
- •Contents
- •Authors
- •Foreword
- •Acknowledgments
- •Introduction
- •Selection of frameworks
- •Description and evaluation of individual frameworks
- •How to use this handbook
- •Overview of what follows
- •Chapter 1 The nature of thinking and thinking skills
- •Chapter 2 Lists, inventories, groups, taxonomies and frameworks
- •Chapter 3 Frameworks dealing with instructional design
- •Chapter 4 Frameworks dealing with productive thinking
- •Chapter 5 Frameworks dealing with cognitive structure and/or development
- •Chapter 6 Seven ‘all-embracing’ frameworks
- •Chapter 7 Moving from understanding to productive thinking: implications for practice
- •Perspectives on thinking
- •What is thinking?
- •Metacognition and self-regulation
- •Psychological perspectives
- •Sociological perspectives
- •Philosophical perspectives
- •Descriptive or normative?
- •Thinking skills and critical thinking
- •Thinking skills in education
- •Teaching thinking: programmes and approaches
- •Developments in instructional design
- •Bringing order to chaos
- •Objects of study
- •Frameworks
- •Lists
- •Groups
- •Taxonomies
- •Utility
- •Taxonomies and models
- •Maps, charts and diagrams
- •Examples
- •Bloom’s taxonomy
- •Guilford’s structure of intellect model
- •Gerlach and Sullivan’s taxonomy
- •Conclusion
- •Introduction
- •Time sequence of the instructional design frameworks
- •Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives (cognitive domain) (1956)
- •Feuerstein’s theory of mediated learning through Instrumental Enrichment (1957)
- •Ausubel and Robinson’s six hierarchically-ordered categories (1969)
- •Williams’ model for developing thinking and feeling processes (1970)
- •Hannah and Michaelis’ comprehensive framework for instructional objectives (1977)
- •Stahl and Murphy’s domain of cognition taxonomic system (1981)
- •Biggs and Collis’ SOLO taxonomy (1982)
- •Quellmalz’s framework of thinking skills (1987)
- •Presseisen’s models of essential, complex and metacognitive thinking skills (1991)
- •Merrill’s instructional transaction theory (1992)
- •Anderson and Krathwohl’s revision of Bloom’s taxonomy (2001)
- •Gouge and Yates’ Arts Project taxonomies of arts reasoning and thinking skills (2002)
- •Description and evaluation of the instructional design frameworks
- •Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives: cognitive domain
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Description and intended use
- •Intellectual skills
- •Cognitive strategies
- •Motor skills
- •Attitudes
- •Evaluation
- •Ausubel and Robinson’s six hierarchically-ordered categories
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Williams’ model for developing thinking and feeling processes
- •Description and intended use
- •Cognitive behaviours
- •Affective behaviours
- •Evaluation
- •Hannah and Michaelis’ comprehensive framework for instructional objectives
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Stahl and Murphy’s domain of cognition taxonomic system
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Biggs and Collis’ SOLO taxonomy: Structure of the Observed Learning Outcome
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Quellmalz’s framework of thinking skills
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Presseisen’s models of essential, complex and metacognitive thinking skills
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Merrill’s instructional transaction theory
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Anderson and Krathwohl’s revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
- •Description and intended use
- •Changes in emphasis
- •Changes in terminology
- •Changes in structure
- •Evaluation
- •Gouge and Yates’ ARTS Project taxonomies of arts reasoning and thinking skills
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Some issues for further investigation
- •Introduction
- •Time sequence of the productive-thinking frameworks
- •Altshuller’s TRIZ Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (1956)
- •Allen, Feezel and Kauffie’s taxonomy of critical abilities related to the evaluation of verbal arguments (1967)
- •De Bono’s lateral and parallel thinking tools (1976 / 85)
- •Halpern’s reviews of critical thinking skills and dispositions (1984)
- •Baron’s model of the good thinker (1985)
- •Ennis’ taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities (1987)
- •Lipman’s modes of thinking and four main varieties of cognitive skill (1991/95)
- •Paul’s model of critical thinking (1993)
- •Jewell’s reasoning taxonomy for gifted children (1996)
- •Petty’s six-phase model of the creative process (1997)
- •Bailin’s intellectual resources for critical thinking (1999b)
- •Description and evaluation of productive-thinking frameworks
- •Description and intended use
- •Problem Definition: in which the would-be solver comes to an understanding of the problem
- •Selecting a Problem-Solving Tool
- •Generating solutions: using the tools
- •Solution evaluation
- •Evaluation
- •Allen, Feezel and Kauffie’s taxonomy of concepts and critical abilities related to the evaluation of verbal arguments
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •De Bono’s lateral and parallel thinking tools
