
Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms / 12-Rhodium Compounds
.pdfTable 12.4. Structural data for Rh24+ compounds supported by amidinato and other (N, N) donor bridging groups
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|||
|
|
||||
Rh2(DPhF)4 |
2.457(1) |
c |
c |
444 |
|
|
|
||||
Rh2(DPhF)4(NCCH3) |
2.459(1) |
2.106(4) |
N |
444 |
|
Rh2(DPhF)4(CNPh) |
2.480(1) |
1.991(4) |
C |
475 |
|
(DPhF)4Rh2(CNPhNC)Rh2(DPhF)4·6CH2Cl2 |
2.496(1) |
1.988(9) |
C |
475 |
|
Rh2(DPhBz)4 |
2.389(1) |
c |
c |
447,448 |
|
|
|
||||
Rh2(DPhBz)4(CO) |
2.435(1) |
1.97(2) |
C |
448 |
|
Rh2(DTolF)4 |
2.434(1) |
c |
c |
446 |
|
|
|
||||
[Rh2(DTolF)4(1,4-CNPhNC).2C6H6] |
2.570(1) |
2.053(4) |
C |
477 |
|
{[Rh2(DTolF)4]3(1,4-CNPhNC)2}.6H2O |
2.520(2) |
2.15(1) |
C |
477 |
|
Rh2(DTolF)3(δ2-NO3)(PPh3)·0.5CH2Cl2 |
2.498(2) |
2.20(1) |
Od |
459 |
|
Rh2(DTolF)3(δ2-NO3)(py) |
2.476(1) |
2.286(6) |
Od |
459 |
|
cis-Rh2(DTolF)2(µ-O2CCF3)2(H2O)2·0.5C6H6 |
2.425(1) |
2.311(3) |
O |
445 |
|
|
|
2.319(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-Rh2(DTolF)2(µ-O2CCF3)2(NCCH3)2 |
2.474(5) |
2.265(5) |
N |
462 |
|
|
|
2.267(5) |
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(NCCH3)6](BF4)2 |
2.559(1) |
2.208(7) |
N |
461,462 |
|
|
|
2.235(7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(bpy)(NCCH3)3](BF4)2.Me2CO |
2.578(1) |
2.107(3) |
N |
474 |
|
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(bpy)(NCCH3)4](BF4)2 |
2.638(3) |
2.208(7) |
N |
474 |
|
|
|
2.316(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(bpy)2(NCCH3)](BF4)2 |
2.5821(5) |
2.116(4) |
N |
474 |
|
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(phen)(NCCH3)3](BF4)2.2C2H5OC2H5 |
2.581(1) |
2.128(2) |
N |
474 |
|
cis-[Rh2(DPhFF)2(dppz)(NCCH3)4](BF4)2·3.5C6H5Me |
2.581(1) |
2.195(5) |
N |
827 |
|
|
|
2.173(5) |
|
|
|
cis-Rh2(DTolF)2(O2CC6H4CN)2(py)2 |
2.469(1) |
2.296(5) |
N |
471 |
|
H-H cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(9-EtGuaH)2(NCCH3)](BF4)2 |
2.514e |
2.142e |
N |
462 |
|
H-T cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(9-EtAdeH)2(NCCH3)](BF4)2 |
2.510(3) |
2.06(2) |
N |
461,462 |
Dunbar andChifotides |
|
Compounds Rhodium |
|
515 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax)b |
Donor |
ref. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
cis-Rh2(DTolF)2(µ-PPh2Py)2(δ1-O2CCF3)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.541(1) |
2.327(4) |
O |
472 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.407(4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(µ-O2CCF3)(oxodmnp)(H2O)]·½Et2O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.449(1) |
2.186(4) |
O |
467 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
cis-[Rh2(DTolF)2(pypz)2(DMSO)2](O2CCF3)2·DMSO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f |
2.263(9) |
O |
467 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rh2(DTolF)(µ-O2CCF3)(dppe)(δ1-O2CCF3)(p-toluidine) |
|
|
|
|
|
2.606(1) |
2.148(3) |
N |
473 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[Rh |
2 |
(DTolF)(µ-O |
CCF |
){Ph(C |
|
H |
)P(CH |
) PPh |
}(dppe)]O |
CCF |
.0.5H |
2 |
Og |
2.733(1) |
2.367(2) |
Pg |
465 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
6 |
4 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Rh2(DAniF)4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.452(1) |
c |
c |
442 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.415(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
cis-Rh2(DAniF)2[Br2calix[4]arene(CO2)2](CH3OHax)h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.438(1) |
2.301(2) |
O |
