. rule
-- cost min. rule
![]() -- Profit maximization rule(eq. in LR)
-- Profit maximization rule(eq. in LR)
Wage determination under Perfect competition.
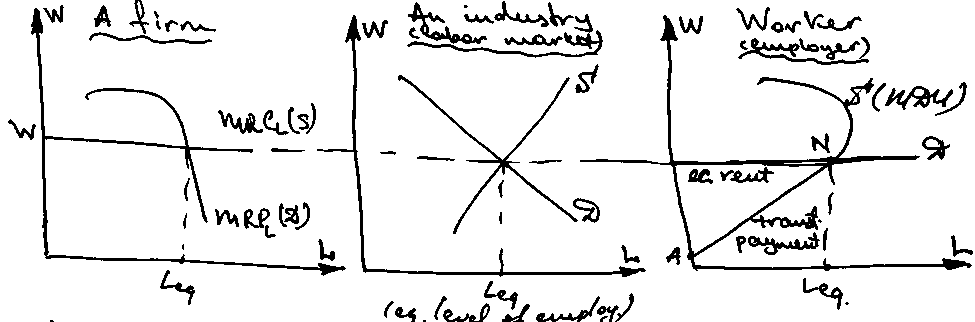
Transfer payments – shows at what levels of the wages workers are willing and able to be at the labor market.
MDU↑(marg. disutility of labour) P↑ to compensate disutility
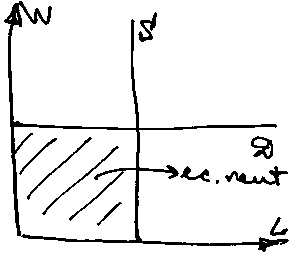 Economic
rent – the difference between the
current market wage rate and the transfer payments.
Economic
rent – the difference between the
current market wage rate and the transfer payments.For absolutely unique worker all the earnings are economic rent.
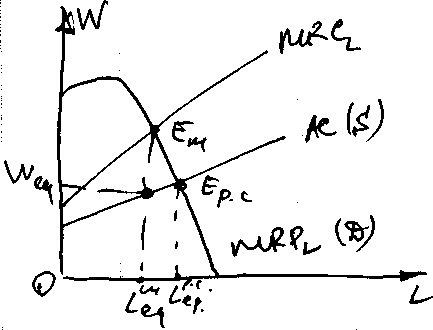
Wage determination under imperfect competition.
Monopsony – monopoly of an employer on the market.
To attract more workers W↑ to all the workers.
!!! As there is no competition between employers W will be as low as possible.
![]()
Conclusion: Monopsony underemployes and underpays to workers.
The theory of distribution of income II. Capital(k) and Land.
Concepts of capital.
Marx: K is the industrial (economic) relation between the worker/owner. This relation can be presented in different forms (equipment, labor force, goods produces, etc).
Classical/Neoclassical: K is identified with manufacture goods used to produce final G/S.
Modern Economists: recognize different forms of K. It can be:
Tangible |
Intangible |
Equipment, residential structures, non-residential structures, inventories of inputs/outputs…. |
Human K (investments in education, training, etc), R/D, goodwill of the firm…. |
K yields valuable productive services over time. It is used to produce final G/S.
