
Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms / 12-Rhodium Compounds
.pdfCompound |
|
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|
|
|
atom(s) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3(TMPP-O)]2·1.25CH2Cl2 |
|
2.452(2) |
2.289(9) |
O |
567 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.995(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.316(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.287(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3{Ph2P(o-ClC6H3)}(H2O)2]·CHCl3 |
|
2.426(1) |
2.325(2) |
O |
534 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.318(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3(δ1-O2CCF3){δ2-Ph2P(o-ClC6H4)}(H2O)] |
|
2.469(1) |
2.196(4)l |
O |
379 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.577(2)m |
Cl |
|
|
|
[Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3(δ1-O2CCF3){δ2-Ph2P(o-ClC6Ν4)}(Ν2O)] |
|
2.449(1) |
2.196(4)l |
O |
378 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.577(2)m |
Cl |
|
|
|
|
Bis-carboxylato compounds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CH)2(bpy)2Cl2]·2H2O |
|
2.584g |
2.514(3) |
Cl |
344 |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CH)2(bpy)2Cl2]·4H2O |
|
2.578(1) |
2.521(3) |
Cl |
345 |
|
|
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CH)2Cl2(phen)2 |
|
2.576(1) |
2.504(1) |
Cl |
343 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.496(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(dmg)2(PPh3)2]·H2O |
|
2.618(5) |
2.476(9) |
P |
336 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.494(9) |
|
|
|
|
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(CF3COCHCOCH3)2(py) |
|
2.534(1) |
2.13(1) |
N |
341 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.106n |
Cn |
|
|
|
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(CF3COCHCOCF3)2(py)2 |
|
2.523(2) |
2.27(1) |
N |
340 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.21(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chifotides |
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6](BF4)2·4CH3CN |
|
2.534(1) |
2.232(4) |
N |
361 |
Rhodium |
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)4(py)2](BF4)2 |
|
2.548(2) |
2.231(9) |
N |
361 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.238(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6(BF4)2][Re2Cl8] |
|
2.509(4) |
2.23(3) |
N |
363 |
Dunbarand |
Compounds |
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)3(PCy3)2](BF4)2 |
|
o |
o |
P |
742 |
||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)(NCCH3)4](BF4)2·CH3CN |
|
2.539(1) |
2.188(6) |
N |
373 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.229(6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
495
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
atom(s) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2(H2O){(CH3)2CHOH}][B(C6H5)4]·H2O |
2.526(1) |
2.231(2)l |
O |
358 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.264(2)p |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2Cl2]·3H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
2.574(1) |
2.525(5) |
Cl |
350 |
||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2Cl2]·2H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
2.601(1) |
2.532(1) |
Cl |
358 |
||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2Br2]·3H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
2.586(1) |
2.672(1) |
Br |
358 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.629(1) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2I2] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.590(3) |
2.769(4) |
I |
358 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.848(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
cis-[Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
3 |
) |
2 |
(δ2-Hdpa) |
|
Cl ]·6H |
2 |
O |
|
2.593(1) |
2.582(2) |
Cl |
171 |
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.562(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2(NCCH3)2](PF6)2·2CH3CN |
2.548(1) |
2.228(8) |
N |
351 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.185(8) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(phen)2Cl2]·H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
2.561(2) |
2.509(5) |
Cl |
352 |
||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(phen)2Cl2]·10.5H2O |
|
2.554(1) |
2.535(2) |
Cl |
352 |
||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(phen)2(py)2](PF6)2·(CH3)2CO |
2.559(1) |
2.242(4) |
N |
356 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.199(4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(phen)2(Me-Im)2](ClO4)2 |
2.556(1) |
