
- •Abc of Commerce
- •080102 «Мировая экномика»
- •Рецензенты:
- •Г.И. Лушникова
- •С.В. Бондаренко
- •Шоркина Ольга Дмитриевна
- •650992, Г. Кемерово, пр. Кузнецкий, 39. Тел. 25-74-16.
- •Введение
- •Unit 1 production meaning of productuon
- •1.1. Active word list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •1.2. Word- building.
- •1.3. Choose the synonym to the word.
- •1.4. Translate the sentences paying attention to the words and phrases in bold type. If it is necessary consult a dictionary.
- •1.5. Read text 1a. Pay attention to the difference between producers. Text 1a Meaning of Production
- •Comprehension
- •1.6. Answer the following questions.
- •1.7. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •1.8. Read text 1b to find answers to the given questions.
- •Text 1b Types of Commercial Work
- •1. What are the differences between home and foreign trade?
- •3. Who provides personal services to the public?
- •4. What industries can production be divided into?
- •5. Why are all production firms interdependent?
- •6. What is the difference between a producer and a consumer?
- •1.9. Which words go together?
- •1.10. Complete the sentences by choosing suitable phrases from the right-hand column.
- •1.11. Find the correct word from the box below to complete each sentence.
- •1.12. Skim through text 1c and formulate its main idea.
- •Text 1c Factors of Production
- •1.13. Translate into English.
- •1.14. Problem solving.
- •Unit 2 retailing
- •2.1. Active word list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •2.2. Word –building.
- •2.3.Which words go together?
- •2.4. Read text 2a. Answer the questions after the text. Text 2a The Place Of Retailers In Production
- •Comprehension
- •2.5. Answer the following questions.
- •2.6. Which words go together?
- •2.7. Complete the sentences by choosing suitable phrases from the right-hand column.
- •2.8. Read and translate text 2b and define if the statements below the text are true or false.
- •Text 2b Department stores, Discount stores, Hypermarkets
- •2.9. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •2.10. Skim through text 2c and formulate its main idea.
- •Text 2c Mail Order Firms. Cooperative – Retail Societies
- •2.11. Give as many variants as possible to complete the following sentences.
- •2.12. Translate into English.
- •2.13. Case study
- •Yedo Department Stores: fact file
- •Yedo Department Stores: extract from twcb’s market report
- •3 Competition
- •4 Trends
- •Unit 3 wholesaling
- •3.1. Active word-list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •3.2. Word- building.
- •Recall the meaning of the suffixes.
- •Наречие:
- •3.3. Translate the sentences paying attention to the words and phrases in bold type. If it is necessary consult a dictionary.
- •3.4. Read text 3a. Answer the questions after the text.
- •Text 3a The Work Of Wholesalers
- •Comprehension
- •3.5. Answer the following questions.
- •3.6. Which words go together?
- •3.7. Complete the sentences by choosing suitable phrases from the right-hand column.
- •3.8. Read and translate text 3b and define if the statements below the text are true or false. Text 3b Methods Used By Wholesalers To Increase Sales
- •Summary Wholesalers
- •M anufacturers
- •3.9. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •3.10. Skim through text 3c and formulate its main idea.
- •Text 3c Franchising
- •3.11. Translate into English.
- •3.12. Write the number of each picture next to the correct method of transportation.
- •3.13. Match the terms on the left to the descriptions on the right.
- •3.14. Case study Marcia Lee jeans Background
- •Unit 4. Channels of distribution
- •4.1. Active word-list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •4.2. Word- building.
- •4.3. Read text 4a. Get ready to discuss its information. Channels Of Distribution
- •Summary
- •Comprehension
- •4.4. Answer the following questions.
- •4.5. Which words go together?
- •4.6. Find the correct word(s) from the box below to complete each sentence.
- •4.7. Complete the sentences by choosing suitable phrases from the right-hand column.
- •4.8. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •4.9. Give as many variants as possible to complete the following sentences.
- •4.11. Translate into English.
- •4.12. Role-play.
- •Unit 5 middlemen of trade
- •5.1. Active word-list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •5.2. Word - building.
- •5.3. Translate the sentences paying attention to the words or phrases in bold type.If it is necessary consult a dictionary.