484 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rh2(DPhF-3,5-Cl2)4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.458(1) |
c |
c |
442 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Rh2(DPhTA)4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.377(3) |
c |
c |
451 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Rh |
2 |
(DTolTA) (CO) |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.542(1)j |
c |
c |
455 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rh |
2 |
(DTolTA) (NO)(CO)k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.518(1) |
c |
c |
455 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh2(DTolTA)2(CO)2(PPh3)2]PF6·CH2Cl2i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.698(1)j |
c |
c |
456 |
||||||||||||||||||||
[Rh2(DTolTA)2(bpy)(CO)2]BF4·CH2Cl2i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.646(1)j |
c |
c |
453 |
|||||||||||||||||||
[Rh2(DTolTA)2(bpy)(NCCH3)3](PF6)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.534(2) |
2.080(9) |
N |
454 |
|||||||||||||||||
[Rh |
2 |
(DTolTA) |
2 |
(CO)(δ1-O |
PF |
)(µ |
-O |
PF )(bpy)] |
·2.3C |
6 |
H |
14 |
|
|
|
2.505(4) |
2.23(2) |
O |
454 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.38(1) |
|
|
{[Rh |
(DTolTA) |
2 |
(CO)(bpy)(µ-I)] }(PF ) |
·2.5CH |
2 |
Cl |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.544(1) |
2.760(1) |
Il |
453 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
6 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.670(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
[Rh2(DPhAc)2(PPh3)2(CO)2]PF6·2C6H14i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.771(1)j |
c |
c |
458 |
|||||||||||||||||||
{Rh |
2 |
(DPhAc) |
2 |
[P(OPh) |
] |
(CO) }PF i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.685(1)j |
c |
c |
458 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
{Rh2(DPhAc)2(PPh3)[P(OPh)3](CO)2}PF6i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.728(1)j |
c |
c |
458 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Rh2(tpg)4·CH2Cl2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.408(1) |
c |
c |
500 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supramolecular building blocks supported by (N, N) donor groups |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
[Rh2(cis-DAniF)2(µ2-C2O4)]4 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.440(1) |
n |
n |
478 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.454(1) |
|
|
|
[Rh2(cis-DAniF)2(µ2-C2O4)]3 |
o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.457[2] |
n |
n |
478 |
|||||||||||||
|
516 |
|
12 Chapter |
|
Bonds Multiple |
|
||
|
|
Atoms Metal Between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
] |
2 |
(µ |
2 |
-O CCH |
CO |
) |
(NC |
H |
CHCHC |
H |
N) |
·3CH |
2 |
Cl |
·0.5Et |
2 |
O} p |
2.434(1) |
2.317e |
N |
479 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.464(1) |
2.254e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.263e |
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
] |
2 |
(µ |
2 |
-O CCH |
CO |
) |
(NCC |
|
H |
|
|
CN) |
·4CH |
2 |
Cl |
} |
|
q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.442(1) |
2.221e |
N |
479 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.216e |
|
|
{[Rh2(cis-DAniF)2]4(µ2-C2O4)4(NCC6F4C6F4CN)4·12.36CH2Cl2} r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.418(2) |
2.333e |
N |
479 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.442(2) |
2.293e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.248e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.163e |
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
] |
2 |
(µ |
2 |
-O CCH |
CO |
) |
(NCC |
|
F |
C F |
CN) ·6.8CH |