2.188(3) |
N |
349 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.207(3) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(4,7-Me2phen)2(Me-Im)2](ClO4)2 |
2.565(1) |
2.223(4) |
N |
349 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.238(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(3,4,7,8-Me4phen)2(Me-Im)2](ClO4)2 |
2.564(1) |
2.18(1) |
N |
349 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.23(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-ampy)2(py)2](PF6)2 |
|
2.587(1) |
2.281(9) |
N |
357 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.25(1) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ1-O2CCH3)(δ2-ampy)2]ClO4 |
2.525(1) |
2.111(6) |
N |
357 |
|||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
3 |
) |
2 |
(δ3-pynp) |
](BF ) |
·C |
|
H |
8 |
2.407(2) |
2.206(9) |
N |
387,388 |
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
4 2 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.408(2) |
2.20(1) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ3-pynp)(δ1-pynp)(NCCH3)2](BF4)(PF6)·2CH3CN |
2.356(1) |
2.158(5)q |
N |
388 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.997(5)r |
|
|
|
496 |
|
12 Chapter |
|
Bonds Multiple |
|
||
|
|
Atoms Metal Between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
atom(s) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh4(µ-O2CCH3)2(µ2-δ3:δ3-tppz)2(MeOH)4](PF6)4·2MeOHs |
2.606(1) |
2.219(7) |
O |
385 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.252(7) |
|
|
cis-[Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
3 |
) |
2 |
(δ3-bpa) |
](PF ) t |
|
|
2.568(1) |
2.189g |
N |
206 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
6 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
cis-[Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
3 |
) |
2 |
(δ3-bpa) |
](PF ) u |
|
|
2.600(1) |
2.180g |
N |
206 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
6 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ1-O2CCH3)(δ3-bpa)(δ2-bpa)]PF6·1.5H2O |
2.565(1) |
2.218g |
N |
206 |
|||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)2(py)2](PF6)2 |
|
|
2.584(2) |
2.24g |
N |
206 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.593(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
cis-[Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
3 |
) |
2 |
(dppz) |
(δ1-O |
CCH )(EtOH)]BF |
·EtOH |
2.552(1) |
2.187(3)v |
O |
822 |
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.334(3)v |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(dppn)2(δ1-O2CCH3)(MeOH)]BF4·3MeOH |
2.552(1) |
2.188(5)v |
O |
824 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.292(5)v |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)(dppz)(MeOH)Cl]BF4·3MeOH |
2.553(1) |
2.273(3)w |
O |
825 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.498(1)w |
Cl |
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(py)6](CF3SO3)2 |
|
|
2.639(2) |
2.26(2) |
N |
367 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.23(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(py)6](CF3SO3)2 |
|
|
2.653(1) |
2.238(2) |
N |
368 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.229(2) |
|
|
(CN3H6)5[(PO4)W11O35{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(DMSO)2}]·4H2O |
2.525(2) |
2.465(6) |
S |
841 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.535(6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(µ-Ph2Ppy)2Cl2 |
|
|
2.518(1) |
2.538(3) |
Cl |
515 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.537(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2Cl2(dppm)2·2CH3CN |
|
|
2.622(1) |
2.475(2) |
Cl |
507 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.492(2) |
|
|
cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)(9-EtGuaH)(H2O)2(CH3SO4)]CH3SO4·H2O |
2.511(1) |
2.248(4)l |
O |
395 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.351(4)x |
|
|
H-T cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(9-EtGua)2(MeOH)2]·2MeOH |
2.483(2) |
2.315(7) |
O |
393 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.317(7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
H-H cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(9-EtGuaH)2(Me2CO)(H2O)](BF4)2·H2O |
2.512(1) |
2.27(1)y |
O |
394 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.32(1)l |
|
|
Dunbar andChifotides |
|
Compounds Rhodium |
|
497 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
atom(s) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H-T cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2(9-EtGuaH)2(Me2CO)2](CF3CO2)2·Me2CO |
2.520(5) |
2.18(1) |
O |
393 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh |
(µ-O |