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Halpern’s reviews of critical thinking skills and dispositions
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Baron’s model of the good thinker
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Ennis’ taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities
- •Description and intended use
- •Dispositions
- •Abilities
- •Clarify
- •Judge the basis for a decision
- •Infer
- •Make suppositions and integrate abilities
- •Use auxiliary critical thinking abilities
- •Evaluation
- •Lipman’s three modes of thinking and four main varieties of cognitive skill
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Paul’s model of critical thinking
- •Description and intended use
- •Elements of reasoning
- •Standards of critical thinking
- •Intellectual abilities
- •Intellectual traits
- •Evaluation
- •Jewell’s reasoning taxonomy for gifted children
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Petty’s six-phase model of the creative process
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Bailin’s intellectual resources for critical thinking
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Some issues for further investigation
- •Introduction
- •Time sequence of theoretical frameworks of cognitive structure and/or development
- •Piaget’s stage model of cognitive development (1950)
- •Guilford’s Structure of Intellect model (1956)
- •Perry’s developmental scheme (1968)
- •Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences (1983)
- •Koplowitz’s theory of adult cognitive development (1984)
- •Belenky’s ‘Women’s Ways of Knowing’ developmental model (1986)
- •Carroll’s three-stratum theory of cognitive abilities (1993)
- •Demetriou’s integrated developmental model of the mind (1993)
- •King and Kitchener’s model of reflective judgment (1994)
- •Pintrich’s general framework for self-regulated learning (2000)
- •Theories of executive function
- •Description and evaluation of theoretical frameworks of cognitive structure and/or development
- •Piaget’s stage model of cognitive development
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Guilford’s Structure of Intellect model
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Perry’s developmental scheme
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Koplowitz’s theory of adult cognitive development
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Belenky’s ‘Women’s Ways of Knowing’ developmental model
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Carroll’s three-stratum theory of cognitive abilities
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Demetriou’s integrated developmental model of the mind
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •King and Kitchener’s model of reflective judgment
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Pintrich’s general framework for self-regulated learning
- •Description and intended use
- •Regulation of cognition
- •Cognitive planning and activation
- •Cognitive monitoring
- •Cognitive control and regulation
- •Cognitive reaction and reflection
- •Regulation of motivation and affect
- •Motivational planning and activation
- •Motivational monitoring
- •Motivational control and regulation
- •Motivational reaction and reflection
- •Regulation of behaviour
- •Behavioural forethought, planning and action
- •Behavioural monitoring and awareness
- •Behavioural control and regulation
- •Behavioural reaction and reflection
- •Regulation of context
- •Contextual forethought, planning and activation
- •Contextual monitoring
- •Contextual control and regulation
- •Contextual reaction and reflection
- •Evaluation
- •Theories of executive function
- •Description and potential relevance for education
- •Evaluation
- •Some issues for further investigation
- •6 Seven ‘all-embracing’ frameworks
- •Introduction
- •Time sequence of the all-embracing frameworks
- •Romiszowski’s analysis of knowledge and skills (1981)
- •Wallace and Adams’‘ Thinking Actively in a Social Context’ model (1990)
- •Jonassen and Tessmer’s taxonomy of learning outcomes (1996/7)
- •Hauenstein’s conceptual framework for educational objectives (1998)
- •Vermunt and Verloop’s categorisation of learning activities (1999)
- •Marzano’s new taxonomy of educational objectives (2001a; 2001b)
- •Sternberg’s model of abilities as developing expertise (2001)
- •Description and evaluation of seven all-embracing frameworks
- •Romiszowski’s analysis of knowledge and skills
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Jonassen and Tessmer’s taxonomy of learning outcomes
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Hauenstein’s conceptual framework for educational objectives
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Vermunt and Verloop’s categorisation of learning activities
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Marzano’s new taxonomy of educational objectives
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Sternberg’s model of abilities as developing expertise
- •Description and intended use
- •Evaluation
- •Some issues for further investigation
- •Overview
- •How are thinking skills classified?