- •5.4. Read text 5a. Pay attention to the difference between the middlemen of trade. Text 5a The Middlemen Of Trade
- •Types of middlemen
- •Summary The middlemen of trade
- •Comprehension
- •5.5. Answer the following questions.
- •5.6. Which words go together ?
- •5.7. Find the correct word(s) from the box below to complete each sentence.
- •5.8. Complete the sentences by choosing suitable phrases from the right-hand column.
- •5.9. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •5.10. Complete each sentence below with a word or phrase from the box.
- •5.11. Translate into English.
- •5.12. Case study Background
- •Brainstorming Session
- •Unit 6 foreign trade
- •6.1. Active word-list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •6.2. Word - building.
- •6.3. Match English and Russian pairs of words.
- •6.4. Translate the sentences paying attention to the words and phrases in bold type. If it is necessary consult a dictionary.
- •6.5. Read text 6a. Answer the questions after the text. Text 6a
- •International Specialization
- •6.6. Answer the following questions.
- •6.7. Give either Russian (a) or English (b) equivalents to the phrases.
- •6.8. Read text 6 b to find answers to the given questions.
- •Text 6 b Difficulties Faced By Exporters
- •Comprehension
- •6.9. Answer the questions.
- •6.10. Which words go together ?
- •6.11. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •6.12. Skim through text 6c and formulate its main idea.
- •Text 6c The Customs And Excise
- •Comprehension
- •6.13. Answer the questions.
- •6.14. Translate into English.
- •6.15. Case study.
- •Reasons for falling profits
- •Unit 7 marketing
- •7.1. Active word-list. Read the words and word combinations and learn them.
- •Key words
- •7.2. Word - building.
- •RСуществительное: отвлеченное понятие ecall the meaning of the suffixes.
- •7.3. Read and translate. Guess the meaning of international words.
- •7.4. Translate the sentences paying attention to the words and phrases in bold type. If it is necessary consult a dictionary.
- •7.5. Read text 7a and get ready to discuss its information. Text 7a Marketing
- •Comprehension
- •7.6. Answer the following questions.
- •7.7. Give either Russian (a) or English (b) equivalents to the phrases.
- •7.8. Read the text attentively. Divide it into logical parts. Find or compose the topic sentences of each part. Use the material of the tasks above.
- •7.9. Read text 7b and define if the statements below the text are true or false.
- •Text 7b Pricing
- •7.10. Say if the statements are true or false. Correct the false variant.
- •7.12. Read text 7c to find answers to the given questions.
- •Text 7c More About "The Marketing Mix "
- •What is product? Why are forward – thinking companies developing new products?
- •2. What is place?
- •3. What must each stage add to the product? What is "breaking the bulk"?
- •4. What is place? What takes account of the value of a product?
- •5. What is promotion?
- •6. What is a "unique selling proposition"?
- •7.13. Case study Building relationships
- •Supplementary reading unit 1
- •Integration Of Russia In The World Economy
- •Production Costs
- •Unit 2 Self-Service
- •Selling Techniques
- •Unit 3 Buying Wholesale
- •The wholesale firm
- •Unit 4, 5 Merchant-Wholesalers
- •International Trade
- •Terms of Contract
- •Foreign Trade
- •Unit 7 Marketing and Promotion
- •Channels Of Marketing
- •Appendix 1
- •Conversational formulars
- •References
- •Contents
- •Шоркина Ольга Дмитриевна
- •650992, Г. Кемерово, пр. Кузнецкий, 39. Тел. 25-74-16.
3.11. Translate into English.
1. Оптовые фирмы закупают сырье у добывающих компаний и затем продают его перерабатывающим и строительным фирмам.
2. Готовая продукция покупается оптовиками большими партиями, которые разбиваются на более мелкие партии товара и продаются в розничную торговлю.
3. Оптовики забирают товар у производителей, и розничным торговцам не приходится предоставлять транспорт.
4. Для того, чтобы розничные торговцы могли быстро получать поставки, оптовики поддерживают широкий ассортимент товара на складе.
5. Оптовые фирмы могут упаковывать некоторые товары для розничных торговцев, например, разливать напитки в бутылки, а также доставлять товар в магазины.
6. Поскольку по мере роста розничные торговцы стали покупать продукцию непосредственно у производителей большими партиями, оптовики начали терять свою долю рынка.