CCF ) |
(δ1-O |
CCF |
) |
(bpy) |
]·Me |
CO |
|
|
|
2.570(6) |
2.19(3) |
O |
351 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.30(4) |
|
|
Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCF ) |
(δ1-O |
CCF |
) |
(bpy)(THF)(H |
O)·THF |
|
|
2.520(3) |
2.25(1)z |
O |
373 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.27(1)l |
|
|
Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCF ) |
(δ1-O |
CCF |
) |
(py) |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.56(1) |
2.32(6) |
N |
376 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.54(1) |
2.26(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.25(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.22(3) |
|
|
Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ1-O2CCH3)2(CO)2(MeOH)2 |
|
|
|
|
2.535(1) |
2.202(3) |
O |
380 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
[Rh |
(µ-O |
CCΝ |
) |
(δ1-O |
CCΝ |
){δ2-Ph |
P(o-CΝ |
OC Ν |
)}(Ν |
O)] |
2.439(3) |
2.25(1)l |
O |
377 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
3 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
6 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.35(1)aa |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(HO2CCH3)2 |
|
|
|
2.508(1) |
2.342(5) |
O |
522,523 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Ν-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCΝ3)2[Ph2P(P6Ν4)]2(py)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.556(2) |
2.281(9) |
N |
523 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Ν-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[Ph2P(C6Ν4)]2(PPh3)2·2C7Ν8 |
|
|
2.630(1) |
2.560(2) |
P |
547 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)][(p-ClC6H3)P(p-ClC6H4)2](HO2CCH3)2}·1/2C6H6 |
2.513(1) |
2.338(2) |
O |
538 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.346(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[(p-FC6H3)P(p-FC6H4)2]2(HO2CCH3)2} |
2.488(3) |
2.29(1) |
O |
539 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[(m-CH3C6H3)P(m-CH3C6H4)2]2(HO2CCH3)2}·CH3CO2H |
2.502(3) |
2.412(5) |
O |
540 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.317(4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[c-C5H9)7Si8O12(CH2)2P(C6H4)Ph][Ph2P(C6H4)](HO2CCH3)2 |
2.508(1) |
2.346(3) |
O |
541 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[PhP(C6H4)(o-BrC6F4)]2 |
|
|
|
2.475(1) |
2.764(2)m |
Br |
555 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[PhP(C6H4)(o-BrC6F4)]2(H2O) |
|
2.485(1) |
2.983(1)m |
Br |
555 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.292(6)l |
O |
|
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-O2CCH3)[PhP(C6H4)(o-BrC6F4)][Ph2P(o-BrC6F4)]c |
2.519(3) |
2.62(2)m |
Br |
374 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.43(2)e |
O |
|
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCΝ3)2(δ2-O2CCΝ3)[Ph2P(C6Ν4)][Ph2P(o-ClC6Ν4)]c |
2.529(1) |
2.573(4)m |
Cl |
375 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.27(1)e |
O |
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[PhP(C6H4)(C6F5)]2(H2O)2 |
|
|
|
2.496(2) |
2.367(1) |
O |
542 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
498 |
|
12 Chapter |
|
Bonds Multiple |
|
||
|
|
Atoms Metal Between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
atom(s) |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[(m-CH3OC6H3)P(m-CH3OC6H4)2]2(H2O)(HO2CCH3) |
2.491(1) |
2.313(9)l |
O |
543 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.363(1) |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCMe3)2[PhPMe(C6H4)]2(py)2·2CHCl3 |
2.535(5) |
2.27(1) |
N |
544 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.31(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCMe3)2{Me2P(C6H4)}2(H2O)2 |
2.492(1) |
2.360(9) |
O |
545 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.351(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCPh3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(py)2 |
|
|
2.559(1) |
2.302(4) |
N |
546 |
||||||||||||||
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2(TMPP-O)2·2CH2Cl2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.562(2) |
2.315(9) |
O |
567 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.323(9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(py)2 |
|
|
|
2.582g |
2.293g |
N |
548 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.263g |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(HO2CCF3)2 |
2.515g |
2.361g |
O |
548 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.335g |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CC2F7)2[PhP(C6H4)(C6F5)]2(H2O)2 |
2.530(2) |
2.34(1) |
O |
542 |
||||||||||||||||
