
- •Vocabulary 138
- •Electric current serves lis in a thousand ways
- •Exercises
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Exercises
- •Lightning
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Magnetism
- •Exercises
- •Idioms early history
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Lomonosov
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Volta's short biography
- •Electric current
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •What is heat?
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Electric circuit
- •Voltmeter
- •Conductors and insulators
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Insulator surface treatment
- •Electromotive force and resistance
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •Heating effect of an electric current
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •III. Complete the following sentences:
- •IV. Answer the following questions:
- •V. Translate the following word combinations:
- •VI. Define the meaning of the prefixes in the following words, translate them:
- •IX. Translate tfie following sentences paying attention to the words in bold type:
- •X. Read and retell the following text.
- •If there were no electricity
- •XI. Speak on the heating effect of an electric current.
- •IV. Translate the following sentences and define the functions of tfie word that
- •V. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words in bold type:
- •VI. Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions and form sentences with the following infinitives: -
- •VII. Compare:
- •VIII. Translate the following sentences, paying atten- tion to the words in bold type:
- •IX. Form nouns from the following verbs and translate them:
- •X. Give a short summary of the text.
- •XI. Look at Fig. 9 and describe Oersted's discovery.
- •XII. Describe fig. 10.
- •VI. Read the following abbreviations:
- •VII. Define the following terms:
- •IX. Form five sentences combining suitable parts of the sentence given in columns I and II:
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Define the following terms:
- •V. (a) Choose the right term; (b) explain the statement:
- •VI. Translate the following sentences:
- •VII. Translate the following text:
- •VIII. Retell the text.
- •Transformers
- •3 Single-pnase transformers stepping generator voltage up to 275.000 volts
- •2300 To 230 volt
- •2300 Volt motor
- •230 Volt induction motor
- •Transmission system
- •IV. Form as many words as possible using suffixes and prefixes. Define what parts of speech the new words are and translate them:
- •V. Form nouns from the following words using suitable suffixes:
- •VI. Translate the following word combinations:
- •VII. Arrange the following words and expressions in pairs of a) synonyms, b) antonyms:
- •IX. Compare:
- •X. Translate the following text:
- •XI. Retell the text
- •IV. Translate the following sentences using the Passive Voice:
- •V. Form sentences according to the models given below:
- •VI. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Answer the following questions:
- •V. Define the following terms:
- •VI. Form six sentences using the following nouns quali- fied by adjectives:
- •VII. Translate the following text:
- •VIII. Describe Fig. 15.
- •IV. Translate the following sentences:
- •V. Translate the following sentences:
- •VII. Give a heading to each paragraph of the text. Explain why you have given such a heading.
- •VIII. Speak on:
- •IX. Translate the following text:
- •Active Words and Expressions
- •Exercises
- •IV. Translate the following words and word-combinations:
- •V. Answer the following questions:
- •VIII. Speak on the possible uses of solar energy.
- •IX. Read and retell the following story;
- •1. Energy
- •2. Electric fish
- •4. Surface tension
- •5. Electric meter
- •7. Refrigerator
- •10. Electron theory
- •11. Thermocouple and photocell
- •12. Electric lamp
- •13. Faraday's discovery
- •15. Steam turbine
- •16. Units of measurement
- •17. Plasma generator
- •18. Laser
- •19. Semiconductors
- •20. Steam power station
- •21. Hydroelectric power station
- •22. Current flow
- •23. Gases, solids, liquids and plasma
- •Idioms, Conjunctional and Prepositional Phrases
- •Vocabulary
- •Impulse wheel ['impals ,wi:l] активная турбина
Electric circuit
The elecjric circuit is the subject,to be dealt with;\r\ the present article' But what does the above term really mean? We know the circuit to be a complete patji wMchswries tfie current from the source of supply to the toad and then carries it again fnpm the load back to the source.
The purpose of the electrical, source is to produce the necessary electromotive fprce required for. the flow of current through the circuit.