2 |
Cl |
|
} |
p |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.435(1) |
2.204(9) |
N |
480 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
4 |
|
|
6 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.24(1) |
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
] |
2 |
(µ |
2 |
-O CCH |
CO |
) |
[C |
N |
(C |
|
H N) |
] |
·3CHCl |
3 |
·CH |
|
Cl |
|
} s |
|
|
|
|
|
2.465[2] |
2.35[5] |
N |
481 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
] |
2 |
(µ |
2 |
-O CCH |
CO |
) |
} |
[C |
N |
(C |
H |
|
N) |
] |
·4.1CH |
2 |
Cl |
|
|
·Et |
|
O·H |
O} |
t |
2.460[5] |
2.31[1] |
N |
481 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
{[Rh2(cis-DAniF)2]6[µ3-1,3,5-C6H3(CO2)3]4(CH3CNax)7.5}·13.9CH3CNo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.428- |
2.20[10] |
N |
482 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.438e,u |
|
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
(CH |
|
CN |
) |
](bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane-1,3-dicarboxylate)} ·8CH |
3 |
CNm |
2.449(2) |
2.228e |
N |
483 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
ax 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.233e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.245e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.272e |
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
(CH |
|
CN |
) |
](µ -O |
CC |
F CO |
|
)} |
·3CH Cl m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.446(1) |
2.196e |
N |
483 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
ax 2 |
|
2 2 |
|
|
6 |
4 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.459(1) |
2.246e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.251e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.256e |
|
|
Dunbar andChifotides |
Compounds Rhodium |
517
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compound |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax)b |
Donor |
ref. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
{[Rh2(cis-DAniF)2(CH3CNax)2](1,4-cubanedicarboxylate)}4·2.8CH3CNm |
|
2.432(2) |
2.162e |
N |
483 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.448(2) |
2.179e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.236e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.241e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.246e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.254e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.255e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.261e |
|
|
{[Rh |
2 |
(cis-DAniF) |
2 |
(CH |
3 |
CN |
ax |
) |
2 |
](µ -O |
CC |
H |
CO |
)} |
·3CH |
3 |
CN·2CH |
2 |
Cl m |
|
2.445(1) |
2.240e |
N |
483 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 2 |
6 |
4 |
2 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.453(2) |
2.254e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.269e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.263e |
|
|
{Et2O |
|
[cis-Rh2(DAniF)2(CH3CNax)]4[calix[4]arene(CO2)4]2}·10CH3CNv |
|
2.429(1) |
2.16(1) |
N |
484 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.422(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
[{NEt |
4 |
[cis-Rh |
2 |
(DAniF) |
L] |
|
[calix[4]arene(CO |
) ] |
}]BF |
|
·3.5CH |
3 |
CNv,w |
|
2.410(2) |
2.16(1)x |
Nw |
484 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
2 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.413(4) |
2.20(1)x |
Ow |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.417(2) |
2.34(2)y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.428(2) |
2.316(8)y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other (N, N) donor ligands |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