H-T cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2{[PhP(C6H4)(C5H4)]Fe(C5H5)}2(HO2CCH3)2] |
2.504(1) |
2.392(6) |
O |
549 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.295(6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
H-H cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(HO2CCH3)2 |
2.493(1) |
2.498(7) |
O |
525 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.198(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
H-H cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[(ClC6H3)P(p-ClC6H4)2]2(HO2CCH3)2 |
2.511(2) |
2.39(1) |
O |
525 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.22(1) |
|
|
H-H cis-{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[PhP(C6H4)(o-ClC6H4)][Ph2P(C6H4)](PPh3)}·2C6H6 |
2.558(1) |
2.370(2) |
P |
550 |
||||||||||||||||
H-H cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2{µ2-(CH2)PPh2}{µ2-(C6H4)PPh2}(PPh3)]·2CH2Cl2 |
2.532(2) |
2.297(4) |
P |
551,552 |
||||||||||||||||
H-H cis-{Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2{[PhP(C6H4)(C5H4)]2Fe}(HO2CCH3)]}·CH2Cl2 |
2.508(4) |
2.26(2) |
O |
549 |
||||||||||||||||
H-H cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2[(C4H3S)2(C4H2S)P]2(py)2 |
2.576(1) |
2.145g |
N |
553 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.378g |
|
|
cis-Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
) {δ2-Ph |
P(o-CH |
OC |
H |
)} |
Cl |
2 |
2.560(1) |
2.298(7) |
O |
377 |
|||||
|
|
3 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
6 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.342(7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
cis-Rh |
2 |
(µ-O |
2 |
CCH |
) {δ2-Ph |
P(o-ClC |
|
H |
)} |
Cl |
2 |
|
|
2.569(1) |
2.587(1) |
Cl |
377 |
|||
|
|
3 |
2 |
2 |
6 |
4 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.592(1) |
|
|
Dunbar andChifotides |
|
Compounds Rhodium |
|
499 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
|
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a (Å) |
r (Rh–Lax) (Å)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
atom(s) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(2S,5S-2,5-dimethyl-1-phenylphospholane)2(HO2CCH3)2 |
2.504(1) |
2.370(3) |
O |
558 |
|||||||||||
cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2(δ1-O2CCF3)2(1S,2S,5R-hprmph)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.580(1) |
2.262(1) |
O |
560 |
||||||
cis-[Rh |
(µ-O |
CCF ) |
(δ1-O |
CCF |
) |
(1S,2S,5R-hprmph) |
]·1/2CHCl |
3 |
2.587(1) |
2.250(5) |
O |
557,559 |
|||
2 |
2 |
3 2 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh |
(µ-O |
CCF ) |
(δ1-O |
CCF |
) |
(1R,2R,5S-hprmph) |
|
]·2H |
2 |
O |
|
2.601(1) |
2.25(1) |
O |
557 |
2 |
2 |
3 2 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mono-carboxylato compounds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)(δ3-tpy)2Cl2](H3O)Cl2·9H2O |
|
|
|
|
|
2.634(1) |
2.517(2) |
Cl |
205 |
||||||
[Rh2(µ-O2CPh)(δ3-tpy)2(NCCH3)2](BF4)3·CH3CN |
|
|
|
|
|
2.629(1) |
2.154(5) |
N |
351 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.181(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
[Rh(µ-O2CCF3)(µ-CO)(THF)]4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.551(1) |
2.220(5) |
O |
310 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.624(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distances are given with up to 3 decimal digits.
Square brackets refer to average values; parentheses refer to unique values. Compound contains chelating acetate group.
Axial bond to N of chelating bpy.
Pseudoaxial bond to O of chelating acetate group.
L1: 2-aryl-4,6-bis(2-(7-pyridyl)-1,8-naphthyridyl)-pyrimidine. Esds not reported.
Rh–N pyrimidine distance.
The shorter of these two distances corresponds to Rh–O(methanol), the longer one to Rh–O(methoxy).
The shorter of these two distances corresponds to Rh–O(carbonyl), the longer one to Rh–O(methoxy).
k Distance to the methoxy O atom of one phenyl ring. l Distance to H2O molecule.
m Distance to halogen atom of the phosphine.
n The vacant ax site of the dirhodium unit interacts with the α-carbon atom of a `- diketonato ligand of an adjacent dimetal unit.
o |
Distance not reported due to crystallographic disorder. |
p |
Distance to ax (CH3)2CHOH molecule. |
q |
Rh-N distance to a monodentate ax naphthyridine unit. |
r |
Rh-N distance to the pynp ligand that is coordinated in a tridentate fashion. |
s |
Tetranuclear Rh46+ compound. |
t |
C2 symmetry. |
u |
Cs symmetry. |
v |
The shorter of the two Rh–O distances corresponds to Rh–O(carboxylate), the longer |
one to Rh-O(alcohol).
w The longer distance corresponds to the Rh–Cl bond, the shorter one to Rh–O(MeOH).