7.ыБыстропортящиеся, технические и крупногабаритные товары никогда не были рынком (областью торговли) для оптовиков.
8. Розничные сети состоят из небольших магазинов, делающих закупки у определенных оптовых фирм, управляющих сетью.
9. Небольшие магазины получают выгоду от рекламы, осуществляемой розничной сетью, а также они могут получать от сети ссуды на модернизацию.
10. Склады самовывоза не предоставляют кредит или доставку, но функционируют как большие супермаркеты с системой самообслуживания и торговли за наличные.
3.12. Write the number of each picture next to the correct method of transportation.
cargo plane _____ despatch rider _____
delivery van ____ freight train _____
container ship ____ container lorry ____
b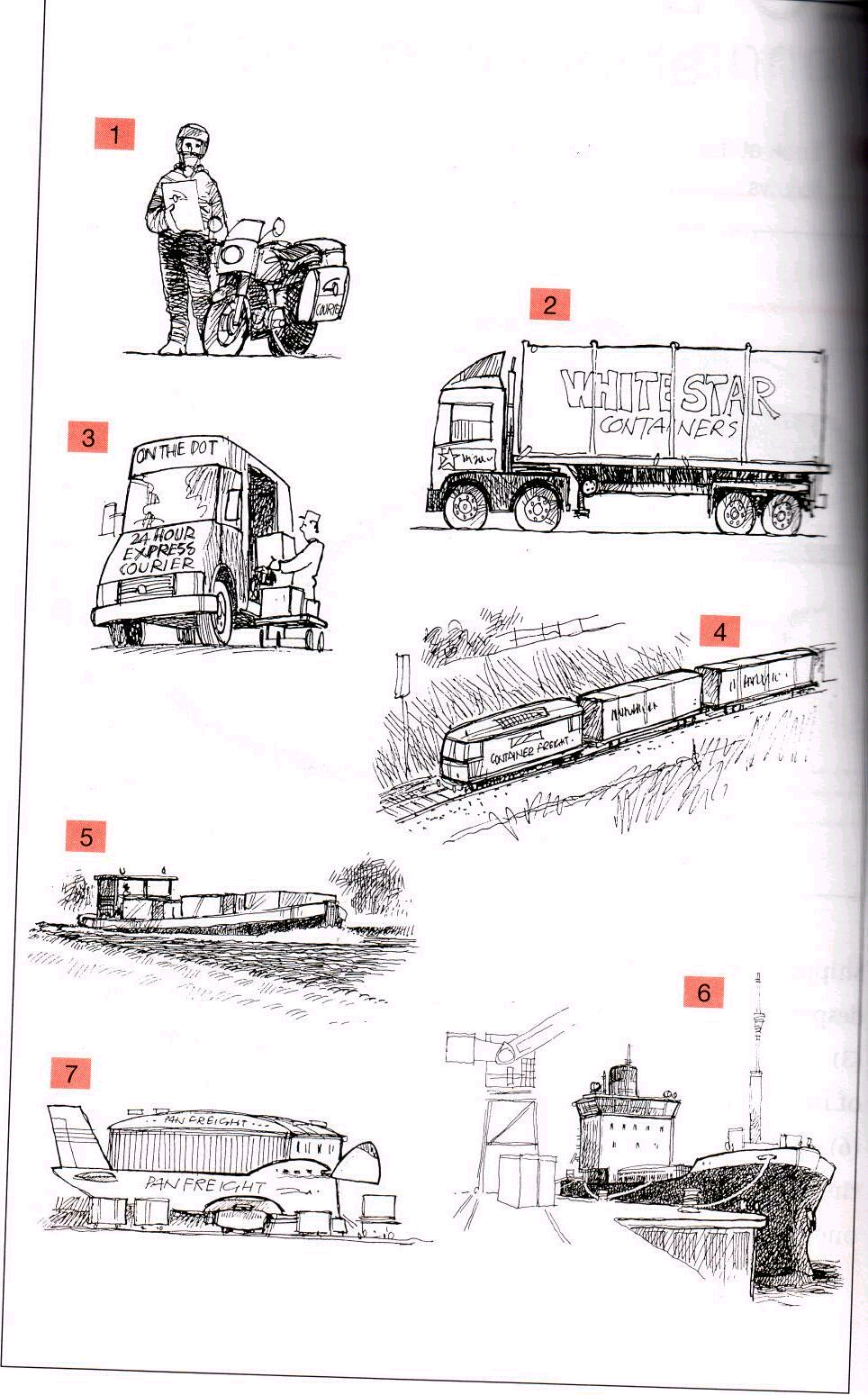 arge
.
arge
.