Rh2(3,5-Me2pz)4(NCCH3)2·2CH3CN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.353(3) |
2.202(5) |
N |
398 |
||||||||||||||
Rh2(µ-pz)2(I)2(CO)2[P(OMe)3]2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.660(1) |
2.741(1) |
I |
486 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.746(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
cis-Rh2I2(CO)2(µ-pz)2(µ-dppm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.612(3) |
2.710(3) |
I |
520 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.736(3) |
|
|
trans-[Rh2I2(CO)2(3,5-Me2pz)(µ-dppm)2]ClO4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.725(2) |
2.757(2) |
I |
521 |
||||||||||||||||
trans-(2,2)-Rh2(ap)4(NCPh) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.412(1) |
2.19(1) |
N |
493,494 |
||||||||||
[Rh2(µ:δ3-pynp)2(δ2-pynp)Cl2](PF6)2·CH3CNz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.567(1) |
2.190(5) |
N |
498 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.160(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
518 |
|
12 Chapter |
|
Bonds Multiple |
|
||
|
|
Atoms Metal Between |
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax)b |
Donor |
ref. |
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|||
|
|
||||
[Rh2(µ-pdz)2(pdz)4(NCCH3)2](ClO4)4·H2Oz |
2.557(2) |
2.24(2) |
N |
499 |
|
|
|
2.19(2) |
|
|
|
Rh2(µ:δ3-dpa)2(µ:δ2-dpa)2 |
2.400(1) |
2.386(3) |
Naa |
171 |
|
|
|
2.349(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Rh2{µ-(C5H3N)NH(C5H4N)}2(δ2-Hdpa)2Cl2]·CH3OH |
2.567(2) |
2.205(9) |
N |
497 |
|
Rh2(pz)2[Ph2P(C6F4)]Br(CO)[Ph2P(o-BrC6F4)]·CHCl2·H2O |
2.581(1) |
2.561(2) |
Br |
487 |
|
|
|
2.660(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rh2(3,5-Me2pz)2[µ-P(o-C6F4)Ph2]Br(CO){δ2-P(o-BrC6F4)Ph2}·H2O |
2.583(1) |
2.597(1) |
Br |
488 |
|
|
|
2.644(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rh2(mbzapH)2(CO)2Cl |
2.639(2) |
2.466(4) |
Cl |
496 |
a |
Distances are given with up to 3 decimal digits. |
b |
In some cases the average Rh–L bond lengths are quoted. In these instances the estimat- |
|
ed deviation, which is given in square brackets, is calculated as [ ] = [Ψn¨i2/n(n < 1)]1/2, |
|
in which ¨i is the deviation of the ith of n values from the arithmetic mean of the |
|
set. |
c |
No ax ligand. |
d |
Pseudoaxial bond to chelating nitrate group. |
e |
Esds not reported. |
f |
Distance not reported; quality of diffraction data insufficient for detailed structural |
|
analysis. |
g |
The molecule contains an orthometalated bridging dppe and a chelating dppe. |
h |
Br2calix[4]arene(CO2H)2: 25,26,27,28-tetrapropoxy-5,17-dibromo-calix[4]arene- |
|
11,23-dicarboxylic acid. |
i |
Mixed valence Rh 3+ compound. |
|
2 |
j |
Formal bond order 0.5. |
k |
The compound contains a ‘bent’ NO< group. |
l |
Iodide ions are bridging two Rh24+ units. |
m Molecular square.
Not reported. Molecular triangle. Tubular structure. Sheet-like structure.
Infinite tubes of square cross sections. Zig-zag 1-D tunnel.
Helices.
Range of distances.
calix[4]arene(CO2H)4: 25,26,27,28-tetra-n-propoxycalix[4]arene-5,11,17,23-tetra- carboxylic acid.
wL = 50% CH3CN and 50% H2O; four of the eight ax sites are occupied by two CH3CN and two H2O molecules.
x Rh–N distance to ax CH3CN molecule. y Rh–O distance to ax H2O molecule.
z Contains neutral nitrogen bridging ligands.
aaThe two tridentate dpa ligands are involved in quasi-axial bonds which are unusual for Rh24+ compounds supported by (N, N) bridging groups.
Dunbar andChifotides |
Compounds Rhodium |
519

520Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms Chapter 12