x Distance to O of CH3SO4< group. y Distance to O of carbonyl group. z Distance to O of THF.
aa Axial bond to O atom of the phosphine.
|
500 |
|
12 Chapter |
|
Bonds Multiple |
|
||
|
|
Atoms Metal Between |
Rhodium Compounds 501
Chifotides and Dunbar
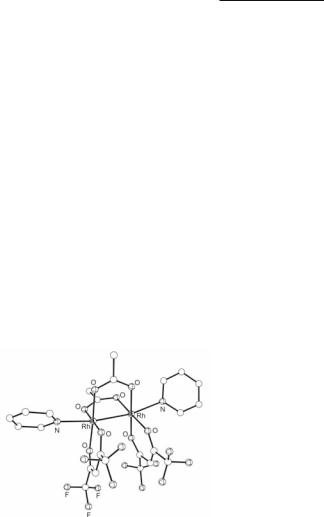
The first such bis-carboxylate complex to be structurally characterized is the mixed acetate/ dimethylglyoxime derivative cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-dmg)2(PPh3)2 with two acetate ligands in a cisoid arrangement, the dmg ligands chelating at eq positions, and the PPh3 molecules occupying ax sites.336 The Rh–Rh distance of 2.618(5) Å is longer than that in Rh2(O2CCH3)4(PPh3)2 (2.451(1) Å)278 and far shorter than that in the related complex Rh2(dmg)4(PPh3)2 (2.936(2) Å);337,338 the lengthening of the Rh–Rh bond compared to Rh2(O2CCH3)4(PPh3)2 has been attributed to the repulsion between the dmg ligands, which are close to achieving the maximum torsion angle, and the constraints imposed by the small ‘bite’ of the bridging acetate groups.299,336 The structure of cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-dmg)2(PPh3)2 serves as the prototype for a variety of neutral Rh24+ species that are supported by a pair of bridging carboxylate ligands in a cisoid arrangement. One such group comprises Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(`- diketone)2L2 compounds (the `-diketone ligand represents the anions of 2,4-pentanedione or its trifluoro or hexafluoro derivatives and L is pyridine).339 Their close structural relationship to the dmg complex has been confirmed by the X-ray crystal structure determination of cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-CF3COCHCOCF3)2(py)2 (Fig. 12.15).340 In both cases, the chelating ligands are not eclipsed, but have a significant twist of c. 10-20° with respect to each other. The mono-pyridine adduct cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-CF3COCHCOCH3)2(py) exhibits an unusual interaction (3.106 Å) between the vacant ax site of each dimetal unit and the α-carbon atom of a `-diketonato ligand of an adjacent dirhodium unit.341
Fig. 12.15. Molecular structure of cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-CF3COCHCOCF3)2(py)2.
Compounds that possess similar structures to those previously described are those of general formulae [Rh2(µ-O2CR)2(δ2-N-N)2]2+ (R = H, CH3, or PhCH(OH); N-N = 2,2'-bipyridine- (bpy), 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) and substituted phen, ampy or HN=CHCH=NH) with the N-N donors chelating at eq sites of the dirhodium unit;105,206,342-358 the reduced Rh23+ species for a number of these compounds have been studied by EPR spectroscopy.359 Pertinent compounds of the aforementioned class, that have been crystallographically determined, are listed in Table 12.2.