The path along which the electrons travel must be complete or no electric power can be supplied frorn the source to the load. Thus we close the circuit when we switch on our electric lamp.
If the circuit is broken or, as we generally say, "opened", anywhere, the current is known to stop everywhere. Hence, we
break the circuit when we switch off our electrical devices. Generally speaking у the current may pass tfirough solid conductors, liquids, gases, vacuum, or any combination of these. It may flow in turn over transmission lines from the power stations through transformers, cables and switches, through lamps, heaters, rjiotors and so on.
There are various kinds of electric circuits such as: open circuits, closed circuits, series circuits, parallel circuits and short circuits.
To understand the difference between the following circuit connections is not difficult at all. When electrical devices are connected so that the current flows from one device ,to another,,'they are said to be connected in series* Under such conclitions the current flow is the. same in all parts of the circuit, as there is only a single path aldttg which it may flow. The electric bell circuit is considered (o be a typical example of a series circuit. The parallel circuit provides two or
Battery of Ammpt*r Varindie resistance
4 cells
^rnmeier j ^
ar
rheostat'
cells
^rnmeier j ^
ar
rheostat'
Voltmeter
&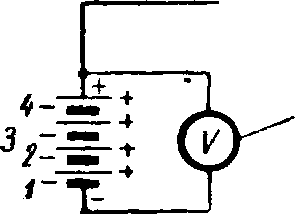
Fig. 6. A simple electric circuit.
more paths for the passage of current. The circuit is divided in such a way that part of the current flows through one path, and part through another. The lamps in your room and your house are generally connected in parallel.
Now we shall turn our attention to the short-circuit sometimes called "the short". The short jcircuit is produced when the current is allowed to return to the source of supply without control and without doing the torork that we want it to do. The short circuit of ten. results from cable fault or wire fault. Under certain conditions, the short may cause fire because "the current flows where it was not supppsed'tojlow. If the current flow is too great a fiisexu to be used as a safety devifce to stop the current flow.
The fuse njijsf be placed in every circuit where there is a danger of overbading the line. Thtn all the current to be sent will pass through the fuse.
When a short circuit.or an overload causes more current
* ii
to flow than the carrying capacity- of the wire, the wire be-i comes hot and sets fire to the insulation. If the flow of current is greater than the carrying capacity of the fuse, the fuse melts and opens the circuit,.
A simple electric circuit is illustrated in Fig. 6. In this figure a 4-ceil battery has been used, the switch being in an open position. If the switch is in a closed position, the current will flow around the circuit in the direction shown by the arrows.
Active Words and Expressions
cable, to carry, closed, circuit, complete, conductor, to deal with, fault, fuse, generally speaking, load, open circuit, short circuit, to supply, switch, transmission line
Exercises
/. Translate the following sentences and define the function of the infinitive:
1. The current is known to flow when the circuit is closed. 2. Tastop the current flow is to break the circuit in some point. 3. To stop the current flow you must open the circuit. 4. A fuse is expected to melt and break the circuit.
Various switches are used to open or to close a circuit.
A switch is a device to break or to close the circuit. 7. We know tlje circuit to.be a path of an electric current. 8. We may expect a short circuit to result from wire fault. 9. The overloading of the line is likely to produce a short circuit. 10. Ampere supposed the current to flow from the positive pole of the source to the negative pole.
//. Find the infinitive in the text and define its function.
III. Answer the following questions:
1. What is discussed in the present article? 2. What do we call an electric circuit? 3. What kinds of circuits do you know? 4. When is a "short" produced? 5. What does a short circuit often result in? 6. What safety device is used in the circuit when the current is too great? 7. What do we mean liquids and gases .... 4. The magnitude of the current ... the voltage and resistance may vary from a small amount to a very large quantity. 5. ... a cold object and a hot one are brought into contact, the former gets warmer and the latter gets colder. 6. Fuses are used ... safety devices.
IX. Describe fig. 6.
X. Retell the text.
LESSON FOURTEEN
THE ATTRIBUTE. ATTRIBUTIVE CLAUSES