An example of a symmetrically bridging (N, N) donor ligand is the anion of 3,5-di- methylpyrazole (3,5-Me2pz; 12.9), which upon reaction of its Na+ salt with Rh2(O2CCH3)4 in CH3CN, affords the yellow compound Rh2(3,5-Me2pz)4(NCCH3)2;398 its Rh–Rh bond length of 2.353(3) Å is the shortest among complexes supported by monoanionic nitrogen donor ligands.398 The reaction of the bis-acetonitrile complex with pyridine affords Rh2(3,5- Me2pz)4(py)2 which converts, at 150 °C under vacuum, to the intense purple colored unsolvated compound Rh2(3,5-Me2pz)4.398 The corresponding unsubstituted pyrazolato complexes have been prepared,398 as well as {[Rh2(µ-pz)2(I)(CNBut)4]2(µ-I)}CF3SO3, which consists of two Rh2(µ-pz)2(I)(CNBut)4 units linked by an iodide ion.485 A few other Rh24+ compounds with pyrazolato bridging groups are Rh2(µ-pz)2(I)2(CO)2[P(OMe)3]2486 and the orthometalated compounds Rh2(pz)2[Ph2P(C6F4)]Br(CO)[Ph2P(o-BrC6F4)]487 and Rh2(3,5-Me2pz)2[Ph2P(C6F4)]Br- (CO)[Ph2P(o-BrC6F4)].488 Various substituted pyrazolate Rh23+ compounds have been studied by fast atom bombardment and collision-induced dissociation mass spectrometry.489
The sodium salt of 2-anilinopyridinate (ap; 12.10) reacts with RhCl3·xH2O in refluxing ethanol to afford the dark-green, air-stable Rh2(ap)4.490,491 This compound, which exhibits two accessible single-electron oxidations,490-493 exists in four geometric isomers490 (Fig. 12.20). The benzonitrile adduct Rh2(ap)4(NCPh) is found as the trans-(2,2) isomer.493,494 The brown microcrystalline adduct Rh2(ap)4(CO), which presumably retains the same ap arrangement of the parent chloride, has been obtained by electrochemical reduction of Rh2(ap)4Cl under a CO atmosphere;493,495 the Rh25+ complex (4,0)-Rh2(ap)4Cl492-494 is discussed in Section 12.6. The orthometalated compound Rh2(mbzapH)2(CO)2Cl2 contains two substituted ap groups (mbzap: 2-((_-methylbenzylidene)amino)pyridine) in a tridentate chelating mode.496 The unusual complex Rh2[µ-(C5H3N)NH(C5H4N)]2(δ2-Hdpa)2Cl2 possesses two chelating 2,2'-dipyridylamine (Hdpa) ligands occupying eq sites and two bridged orthometalated dpa anions in the rare (N, C) coordination mode.497 The adduct Rh2(µ:δ3-dpa)2(µ:δ2-dpa)2 has the unusual feature of two tridentate dpa ligands forming quasi-axial bonds,171 in contrast to the usual Rh24+ paddlewheel complexes supported by (N, N) donor ligands, which normally contain no ax ligands442,444,446,448,451 or at most only one.448,474,475,461,462 The dication in [Rh2(µ:δ3-pynp)2(δ2-pynp)Cl2](PF6)2 (pynp: 2-(2-pyridyl)-1,8-naphthyridine; 12.13), depicted in 12.23, contains one chelating and two bridging pynp ligands.498 The 1,8-naphthyridine (np) complex is proposed to have the composition [Rh2(np)4]Cl4·6H2O, although this has not been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.382 The compound [Rh2(µ-pdz)2(pdz)4(NCCH3)2](ClO4)4 (pdz: pyridazine), which is prepared by reacting Na4[Rh2(µ-SO4)4(H2O)2] with pdz, contains two bridging and four monodentate pdz groups,499 whereas [Rh2(DTolF)2(pypz)2(DMSO)2](O2CCF3)2 contains two short ‘bite’ nitrogen pyridopyrazine (pypz) ligands in a cisoid arrangement.467
 2+
2+
12.23
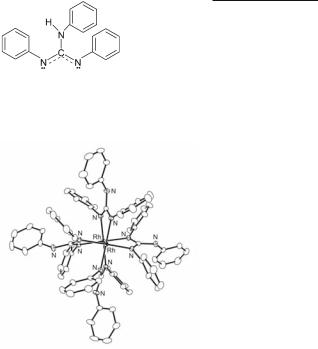
Among compounds supported by (N, N) donor groups with one of the shortest known Rh–Rh bond distances is the complex Rh2(tpg)4 (Fig. 12.26; Rh–Rh = 2.408(1) Å) with the strong organic base tpg (tpg: N,N',N''-triphenylguanidinate; 12.24);500 the photochemical and biological properties of this compound are succinctly discussed in Section 12.7.3.
Rhodium Compounds 521
Chifotides and Dunbar
12.24
Fig. 12.26. Molecular structure of Rh2(tpg)4.