Compounds in which the open eq sites of the bis-acetate dirhodium core are occupied by monodentate ligands (e.g., CH3CN) were first obtained by treatment of Rh2(O2CC3H7)4 with the weakly complexing acid CF3SO3H in CH3CN; the [Rh2(O2CC3H7)2]2+ unit was detected by NMR spectroscopy, but the product was not fully characterized.360 Subsequently, the compounds cis-[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6]X2, X = BF4- or CF3SO3-, were prepared by treating Rh2(O2CCH3)4 with Me3OBF4 or CF3SO3H in CH3CN.361 The enhanced lability of ax CH3CN molecules compared to those occupying eq sites is supported by the fact that the py ligands replace ax CH3CN in the reactions of [Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6]2+

502Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms Chapter 12
with |
pyridine to |
afford cis-[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)4(py)2](BF4)2,361 or compounds |
of |
the type |
[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)4L2]2+ (L = H2O, DMSO, thiourea and NSC-) |
depending on the identity of the donor molecule.362 The argument is further supported by the considerably shorter Rh–Neq to Rh–Nax distances in cis-[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6](BF4)2 (e.g., Rh–Neq = 1.985(4) Å and Rh–Nax = 2.232(4) Å)361 and the octachlorodirhenate
salt cis-[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)6(BF4)2][Re2Cl8] (e.g., Rh–Neq = 1.97(3) Å and Rh–Nax = 2.26(4) Å).363 The substitutional inertness of the eq M-NCCH3 bonds towards
CD3CN exchange in cis-[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(NCCH3)4]2+, compared to the isostructural Mo species, has been attributed to the different M–M (M = Rh, Mo) MO configurations (μ2/4β2β*2/*4 and μ2/4β*2 for Rh24+ and Mo24+, respectively).364 On the other hand, the reactions of the dirhodium cation with acetate, bpy and phen proceed at reasonable rates at room temperature.364
Apart from the mixed acetate/acetonitrile ligand sets, cationic Rh24+ species with mixed acetate/water or acetate/pyridine ligands have been isolated. There is evidence that, in acidic aqueous solutions, the species [Rh2(O2CCH3)3]+ and [Rh2(O2CCH3)2]2+ are present.365 It is also claimed that the cations [Rh2(O2CCH3)3(H2O)4]+ and [Rh2(O2CCH3)2(H2O)6]2+ have been isolated as their perchlorate salts and characterized by infrared and electronic spectroscopies.366,367 Treatment of the two mixed acetate/water complexes with pyridine affords [Rh2(O2CCH3)3(py)4]+ and [Rh2(O2CCH3)2(py)6]2+;366 the corresponding trifluoromethanesulfonate salts [Rh2(O2CCH3)3(py)4]CF3SO3 and cis-[Rh2(O2CCH3)2(py)6](CF3SO3)2 have been structurally characterized.367,368 Reports of mixed ligand Rh24+ species include several acetate/ phosphate,369 formate/carbonate,370 acetate/sulfate complexes371 as well as others that have been characterized by infrared and electronic spectroscopies but not structurally determined.369,371
Among adducts with three bridging acetate groups, an unusual structure is encountered in Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3(δ2-O2CCH3)(bpy) which has chelating acetate and bpy ligands (Fig. 12.16).372,373 Not unexpectedly, the ax Rh–O bond of 2.466(8) Å is longer than the corresponding eq interaction of 2.051(8) Å. The appearance of a chelating acetate group is rather unusual but has been encountered in the orthometalated
compounds cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-O2CCH3)[PhP(C6H4)(o-BrC6F4)][Ph2P(o-BrC6F4)]374 and cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ2-O2CCH3)[Ph2P(C6H4)][Ph2P(o-ClC6H4)]375 (Table 12.2). Conversely,
eq monodentate carboxylate groups are encountered more frequently as in [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2-
(δ1-O2CCH3)(δ3-bpa)(δ2-bpa)]PF6,206 [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ1-O2CCH3)(δ2-ampy)2]ClO4,357 Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2(δ1-O2CCF3)2(bpy)(THF)(H2O)·THF,373 Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)2(δ1-O2CCF3)2(py)4,376
[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3(δ1-O2CCH3){Ph2P(o-CH3OC6H4)}(H2O)],377 [Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3(δ1-O2CCF3)- {Ph2P(o-ClC6H4)}],378 [Rh2(µ-O2CCF3)3(δ1-O2CCF3){δ2-Ph2P(o-ClC6H4)}(H2O)]379 and Rh2(µ- O2CCH3)2(δ1-O2CCH3)2(CO)2(MeOH)2.380
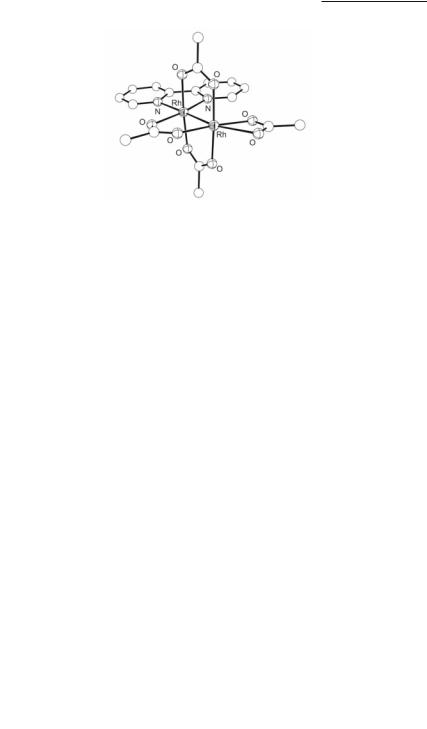
Rhodium Compounds 503
Chifotides and Dunbar
Fig. 12.16. Molecular structure of Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3(δ2-O2CCH3)(bpy).