3.13. Match the terms on the left to the descriptions on the right.
1 air freight 2 despatch rider 3 shipping line 4 courier service 5 rail freight operator 6 road haulage contractor
|
a a business specializing in rapid delivery transportation of small items, usually by van or motorbike. b a company specializing in moving heavy goods and raw materials by train. c the business of moving large quantities of goods by air. d a company specializing in transportation of goods by sea, typically using container vessels (large ships designed to transport goods) based at container ports. e a company that transports goods by lorry. Major road distribution networks link so-called dry port facilities, often located near major airports and road junctions. f someone who works for a courier company delivering small items by motorbike. |
3.14. Case study Marcia Lee jeans Background
Marcia Lee Jeens is based in New York. Its brand is well known in the United States. The jeans sell in the price ranges and appeal to fashion conscious people aged 15 to 40. They are distributed in major department stores throughout the country.
At present, the jeans are made in the US by a number of factories on the East coast, none of which are owned by Marcia Lee Jeans. Competition in this segment of the market is strong, so the company has to keep costs as low as possible in order to remain profitable.
In the next 10 years, Marcia Lee plans to expand in Europe and South east Asia so that it becomes a global company. To do this, it has decided to build its own factory in an overseas country. The factory will have approximately 2,000 workers who will produce the jeans. These workers will be recruited locally. Denim, the raw material which is used to make the jeans, will be imported from several countries.
The company is considering four countries as a location for the factory. There is some information about each country. They are code named A, B, C, and D.
Task
You are members of the planning committee which must choose a location for the new factory.
Work individually. Study the four countries and rank them in order of suitability as a location.
Work in small groups. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each location.
Meet as one group with one of you leading the discussion. Decide which is the most suitable location for the new jeans factory.
COUNTRY A
Economy
Growth: 2% per year
Inflation rate: 5%
Interest rates: 10%-15%
Unemployment rate: 25%-30%
The country has a lot of debts and is trying to modernise its economy.
Transport
Good rail network but poor roads
New international airport
The main seaport is in poor condition.
Labour
Unskilled labour available. A lot of training needed for jeans production
No unions in most industries
Wage rates: very low
Comments
The country has a military government. Bribery is common. Political problems: the people in the north want to become an independent state. The goverment will contribute 30 % towards the cost of a new factory.
COUNTRY B
Economy
Growth:1.5%
Inflation rate: 0.5%
Interest rates: 8% -10%
Unemployment rate:3%
A modern industrial country with many manufacturing industries
Transport
Has a fully integrated road and rail network
International airport
No seaport
Labour
Not a lot of skilled labour available
Strong unions
Wage rate: high
Comments
The country has a stable government. It is a member of a large trading group. There are strict new laws on pollution. There are no tax incentives for building new factories. Business tax is very high.
COUNTRY C
Economy
Growth: 8%
Inflation rate: 10%
Interest rates: 4% - 6%
Unemployment rate: 12%
Currency exchange rate: unstable
Transport
Good transport around the main seaports
Small but well-managed airport
Road network needs investment
Labour
Not much skilled labour available
Very strong unions in the clothing industry
Wage rates: low but rising fast
Comments
The first free elections for a democratic government were held last year. There are limits on the profits which companies can take out of the country. Not much paperwork required for importing and exporting goods. There is a strong protest movement against international companies, which are accused of harming firms.
COUNTRY D
Economy
Growth: 4%
Inflation rate: 5%
Interest rates: 8% - 12%
Unemployment rate: 12%
Government encourages the privatisation of industry
Transport
Road and rail network is in poor condition
Government has started a big investment programm for the transport system. It will take 5-10 years to complete.
Labour
Large supply of skilled workers, but they are not used to working long hours
Strong unions
Wage rates: low
Comments
A lot of paperwork is required for new businesses. There are problems with air and water pollution. Profits are tax free for the first three years after a factory has been built. Companies must pay 5% of their profits into a fund for training their workers.