12.3.4 Complexes supported by sulfur donor bridging ligands
The structurally characterized compounds of this category are listed in Table 12.5. Apart from the thiocarboxylato group 12.3, τ-thiocaprolactamate (tcl; 12.25) is another example of an (S, O) donor bridging ligand. The compound Rh2(tcl)4 is prepared from Rh2(O2CCH3)4 by ligand exchange of the acetate groups with tcl.501 In contrast to the analogous lactam adducts [Rh2(pyro)4(Hpyro)2] and [Rh2(vall)4(Hvall)2], which exhibit the usual cis-(2,2) arrangement430 (Fig. 12.20a), Rh2(tcl)4(tclH) and Rh2(tcl)4(CO) exhibit the (4,0) polar geometry 12.20; the tclH and CO molecules are coordinated to the S4 end of the dirhodium unit.501 In order to address the polarity of the Rh–Rh bond, ab initio calculations have been performed on the ground and lowest ionized states of the previous compounds.502
Table 12.5. Dirhodium compounds supported by (S, N), (S, O), (S, S), (P, N) donor and phosphine bridging ligands
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax) |
Donor |
ref. |
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|
(4,0)-Rh2(tcl)4(tclH) |
2.497(1) |
2.388(1) |
S |
501 |
(4,0)-Rh2(tcl)4(CO) |
2.495(1) |
1.913(7) |
C |
501 |
[Rh2(µ-pyS)2Cl2(CO)2(δ1-pySH)2]·2CHCl3 |
2.652(4) |
2.547(4) |
Cl |
503 |
Rh2(But-S4)2·4.5Me2COb |
2.329(2) |
2.341(2) |
S |
642 |
(4,0)-Rh2(mmtz)4(PPh3) |
2.603(1) |
2.350(2) |
P |
504 |
H-T cis-[Rh2I2(CO)2(µ-mtz)2(µ-dppe)]·0.5THF |
2.748(1) |
2.794(1) |
I |
505 |
|
|
2.788(1) |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2(CO)2Cl4(µ-btmp)2 |
2.733(3) |
2.418(1) |
Cl |
506 |
|
|
2.470(1) |
|
|
Rh2(δ1-C6H5S)2(µ-C6H5S)2(bpy)2 |
2.549(2) |
2.243(4) |
S |
805 |

522 Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms
Chapter 12
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax) |
Donor |
ref. |
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|
Phosphine and (P, N) donor bridging groups |
|
|
||
cis-Rh2(µ-Cl)2(dppm)2Cl2·3CH3CN·H2O |
2.523(2) |
2.466(6) |
Cl |
507 |
|
|
2.457(6) |
|
|
H-T cis-Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(dmpm)2Cl2·CH2Cl2 |
2.770(3) |
2.561(6) |
Cl |
507,563 |
|
|
2.527(6) |
|
|
Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(µ-Cl)2(PMe3)2·C7H8·C4H8O |
2.506(1) |
2.363(4) |
P |
562 |
|
|
2.348(4) |
|
|
Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(µ-Cl)2(PPh3)2 |
2.499(1) |
2.403(2) |
P |
562 |
Rh2(CO)(µ-Cl)Cl3(dppm)2·CH2Cl2·C6H6·H2O |
2.691(3) |
2.448(7) |
Cl |
508 |
|
|
2.384(7) |
|
|
trans-Rh2(CO)2Cl4(dmpm)2·CH2Cl2 |
2.759(5) |
2.480(1) |
Cl |
510 |
|
|
2.478(1) |
|
|
trans-Rh2(µ-SO2)(µ-dppm)2Cl2 |
2.784(1) |
2.342(2) |
Cl |
513 |
|
|
2.341(2) |
|
|
Rh2[µ-PhP(py)2]2Cl4 |
2.687(1) |
2.345(3) |
Cl |
516 |
Rh2(µ-CO)Cl2(µ-Ph2Ppy)2 |
2.612(1) |
2.355(1) |
Cl |
519 |
trans-Rh2(µ-Ph2Ppy)2(µ-NO3)(CO)Cl3·CH2Cl2 |
2.589c |
d |
Cl |
517 |
H-T Rh2(succinimidate)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(H2O)2· |
