
- •Price and output determination under the perfect competition. Profit maximization under perfect competition. Firms behavior under perfect competition.
- •Basic characteristics of perfect competition.
- •T otal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •A verage and marginal notions approach to profit max of a firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •The behavior of the firm under perfect competition.
- •Last week was said!!!
- •Equilibrium of the firm in the lr.
- •Profit maximization under monopoly.
- •Monopoly:
- •Dem. And mr of the monopolistic firm.
- •Oligopoly.
- •The basic characteristics of an oligopoly:
- •Explicit collusions:
- •Rules of thumb models.
- •Kinked d-curve. Assumptions:
- •Maximax strategy (optimistic approach). Ex:
- •Cournot model / duopoly (2 firms in industry) 1830s.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Isoprofit curve and the reaction function of firm 2.
- •Market equilibrium in different market structures.
- •Algebraic explanation of the Cournot model.
- •Stackelberg model (quantity leadership model).
- •Contestable markets model.
- •Oligopoly and public.
- •Monopolistic competition.
- •Major characteristics:
- •Lr equilibrium
- •Minuses”-”.
- •Derived dem. For ec. Resources.
- •Equilibrium of the firm on the resource market.
- •Sr equilibrium:
- •Lr equilibrium(all factors are variable):
- •Wage determination under Perfect competition.
- •Wage determination under imperfect competition.
- •The theory of distribution of income II. Capital(k) and Land.
- •Concepts of capital.
- •Measuring k.
- •How does the firm invest?
- •Sell bills/bonds to the households.
- •Sr rentals include:
- •Demand and Supply for k purchase.
- •Fairness and effectiveness
- •Inequality in income and wealth distribution
- •Distr. Of income and wealth characteristics:
- •Pareto efficiency and Edgeworth box.
- •Edgeworth box
- •Pareto efficiency allocation:
- •P rinciple possibility of losses compensation.Icks
- •There are positive and negative external effects, divided into 4 groups:
- •Taxes (Pigourian taxes)
- •Sell the right to pollute for example.
- •Public goods –
Explicit collusions:
Concentration ratio.
HHI – Herfindale – Hirschman Index.
![]() S –share of a firm in industrial output. n – number of firms.
S –share of a firm in industrial output. n – number of firms.
First cartels – end of 19 cent. In many countries they are forbidden – antitrust laws. OPEC – international cartel.
Requirements to be efficient:
Demand for product should be inelastic.
All the members should play to the rules. There is always an incentive to violate the rules.
Implicit collusions. When there are few firms they know each other very well so it is not necessary to meet, so they work out a mutual behavior concerning price policy.
price leadership model. One firm is dominating, it sets a price and other firms follow suit (agree with the policy); if the firms are approximately equal they will become price leaders in turn.
barometric form price leadership. Price leader is not always the biggest firm – the most reliable with a good image. Price leader may want to get rid of the rivals decreases price to the level which is not acceptable to the rivals and keeps at the low level until the weaker rivals go bankrupt and exit the market. Then the price is increased to high level according to the monopolistic position of the price leader predatory pricing policy.
Rules of thumb models.
Average cost pricing (AC) Price = AC + mark up.
Price benchmarks. Tradition for sellers to charge the prices according to trademarks.
Non – collusion models. No agreement.
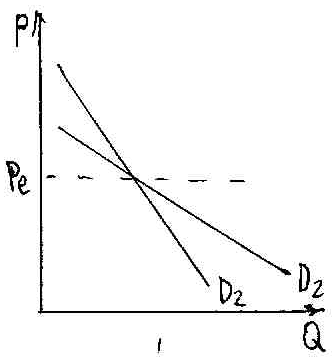
Kinked d-curve. Assumptions:
there is a certain market price.
if a firm increases its price and sets it above the market level, the rival will not follow suit.
if a firm decreases its price, the rivals will follow suit.
T
 here
will be 2 different D curves which correspond to assumptions 2
and 3.
here
will be 2 different D curves which correspond to assumptions 2
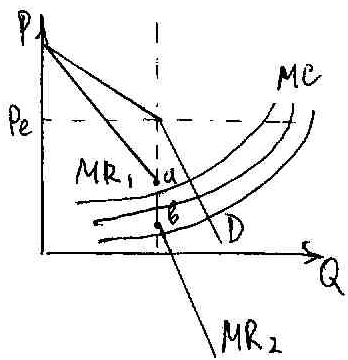
and 3.The final D-curve consists of parts of 2 curves.
D-curve makes a kink. Different Elast in different parts of the curve. Each point has MR-curve of its own. There is a gap between MR-curves.
The idea of the model is to show that in oligopolistic markets there is certain price stability because price competition is very costly and not efficient.
Price stability is not absolute, to a certain extent stability if MC intersects MR in [a;b] Pe;Qe will not change. If outside [a;b] will change.
Game theory. 1944 Veumann, Morgenstern. Assumes that we and the firms are players. There are rules and players can not collude. Outcome depends on the matrix of pay-offs: penalties and prices.
B choices |
|||
A choices |
|
Not confess |
confess |
Not confess |
A: 1 year B: 1 year |
A: 10 years B: free |
|
confess |
A: free B: 10 years |
A: 5 years B: 5 years |
|