The ax ligands L in Rh2(O2CR)4L2 compounds generally are quite labile. Adduct formation starting with Rh2(O2CR)4 is a stepwise process and studies of the formation constants have consistently shown that the first ligand is added much easier than the second.19,175,181 Additionally, there is rapid ligand exchange of the groups in ax positions of tetracarboxylate compounds; the rate depends on the nature of the ax groups as well as the inductive effect and the lypophilicity of the carboxylate chain.381 The X-ray crystal structural determinations of Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3- (δ2-O2CCH3)(bpy) and [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(bpy)(NCCH3)4](BF4)2 with ax-eq and eq-eq bpy moieties, respectively,372,373 as well as those of a set of complexes with the bidentate ampy357,206 and tridentate bpa ligands,206 are important in a broader context as they provide insight into the mechanism of attack of N-donor chelates on the dinuclear unit. As illustrated in Fig. 12.17, a possible sequence of events for this reaction system involves a nucleophilic attack of the base at an ax site of Rh2(O2CCH3)4 to afford an axially bound monodentate adduct a followed by formation of a chelate ring by attack of a second donor atom at an eq site (b; ax-eq adducts) and conversion to the final eq-eq adducts c.206,373
Fig. 12.17. Proposed mechanism of attack of a N-N donor chelate on the dirhodium core.
504Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms Chapter 12
12.18
A series of polyaza cavity-shaped (or crescent-shaped) ligands (12.13-12.18), that typically possess a central 1,8-naphthyridine fragment, have been found to form stable bisand trisacetate dirhodium complexes. In [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3(δ4-bpnp)]PF6, the bpnp ligand (12.14) is binding to two eq and two ax sites of the dimetal unit (Fig. 12.18).382,383 The ligand L1 (L1: 2-aryl-4,6-bis(2-(7-pyridyl)-1,8-naphthyridyl)-pyrimidine; 12.18), which is composed of two bpnp type subunits, forms the tetranuclear complex {[Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)3]2(µ2-δ4:δ4- L1)}(PF6)2 consisting of two separate dirhodium units bridged by a pyrimidine group.384 Two unusual monocarboxylate cations [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)(δ3-tpy)2Cl2]+ 205 and [Rh2(µ-O2CPh)(δ3- tpy)2(NCCH3)2]3+ 351 have been crystallized with tpy (12.15) binding in a tridentate fashion to the dirhodium core and both tpy molecules occupying eq planes. An extrapolation of this chemistry has involved 2,3,5,6-tetra-2-pyridylpyrazine (tppz; 12.17) to afford the novel type metal-metal bonded molecular rectangle [Rh4(µ-O2CCH3)2(µ2-δ3:δ3-tppz)2(MeOH)4]4+ (Fig. 12.19) with two linked reduced Rh23+ units.385 The X-ray crystal structure of the disubstituted pynp cation [Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(δ3-pynp)2]2+, which was initially studied by NMR and electronic spectroscopies,382,386 reveals both pynp ligands (12.13) behaving in a combined bridging/chelating fashion with each pynp moiety occupying one ax and two eq sites of the dimetal unit.387,388 As expected, the Rh–Neq distances are considerably shorter than Rh–Nax (2.04(1) Å and 2.20(1) Å, respectively).388 In another disubstituted pynp product that has been isolated, one pynp ligand is coordinated in the usual tridentate fashion and the second one acts as a monodentate ax ligand.388 These complexes with polyaza, cavity-shaped molecules