2.539(1) |
2.358c |
O |
561 |
2CH2Cl2e |
|
2.374c |
|
|
H-T Rh2(succinimidate)2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(succini- |
2.555(1) |
2.483c,f |
O |
561 |
mide)(H2O)·CH2Cl2e |
|
2.284c,f |
|
|
Rh2[CH3N(PF2)2]3Cl4 |
2.707(1) |
2.416(2) |
Cl |
571 |
Rh2[CH3N(PF2)2]3Br4 |
2.750(8) |
2.555(6) |
Br |
572 |
Rh2{CH3N[P(OCH2CH3F3)2]2}3Cl4·CH2Cl2 |
2.669c,g |
2.362c,g |
Cl |
569 |
cis-{Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(NCCH3)6}(BF4)2·0.5H2Oh,i |
2.656(1) |
2.202(6) |
N |
564 |
|
2.655(1) |
2.196(6) |
|
|
{Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(µ2-C2O4)(py)2}3·6CH3OH· |
2.565(1) |
2.288(3) |
N |
564 |
H2Oj,k |
|
|
|
|
{Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(O2CC6H4CO2)(DMF)2}3·6.5 |
2.514(1) |
2.285(7) |
O |
564 |
DMF·0.5H2Oj,l |
2.507(1) |
2.296(9) |
|
|
|
2.511(1) |
2.304(8) |
|
|
|
|
2.314(8) |
|
|
|
|
2.322(9) |
|
|
|
|
2.335(9) |
|
|
{Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(O2CC6H4C6H4CO2)(py)2}3·4.5 |
2.541(3) |
m |
N |
564 |
|
||||
CH3OH·0.75H2Oj,k |
|
|
|
|
RRR-{Rh6[Ph2P(C6H4)]6(µ2-C2O4)3(py)5(CH2Cl2)} |
2.526(1) |
2.304(5)n |
N |
747 |
·3CH2Cl2j |
2.555(1) |
2.284(4)n |
Cl |
|
|
2.563(1) |
2.269(5)n |
|
|
|
|
2.265(4)n |
|
|
|
|
2.231(4)n |
|
|
|
|
2.650(1)o |
|
|
SSS-{Rh6[Ph2P(C6H4)]6(µ2-C2O4)3(py)5(CH2Cl2)}· |
2.525(1) |
2.229(4)n |
N |
747 |
3CH2Cl2j |
2.557(1) |
2.253(5)n |
Cl |
|
|
2.563(1) |
2.265(5)n |
|
|
|
|
2.272(5)n |
|
|
|
|
2.303(5)n |
|
|
|
|
2.636(2)o |
|
|

Rhodium Compounds 523
Chifotides and Dunbar
Compound |
r (Rh–Rh)a |
r (Rh–Lax) |
Donor |
ref. |
|
(Å) |
(Å) |
atom(s) |
|
SSS-{Rh2[Ph2P(C6H4)]2(O2CC6H4CO2)(py)2}3·6.5 |
2.561(2) |
2.22(1)- |
N |
747 |
CH2Cl2·1.5CH3OH·4H2Oj |
2.556(2) |
2.35(1)p |
|
|
|
2.548(2) |
|
|
|
|
2.533(2) |
|
|
|
|
2.530(2) |
|
|
|
Distances are given with up to 3 decimal digits.
‘But-H2S4’: 1,2-bis(2-mercapto-3,5-di-But-phenylthio)ethane. Esds not reported.
Distance not reported.
The compound has bridging succinimidate (N, O donor) and H-T phosphine groups. The longer distance corresponds to Rh–O(succinimidate), the shorter one to Rh–O(H2O).
Coordinates not available. The distances have been estimated from information provided in ref. 569. Molecule with two cisoid non-labile orthometalated phosphine bridging anions.
First molecule with an inherently chiral metal-metal bonded unit. Racemic mixture; the asymmetric unit contains a pair of S and R molecules.
Molecular triangle consisting of three singly bonded orthometalated cis-{Rh2[Ph2P(C6Ν4)]2}2+ units linked by two dicarboxylate anions.
k The compound exists as a mixture of RRR and SSS stereoisomers. l The compound exists as a mixture of RRS and SSR stereoisomers.
m Distance not reported; quality of diffraction data insufficient for detailed structural analysis. n Rh–N distance to N atom of pyridine ring.
o Distance of Rh to Cl of CH2Cl2. p Range of distances.