- •Domain
- •Content
- •Process
- •Psychological aspects
- •Using thinking skills frameworks
- •Which frameworks are best suited to specific applications?
- •Developing appropriate pedagogies
- •Other applications of the frameworks and models
- •In which areas is there extensive or widely accepted knowledge?
- •In which areas is knowledge very limited or highly contested?
- •Constructing an integrated framework
- •Summary
- •References
- •Index
|
|
|
|
Instructional design |
71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domains addressed: |
Presentation: |
Contexts: |
|
|||
• |
cognitive |
• |
clear description |
• |
education |
|
|
|
|
of theory but |
|
|
|
|
|
|
academic in style |
|
|
|
Broad categories |
Theory base: |
Pedagogical stance: |
|
|||
covered: |
• |
draws upon |
• |
belief in the |
|
|
• |
productive |
|
Piaget and |
|
importance of |
|
|
thinking |
|
Vygotsky |
|
presenting new |
|
• |
building |
|
|
|
learning in such a |
|
|
understanding |
|
|
|
way as to relate prior |
|
• |
information- |
|
|
|
knowledge to new |
|
|
gathering |
|
|
|
knowledge |
|
|
|
|
|
• |
use of advance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
organisers to scaffold |
|
|
|
|
|
|
understanding |
|
|
|
|
|
• |
start with big |
|
|
|
|
|
|
concepts |
|
|
|
|
|
• |
teacher-structured |
|
|
|
|
|
|
learning rather than |
|
|
|
|
|
|
pupil enquiry |
|
Classification by: |
Values: |
Practical illustrations |
|
|||
• |
types of learning, |
• |
rationalist |
for teachers: |
|
|
|
which differ in |
• |
technological |
• |
few examples of how |
|
|
structural |
• |
all students can |
|
to apply the theory |
|
|
complexity |
|
learn if taught well |
|
|
|
• |
superordinate |
• |
opposes |
|
|
|
|
and subordinate |
|
sentimentality |
|
|
|
|
concepts |
|
regarding the critical/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
creative skills |
|
|
|
|
|
|
of young learners |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
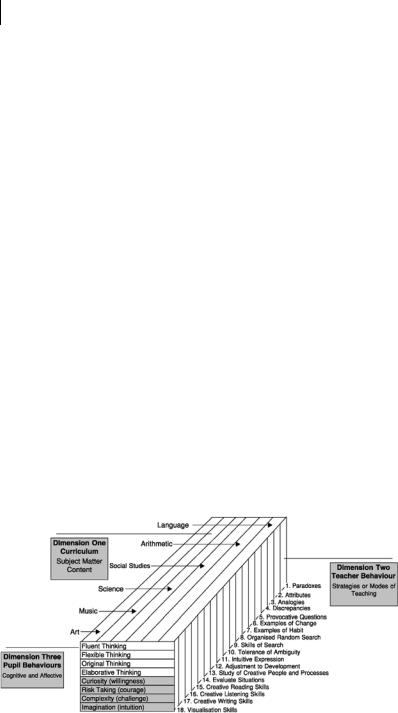
Williams’ model for developing thinking and feeling processes
Description and intended use
In 1970, Williams published the first volume of his work on classroom ideas for encouraging thinking and feeling (Williams, 1970). He makes use of a three-dimensional model (figure 3.1) and argues that developing different teaching strategies and adopting different
72 Frameworks for Thinking
teaching roles across a range of subjects can bring about changes in students’ cognitive and affective behaviours, moving them towards a higher level of creative thinking (see also Williams, 1972).
Williams describes 18 diverse teaching strategies which encourage not only thinking, but also the expression of feelings about both content and the learning process. He provides detailed lesson plans that envisage the three intersecting dimensions of subject content, teacher behaviour and pupil behaviours coming together to encourage creativity. Williams is striving towards an increase in student creative output, placing equal value on cognitive and affective aspects.
Creativity is a complex mental process that is difficult to define or measure. For Williams, it involves putting together new, different and unique ideas by employing the four cognitive and four affective behaviours shown in dimension three of the model in figure 3.1 and outlined below:
Cognitive behaviours
1.fluency – generating a large number of ideas
2.flexibility – being able to change categories
3.originality – being able to come up with a unique thought
4.elaboration – being able to take one idea and embellish it.
Fig. 3.1. Williams’ model for encouraging thinking and feeling.