12.25 |
12.26 |
12.27 |
The bridging ligand 2-mercaptopyridine with (S, N) donor atoms reacts in chloroform with Rh2Cl2(CO)4 to afford the blue-black complex Rh2(µ-pyS)2Cl2(CO)2(δ1-pySH)2503 (12.27). The two 2-mercaptopyridinate (pyS; 12.26) groups span the dirhodium unit in a cis disposition and a H-T orientation (for dirhodium compounds with two bridging ligands possessing different types of donor atoms X and Y, the compound is designated as H-H (12.28) or H-T (12.29) depending on whether the identical atoms of the two ligands are bound to the same or to opposite metal atoms, respectively), whereas the two pySH ligands are in their zwitterionic form. The ax chloride atoms are engaged in N–H···Cl hydrogen bonds that result in pseudo-chelate rings.503 The long Rh–Rh bond distance of 2.652(4) Å may be a consequence of the /-accept- ing capability of the two eq CO ligands, a situation that leads to pronounced weakening of the
Rh–Rh bond.503
Complexes of the (S, N) donor ligands 3-mercapto-5-methylthio-1,2-thiadiazoline (Hmmtz; 12.30) and 2-mercaptothiazoline (Hmtz; 12.31) have been structurally characterized. In particular, Rh2(mmtz)4(PPh3) is found in the polar (4,0) arrangement 12.20 and the ax phosphine ligand is coordinated to the Rh–S4 metal center.504 On the other hand, cis- [Rh2I2(CO)2(µ-mtz)2(µ-dppe)] exhibits two mtz bridging ligands in a H-T arrangement and

524Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms Chapter 12
a bridging dppe moiety, rendering it the first example of a bridged dppe complex with a bifunctional ligand binding through different donor atoms.505 A H-T arrangement of the bridging groups is also found in the (benzylthiomethyl)diphenylphosphine (btmp) complex cis-Rh2(CO)2Cl4(µ-btmp)2.506
12.2812.29
12.30 |
12.31 |
12.3.5 Complexes supported by phosphine and (P, N) donor bridging ligands
The most widely studied phosphine bridging ligands (Tables 12.2 and 12.5) are dmpm (dmpm: Me2PCH2PMe2) and dppm (dppm: Ph2PCH2PPh2). The reaction of Rh2(O2CCH3)4 with Me3SiCl and dppm affords cis-Rh2(O2CCH3)2Cl2(dppm)2.507 Further reaction with additional Me3SiCl or the use of 4 equiv of Me3SiCl affords Rh2(µ-Cl)2(µ-dppm)2Cl2.507 In contrast to the analogous Re2Cl4(dppm)2 compound, which has a transoid arrangement of the phosphine groups, Rh2(µ-Cl)2(µ-dppm)2Cl2 has a cisoid disposition of the dppm ligands and a ‘cradle-like’ structure (Fig. 12.27). The reaction of Rh2Cl4(dppm)2 with CO under pressure affords the A-frame compound Rh2(CO)(µ-Cl)Cl3(dppm)2 (12.32).508 The latter can also be prepared by electrochemical oxidation of trans-Rh2(CO)2Cl2(dppm)2 in the presence of chloride ions.509 The dicarbonyl complex is directly obtained by reacting trans-Rh2(CO)2Cl2(dppm)2 with PhICl2 in dilute CH2Cl2 solutions. As indicated by NMR spectroscopy, it most likely has the symmetrical structure 12.33; this structure is analogous to the one established by X- ray crystallography for Rh2(CO)2Cl4(dmpm)2510 and proposed for Rh2(CO)2Cl2I2(dppm)2,511 and the analogous compounds Rh2(CO)2Br2X2(dpam)2 (X = Br or I; dpam: Ph2AsCH2AsPh2).512 Reactions of Rh2(CO)Cl4(dppm)2 include its conversion to Rh2Cl6(dppm)2 upon oxidation with PhICl2 and the formation of the unsymmetrical complex [Rh2(CO)Cl3(dppm)2]PF6, when Rh2(CO)Cl4(dppm)2 is reacted with AgPF6. The latter has been structurally characterized as the methanol complex [Rh2(CO)Cl3(dppm)2(MeOH)]PF6 (12.34); the weak interaction between the metal atoms is indicated by their distance of 3.010(2) Å.508 The compound trans-Rh2(µ- SO2)(µ-dppm)2Cl2 displays a distorted A-frame geometry with a bridging sulfur dioxide group.513 A-frame dirhodium compounds with bridging dppm groups have been studied by multinuclear NMR spectroscopy.514
The ligand Ph2Ppy (Ph2Ppy: 2-diphenylphosphinopyridine) reacts with Rh2(O2CCH3)4- (MeOH)2 and LiCl mixtures in refluxing toluene to afford the pink complex H-T cis-Rh2(µ-O2CCH3)2(µ-Ph2Ppy)2Cl2 (12.35),515 wherein the Ph2Ppy ligands assume an (N, P) bridging mode, akin to the (C, P) mode encountered in orthometalated phosphine
